DFS를 배우기 전에 먼저 재귀함수를 숙지해야한다.
재귀함수란
- 자기자신을 다시 호출하는 함수
- DFS를 구현하고자 할 때 자주 사용
- 단순한 형태의 재귀함수 예제
- '재귀함수를 호출합니다.'라는 문자열을 무한히 출력
- 어느정도 출력하다가 최대 재귀 깊이 초과 메시지가 출력
# python
def recursive_function():
print('재귀함수를 호출합니다.')
recursive_function()
recursive_function()- 문제 풀이에서 사용 할 때는 무한호출 방지를 위해 종료조건을 반드시 명시
- 종료조건을 포함한 재귀함수 예제
# python
def recursive_function(i):
# 100번째 호출을 했을 때 종료되도록 종료조건 명시
if i == 100:
return
print(i, '번째 재귀함수에서', i+1, '번째 재귀함수를 호출합니다.')
recursive_function(i+1)
print(i, '번째 재귀함수를 종료합니다.')
recursive_function(1)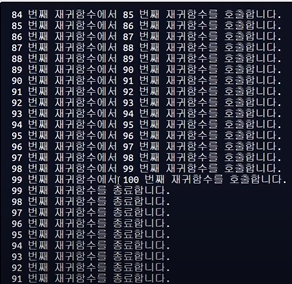
↪ 스택에 쌓이면서 호출 -> 마지막 호출 함수부터 차례대로 종료 (✅참고)
팩토리얼 구현 예제
n! = 1 x 2 x 3 x ... x (n-1) x n
✅수학적으로 0!과 1!의 값은 1
class Main {
// 반복적으로 구현한 n!
// 1*2*3*4*5
public static int factorialIterative(int n) {
int result = 1;
// 1부터 n까지의 수를 차례대로 곱하기
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result *= 1;
}
return result;
}
// 재귀적으로 구현한 n!
// 5*4*3*2*1
// 수학적 식의 원리로 구현하므로 코드가 반복문보다 직관적
public static int factorialRecursive(int n) {
// (중요! 종료조건) n이 1이하인 경우 1을 반환
if(n <= 1) return 1;
// n! = n * (n-1)!를 그대로 코드로 작성하기
return n * factorialRecursive(n - 1);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// 각각의 방식으로 구현한 n! 출력(n = 5)
System.out.println("반복적으로 구현 : " + factorialIterative(5));
System.out.println("재귀적으로 구현 : " + factorialRecursive(5));
}
}유클리드 호제법 예제
- 두 개의 자연수에 대한 최대공약수를 구하는 대표적 알고리즘
- 두 자연수 A, B에 대하여 (A>B) A를 B로 나눈 나머지를 R이라고 하자.
이때 A와 B의 최대공약수는 B와 R의 최대공약수와 같다. - 유클리드 호제법의 아이디어를 재귀함수로 구현 가능
- 예시 : GCD(192, 162) = 6
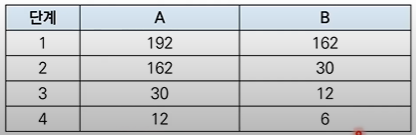
↪ 12와 6의 최대공약수를 구하면 된다 = 6
class Main {
public static int gcd(int a, int b) {
// a가 b의 배수이면
if(a % b == 0) {
return b;
}else{
return gcd(b, a%b);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// 동작 과정 상, 호출 시 a가 b보다 클 필요없다.
System.out.println(gcd(192, 162));
}
}- 재귀함수를 잘 활용하면 복잡한 알고리즘을 간결하게 작성 할 수 있지만(수학적 식의 원리로 구현 가능), 오히려 다른 사람이 이해하기 어려운 형태의 코드가 될 수 있으므로 신중히 사용
- 모든 재귀함수는 반복문을 이용하여 동일한 기능을 구현 할 수 있다. (반복문 또한 재귀함수로 구현 가능)
- 재귀함수가 반복문보다 유리한 경우도 있고, 불리한 경우도 있다.
- 컴퓨터가 함수를 연속적으로 호출하면 컴퓨터 메모리 내부의 스택 프레임에 쌓인다.
그래서 스택을 사용해야 할 때 구현상 스택 라이브러리(스택 자료구조) 대신에 재귀 함수를 이용하는 경우가 많음 (ex. DFS 구현 시)
