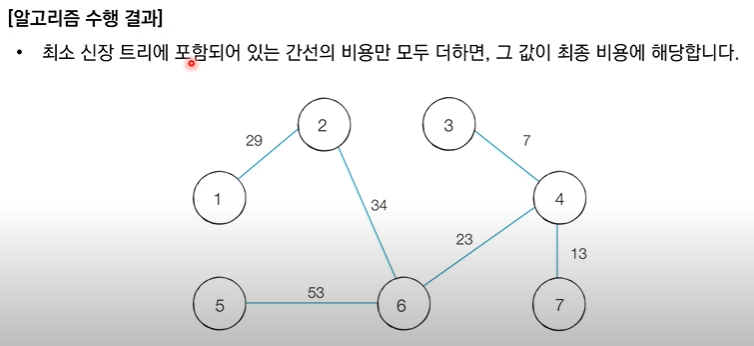
최소 신장 트리 알고리즘
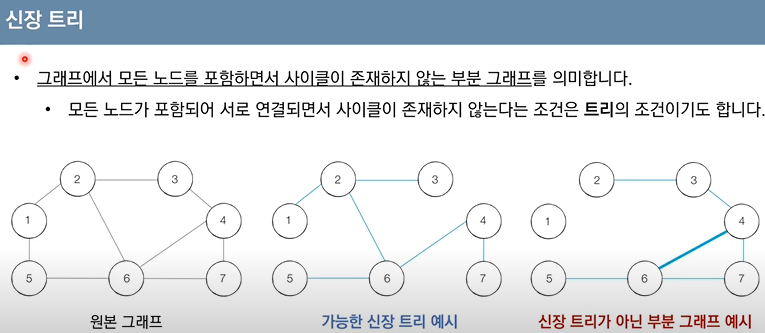 ✅ 일부 간선만을 채택한다는 특징
✅ 일부 간선만을 채택한다는 특징
✅ 세번째 그래프는 모든 노드가 포함되어있지 않음 + 사이클 존재
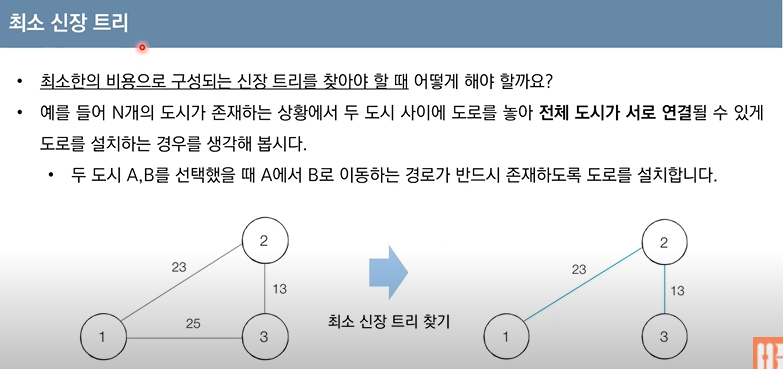 ✅ "반드시 존재하도록" : 신장트리는 모든 노드가 서로 연결되어있으므로 조금 돌아가더라더도 임의의 A,B가 서로 연결 되어있을 것이다.
✅ "반드시 존재하도록" : 신장트리는 모든 노드가 서로 연결되어있으므로 조금 돌아가더라더도 임의의 A,B가 서로 연결 되어있을 것이다.
✅ 최소 신장 트리의 간선 개수는 전체노드-1이다.
크루스칼 알고리즘

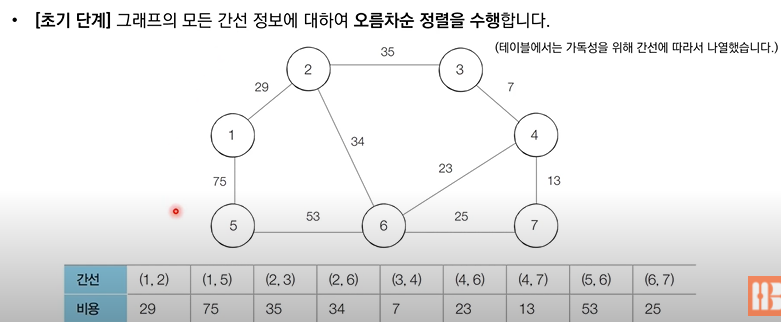
동작 원리
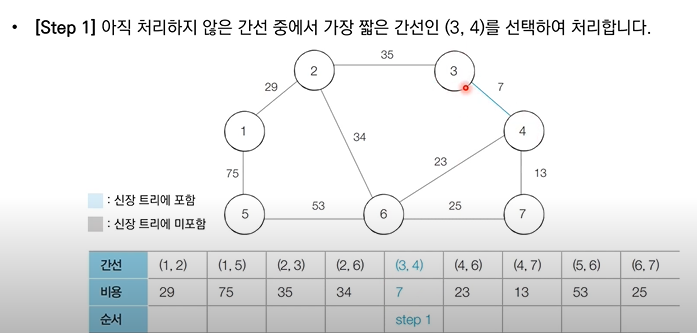 ✅ 3번 노드와 4번 노드는 같은 집합에 속해있지 않으므로 사이클이 발생하지 않을 것이기 때문에 같은 집합에 속하도록 union
✅ 3번 노드와 4번 노드는 같은 집합에 속해있지 않으므로 사이클이 발생하지 않을 것이기 때문에 같은 집합에 속하도록 union
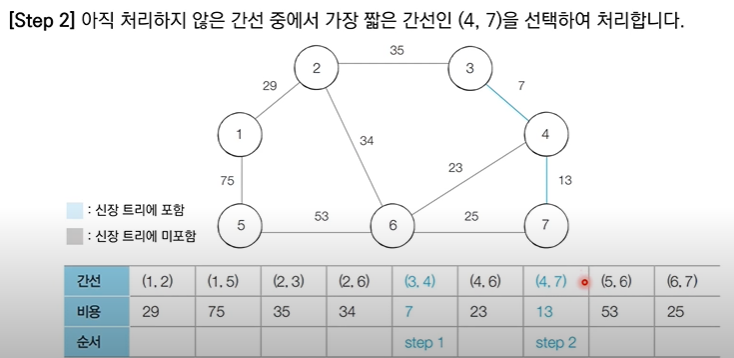
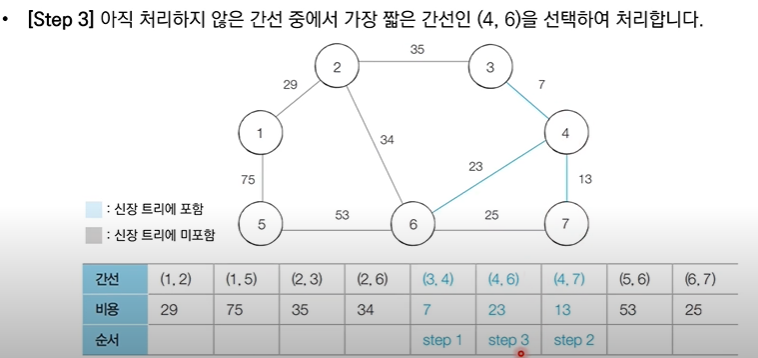
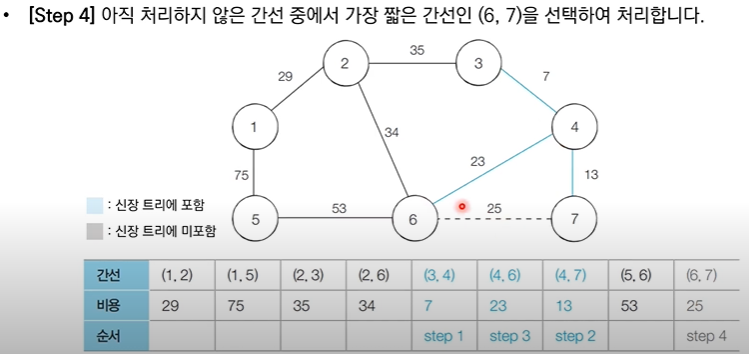 ✅ 6번 노드와 7번 노드는 같은 집합에 속해있기 때문에 사이클이 발생 할 것이므로 union X
✅ 6번 노드와 7번 노드는 같은 집합에 속해있기 때문에 사이클이 발생 할 것이므로 union X
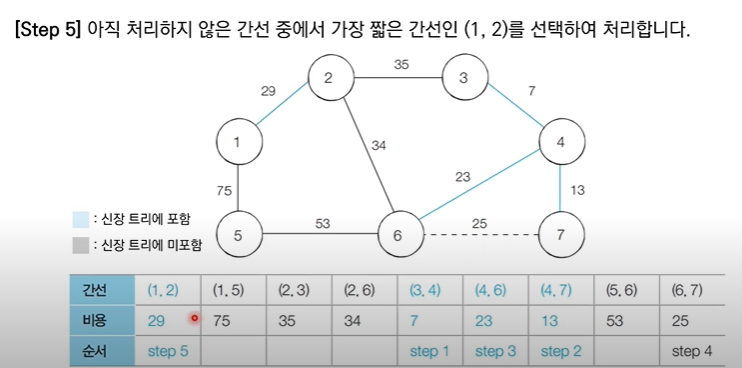
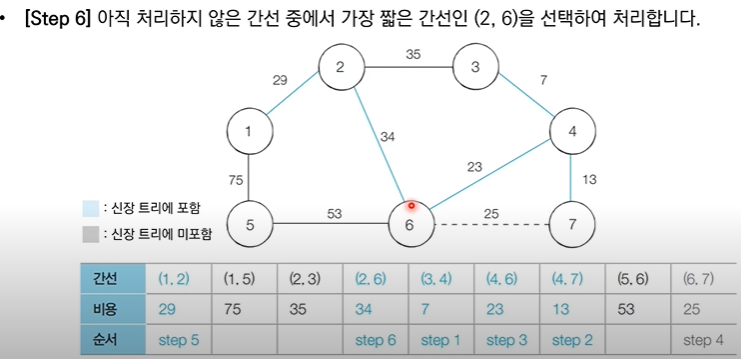
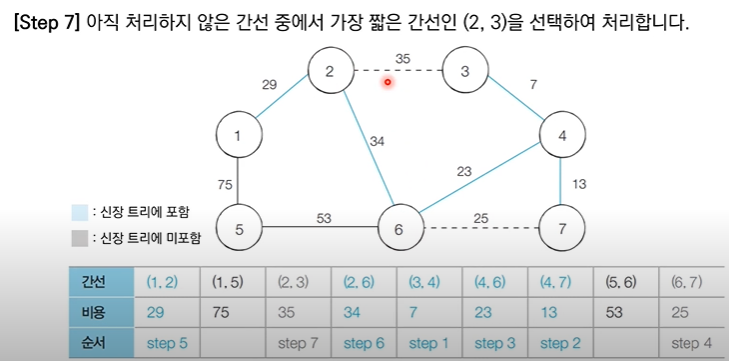
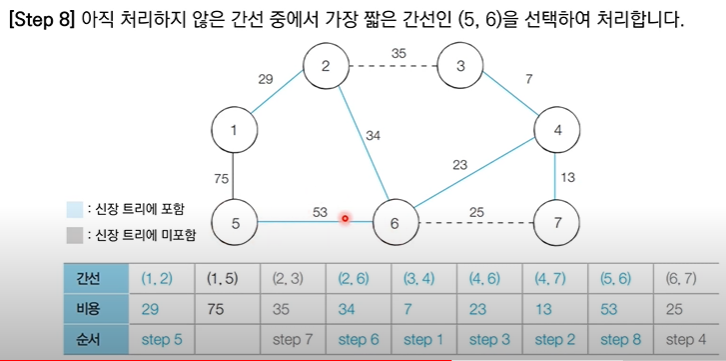
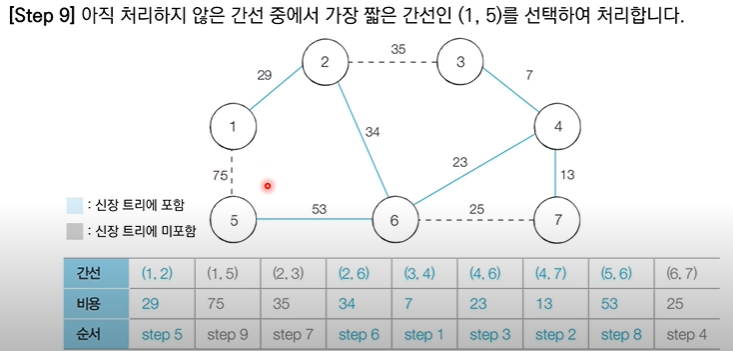
소스
import java.util.*;
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
private int distance;
private int nodeA;
private int nodeB;
public Edge(int distance, int nodeA, int nodeB) {
this.distance = distance;
this.nodeA = nodeA;
this.nodeB = nodeB;
}
public int getDistance() {
return this.distance;
}
public int getNodeA() {
return this.nodeA;
}
public int getNodeB() {
return this.nodeB;
}
// 거리(비용)가 짧은 것이 높은 우선순위를 가지도록 설정
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge other) {
if (this.distance < other.distance) {
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
}
public class Main {
public static int v, e;
public static int[] parent = new int[100001];
// 모든 간선을 담을 리스트
public static ArrayList<Edge> edges = new ArrayList<>();
// 최종 비용을 담을 변수
public static int result = 0;
public static int findParent(int x) {
if (x == parent[x]) return x;
return parent[x] = findParent(parent[x]);
}
public static void unionParent(int a, int b) {
a = findParent(a);
b = findParent(b);
if (a < b) parent[b] = a;
else parent[a] = b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
v = sc.nextInt();
e = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= v; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
// 모든 간선에 대한 정보를 입력 받기
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int cost = sc.nextInt();
edges.add(new Edge(cost, a, b));
}
// compareTo 기준으로 간선을 비용순으로 정렬
Collections.sort(edges);
// 간선을 하나씩 확인하며
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
int cost = edges.get(i).getDistance();
int a = edges.get(i).getNodeA();
int b = edges.get(i).getNodeB();
// 사이클이 발생하지 않는 경우에만 집합에 포함
if (findParent(a) != findParent(b)) {
unionParent(a, b);
result += cost;
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
성능 분석

