딥러닝 하면 떠오르는 mnist 손글씨 데이터셋을 살펴보자.
mnist 손글씨 데이터셋 실습
먼저 라이브러리를 선언한다.
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flattentrain데이터셋/테스트셋을 불러온다.
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
모델의 구조를 정의한다.
model = Sequential([
# 1. 28*28 행렬(입력층)을 1차원으로 변환
Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
# 2. relu라는 옵티마이저로 128개의 은닉층을 생성
Dense(128, activation='relu'),
# 3. 출력층, softmax는 여러가지를 분류할 때 사용한다.
# 0~9까지의 숫자를 예측한다.
Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])모델의 옵션을 선택한다.
model.compile(optimizer='adam', # 학습방법 - 옵티마이저는 아담
# 다중분류는 categorical
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']) # 정확도모델을 학습시키는데 어떻게 학습시킬지 정의한다.
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5, batch_size=32, validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
# 컴퓨터의 램은 8의 배수, 4의배수가 성능이 가장 좋다.
# 보통 batchsize는 8의 배수로 한다.학습과정을 시각화한다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label='accuracy')
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], label = 'val_accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.ylim([0.5, 1])
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()실제로 예측 결과를 시각화
#결과 시각화 정리
import numpy as np
# 테스트 데이터를 사용하여 예측 수행
predictions = model.predict(x_test)
def display_prediction(index, predictions_array, true_label, img):
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
# 이미지 출력
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(img[index], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
# 예측 결과 출력
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array[index])
if predicted_label == true_label[index]:
color = 'blue'
else:
color = 'red'
plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(predicted_label,
100*np.max(predictions_array[index]),
true_label[index]),
color=color)
# 예측 확률 막대그래프 출력
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.bar(range(10), predictions_array[index], color="#777777")
plt.ylim([0, 1])
plt.xticks(range(10))
plt.ylabel('Prediction Probability')
plt.xlabel('Predicted Value')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 첫 번째 예측 결과 시각화
display_prediction(100, predictions, y_test, x_test)
# 두 번째 예측 결과 시각화 (실제로 코드를 실행할 수 있다면 이 부분을 주석 해제하여 실행하세요)
# display_prediction(1, predictions, y_test, x_test)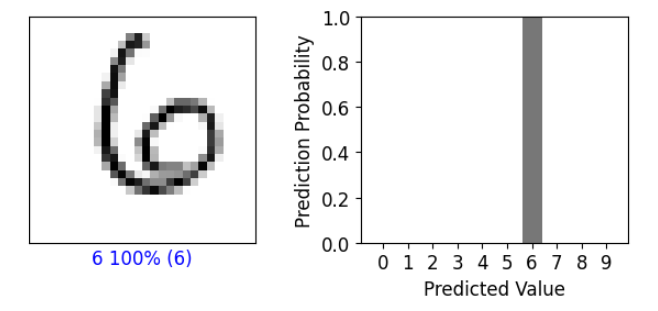
6이라고 잘 예측한 모습을 볼 수 있다.
