CSS
CSS는 Cascading(낙하) Style Sheets의 약자로 우선순위를 가지고 스타일이 적용된다.
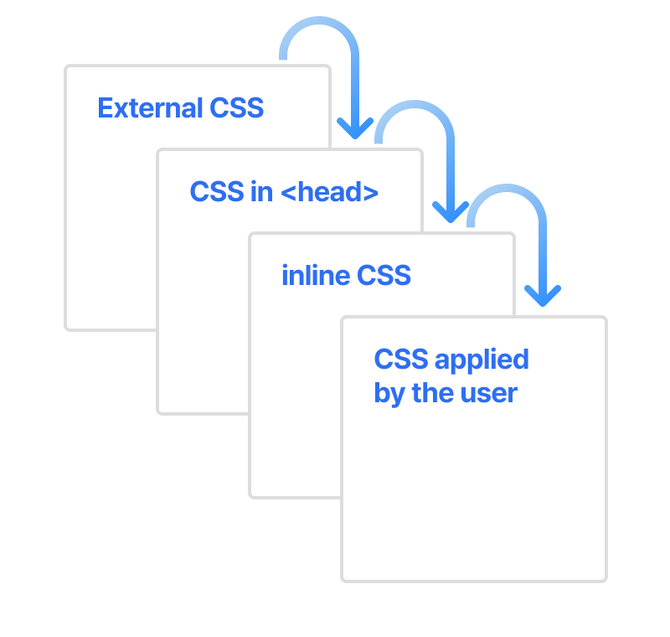
CSS applied by the user라는 스타일이 가장 먼저 실행되는데 이것은 브라우저에 기본 탑재된 느낌이라 우리가 건들기는 힘들다. 따라서 나머지 3개를 잘 수정하여 스타일의 우선순위를 정할 수 있다.
작성방법
선택자 {
속성: 속성값;
}과 같이 구현한다.
주석
css의 주석은 /* */이다.
CSS 적용하기
1. 인라인 방식
html 태그 자체에 style로 속성을 주는 방식이다. 일부 태그는 사용이 불가능하다고 한다.
<p style="color:yellow; background-color:black;">Hello wold</p>2. 내부 스타일
head 태그 안에 style 태그를 사용하는 방식이다. 코드가 길어질수록 HTML 파일 길이가 길어지므로 효율적이진 않다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko-KR">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>내부 스타일</title>
<style>
p {
color:yellow;
background-color:black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello world</p>
</body>
</html>3. 외부 스타일 (권장)
head태그 안에 link 태그를 사용하여 외부 css파일을 참조하는 방식이다. rel은 relation으로 대상 파일의 속성을 나타내고 href는 hyper-references 경로로 참조할 파일의 경로이다.
<!-- index.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko-KR">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>외부 스타일</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello world</p>
</body>
</html>/* style.css */
p {
color:yellow;
background-color:black;
}CSS 선언법
다양한 css 선언법이 존재한다.
1. 태그 선택자
/* html */
<div>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<h2>Hello</h2>
<p>Hello</p>
</div>/* css */
h1{color:red;}
h2{color:red;}
p {color:red;}2. 그룹 선택자
<div>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<h2>Hello</h2>
<p>Hello</p>
</div>/* css */
h1,
h2,
p {color:red;}css도 다른 언어와 마찬가지로 반복을 피하기 위해 같은 내용은 콤마로 연결해 적용한다.
3. 상속
<div>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<h2>Hello</h2>
<p>Hello</p>
<button>Hello</button>
<input type="text" value="hello">
</div>/* css */
div{
color:red;
border: 5px solid pink;
}css에는 상속되는 속성과 되지 않는 속성이 있다. color 속성은 상속이 되지만 ui크기와 관련된 width, height, margin, padding, border 등은 상속이 되지 않는다.
div {
color: red;
border: 5px solid pink;
}
h1 { border: inherit; }위와 같이 inherit으로 선언하면 선택한 요소의 속성값을 부모(5px)에게 상속받는다. initial로 선언하면 기본 스타일 속성을 따른다.
button, input처럼 form 관련 태그들도 상속 받지 않는다.
