
Reducer/context
Reducer
1) useReducer?
상태관리를 담당하는 Hook이다.
useState를 통한 상택관리 및 데이터 CRUD 의 각종 Handler를 하나의 함수로 사용할수 있도록 해준다.
기본적인 형태는 이렇다.
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(리듀서 이름, 초기데이터)state: 상태를 뜻한다. 이 안에 각종 데이터가 들어가게 되는데, 처음에 초기 데이터를 1로 설정하면, 이 state는 1이 되는 것이다.
dispatch는 해당 state에 대애서 crud를 진행하도록 도와주는 함수를 뜻한다. dispatch(진행하고자 하는 작업이름)이런식으로 써주면, 해당 state 수정 작업이 진행되는 것이다.
특정한 작업 타입을 명시해주면, 해당 작업 타입에 따라 일정한 함수를 실행해주는 역할을 담당하게 된다.
하지만 dispatch가 특정한 작업이름을 입력받았을 때, 어던 작업을 수행할 지는 아직 정해져 있지 않다. 해당 부분은 우리가 직접 정해야 하는 것이다.
그것을 정의하는 것이 바로 리듀서이다.아래처럼 작성하면 dispatch 함수 실행시 작업 이름에 해당하는 행동을 실행하게 된다.
export function 리듀서(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case '작업이름':
return 해당 작업이름으로 dispatch 했을 때 실행될 코드
default:
throw new Error(`Unhandled action type: ${action.type}`)
}
}2) useReducer 예제
constants/userData.js
export const userData = [
{
id: 1,
name: 'Leanne Graham',
email: 'Sincere@april.biz',
},
{
id: 2,
name: 'Ervin Howell',
email: 'Shanna@melissa.tv',
},
{
id: 3,
name: 'Clementine Bauch',
email: 'Nathan@yesenia.net',
},
{
id: 4,
name: 'Patricia Lebsack',
email: 'Julianne.OConner@kory.org',
},
{
id: 5,
name: 'Chelsey Dietrich',
email: 'Lucio_Hettinger@annie.ca',
},
{
id: 6,
name: 'Mrs. Dennis Schulist',
email: 'Karley_Dach@jasper.info',
},
{
id: 7,
name: 'Kurtis Weissnat',
email: 'Telly.Hoeger@billy.biz',
},
{
id: 8,
name: 'Nicholas Runolfsdottir V',
email: 'Sherwood@rosamond.me',
},
{
id: 9,
name: 'Glenna Reichert',
email: 'Chaim_McDermott@dana.io',
},
{
id: 10,
name: 'Clementina DuBuque',
email: 'Rey.Padberg@karina.biz',
},
]userData를 사용하는 UserList.jsx컴포넌트 생성
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import { userData } from '../constants/userData'
function UserList() {
const [users, setUsers] = useState(userData)
return (
<div>
{users.map((user) => {
return <p>{user.name}</p>
})}
</div>
)
}
export default UserListuseState를 쓰는 경우에 데이터를 추가하고 싶으면, 이렇게 추가하는 함수를 따로 만들어줘야한다.
cosnt addUser = (user) => {
setUsers([...users, user])하지만 이러한 state 관리 로직이 한 컴포넌트에 너무 많아져도 곤란하고, 너무 흩어져 있어도 곤란하다.
그래서 상태관리를 좀 정돈하고 싶을 때 사용하는 것이 바로 useReducer이다.
userReducer.js
export function userReducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'ADD': // 이 부분은 {type: 'ADD'} 가 들어오면 실행
return [...state, action.data]
default:
throw new Error(`Unhandled action type: ${action.type}`)
}
}현재 ADD 작업만 있다고 가정해서 작성한 것이다.
이제
UserList 컴포넌트를 아래처럼 제작한다.
useState를 제거하고 userReducer를 사용했다는 것이 핵심 포인트이다.
import React, { useReducer } from 'react'
import { userReducer } from '../reducers/userReducer'
import { userData } from '../constants/userData'
function UserList() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(userReducer, userData)
return (
<div>
{state.map((user) => {
return <p>{user.name}</p>
})}
</div>
)
}
export default UserListdispatch 를 사용해서 데이터를 추가한다.
버튼을 만들고 버튼을 눌렀을 때 아래와 같은 코드가 실행 되도록한다.
dispatch({ type: 'ADD', data: { id: 11, name: '11', email: '11' } })이 코드는
- 괄호 안에 명시한 내용을 userReducer에서 action으로 받아옴
- action의 type을 확인해서 ADD인 경우의 함수 내용이 실행됨. 따라서 action의 data 부분을 state에 추가한다.
import React from 'react'
import { useReducer } from 'react'
import { userData } from '../constatnts/userData'
import { userReducer } from '../reducers/userReducer'
function UserList() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(userReducer, userData)
return (
<div>
{state.map((user) => {
return <p>{user.name}</p>
})}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'ADD', data: { id: 11, name: '11', email: 'helloworld.com' } })}>디스패치</button>
</div>
)
}
export default UserList

디스패치 버튼을 누르면 11이라는 데이터가 추가되는 모습을 볼수 있다.
3) 입력값 받아와서 유저 추가하고 싶어
현재는 고정 값을 넘겨주고 있지만 한번 변경해보자.
import React, { useReducer, useState } from 'react'
import { userReducer } from '../reducers/userReducer'
import { userData } from '../constants/userData'
function UserList() {
const [userInput, setUserInput] = useState({
id: '',
name: '',
email: '',
})
const userInputHandler = (e) => {
const { name, value } = e.target
setUserInput({ ...userInput, [name]: value })
}
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(userReducer, userData)
return (
<div>
{state.map((user) => {
return <p>{user.name}</p>
})}
<input name="id" onChange={userInputHandler}></input>
<input name="name" onChange={userInputHandler}></input>
<input name="email" onChange={userInputHandler}></input>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({type:'ADD', data: userInput})}>디스패치</button>
</div>
)
}
export default UserList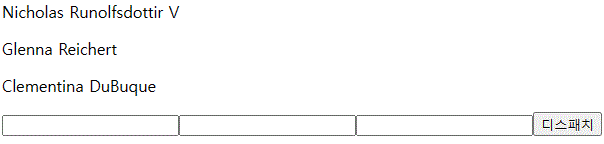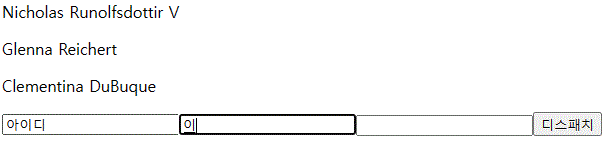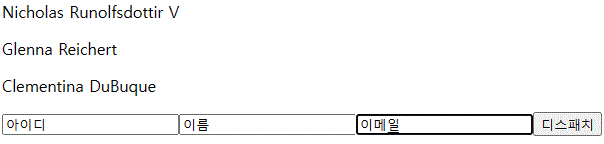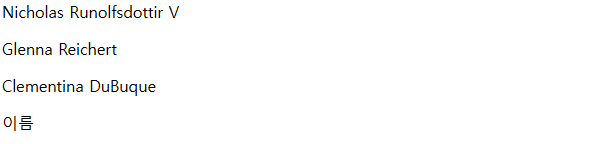
4) 유저 정보를 제거하고 싶어
userReduer에 action type중에서 DELETE를 추가해주고 버튼을 클릭하면 유저 정보가 제거되는 기능을 구현한다.
1) userReducer에 DELETE type에 따른 함수 호출 내용을 작성
case 'DELETE':
return state.filter((element) => element.id !== action.data.id)2) 이제 이 type을 호출하는 버튼을 만들어서 onClick을 하면 DELETE 액션 타입을 dispatch하도록 설정하면 끗!
{state.map((user) => (
<div key={user.id}>
<p>{user.name}</p>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'DELETE', id: user.id })}>삭제하기</button>
</div>
))}
5) 유저 정보 수정도 하고싶은데?
userReducer에서 UPDATE action을 추가한다 (update는 실행되면, 유저의 name 부분을 실행시 인자로 받은 name값으로 변경한다.)
UserList에서 해당 action type으로 dispatch한다.
1) userReducer에 UPDATE type에 따른 함수 호출 내용을 작성
case 'UPDATE':
return state.map((element) => (element.id === action.data.id ? { ...element, name: action.data.name } : element))2) 이제 이 type을 호출하는 버튼을 만들어서 onClick을 하면 UPDATE 액션 타입을 dispatch하도록 설정하면 끗! 이때 data객체로 받아서 수정을 하기 때문에 보낼때에도 data 객체로 보내줘야한다.
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'UPDATE', data: { id: user.id, name: '변경되었습니다.' } })}>이름 변경</button>
Context
1) useContext 개념
특정한 값을 모든 컴포넌트에서 사용할수 있도록 만들어 놓고, 어디서든 특정한 값을 불러와서 사용할수 있도록 해주는 Hool이다.
const UserContext =createContext()
방금 만든 따끈따끈한 context.Provider를 통해서 특정 컴포넌트를 감싸주면, value부분에 명시한 값을 하위컴포넌트에서 항상 사용할수 있게된다.
<UserContext.Provider value={ 여러 컴포넌트에서 사용하고 싶은 값 }>
<UserList />
</UserContext.Provider>하위 컴포넌트에서는 앞서 만들어놓은 context를 불러온 다음 useContext를 써주면 Provider의 value부분을 통해서 넘겨준 그 값을 받아올수 있게 된다.
import { UserContext } from '../App'
const { value 에 넘겨줬던 키 } = useContext(UserContext)- 굳이 필요함..?
예를 들어서 UserList 안에 UserDetail 안에 UserInfo 가 있는 형태에서, 특정한 값이 해당 컴포넌트 전부에서 필요하다고 가정해보자.
app.jsx에서 생성한 데이터를 UserInfo 까지 내려주려면
import UserList from './components/UserList'
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(1)
return (
<UserList count={count}/>
)
}
export default Appimport UserDetail from './components/UserDetail'
function UserList({ count }) {
return (
<UserDetail count={count}/>
)
}
export default UserListimport UserInfo from './components/UserDetail'
function UserDetail({ count }) {
return (
<UserInfo count={count}/>
)
}
export default UserDetail
잉? 이렇게까지 해야한다고?
-> 이런 현상을 props drilling이라고 한다. 대표적인 anti-pattern 으로, 작동은 하겠지만 이렇게 작성하면 해당 props 가 어디서부터 내려운 것인지 특정하기가 어려워진다는 담점이 존재한다. 뿐만 아니라 count 하나가 변경되면 모든 컴포넌트가 다시 렌더링 되는 단점도 있다.
이걸 만약에 useContext를 통해서 해결한다면
import { createContext, useReducer } from 'react'
import UserList from './components/UserList'
import { userReducer } from './reducers/userReducer'
import { userData } from './constants/userData'
export const UserContext = createContext(null)
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(1)
return (
<UserContext.Provider value={{ count }}>
<UserList />
</UserContext.Provider>
)
}
export default Appimport { UserContext } from '../App'
function UserInfo() {
const { count } = useContext(UserContext)
return (
<p>{count}</p>
)
}
export default UserInfo훨씬 간단하다!
2) 예제
유저 정보를 전역에서 저장해놓고 필요한 컴포넌트에서 불러오기 위해 사용한다.
import { createContext } from 'react'
import UserList from './component/UserList'
export const UserContext = createContext(null)
function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState('말랑말랑')
return (
<UserContext.Provider value={{ name, setName }}>
<div className="App">
<UserList />
</div>
</UserContext.Provider>
)
}
export default App
UserInfo 에서는 아래와 같이 useContext(컨텍스트이름) 형태로 사용하면, value 부분의 값을 가져올수 있다.
import React, { useContext } from 'react'
import { UserContext } from '../App'
function UserInfo() {
const { name } = useContext(UserContext)
return <div>{name}님 어서와요!</div>
}
export default UserInfo
이제 App에서 UserInfo를 렌더링 하면

이렇게 다른 컴포넌트에서도 name 값을 가져올수 있게 되었다.
물론 setName도 가능하다.
function UserInfo() {
const { name, setName } = useContext(UserContext)
return (
<>
<div>{name}님 어서와요!</div>
<button onClick={() => setName('바삭바삭')}>바삭해지기</button>
</>
)
}
3) useContext 분리하기
만약 Context나 value가 많아지면 app.jsx에 로직이 많아지는 부작용이 발생할수 있다.
이러한 context 로직은 따로 파일 하나를 생성해서 분리해주는 것이 파일 및 코드 관리에도 좋아보인다.
import React, { createContext } from 'react'
export const UserContext = createContext(null)
export function UserProvider({ children }) {
const [name, setName] = useState('안녕안녕')
return <UserContext.Provider value={{ name, setName }}>{children}</UserContext.Provider>
}이렇게 분리를 해놓으면, 유저와 관련 state를 생성하는 로직과 컴포넌트에 넘겨주는 로직이 UserProvider라는 컴포넌트 하나만 작성하면 모두 해결된다.
이렇게 해주면 app.jsx는 간단하게 사용할수 있다.
import { createContext, useState } from 'react'
import UserInfo from './component/UserInfo'
import UserList from './component/UserList'
import { UserProvider } from './contexts/UserContext'
function App() {
return (
<UserProvider>
<UserInfo />
</UserProvider>
)
}
export default App
usercontext가 이제 app에 있지않기 때문에 컴포넌트도 아래와 같이 수정해준다.
import React, { useContext } from 'react'
import { UserContext } from './../contexts/UserContext'
function UserInfo() {
const { name, setName } = useContext(UserContext)
return (
<>
<div>{name}님 어서와요!</div>
<button onClick={() => setName('바삭바삭')}>바삭해지기</button>
</>
)
}
export default UserInfo
4) 이걸 useRuducer랑 같이 써보기
1) userContext 수정
import React, { createContext, useReducer } from 'react'
import { userReducer } from '../reducers/userReducer'
import { userData } from '../constants/userData'
export const UserContext = createContext(null)
// 위에서 선언한 두가지 Context 들의 Provider 로 감싸주는 컴포넌트
export function UserProvider({ children }) {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(userReducer, userData)
return (
<UserContext.Provider value={{ state, dispatch }}>
{children}
</UserContext.Provider>
)
}app.jsx
import { UserProvider } from './contexts/UserContext'
import UserList from './components/UserList'
function App() {
return (
<UserProvider>
<UserList />
</UserProvider>
)
}
export default App2) UserList 에서 useContext를 사용하여 state와 dispatch를 불러와서 사용한다.
import React, { useContext, useState } from 'react'
import { UserContext } from '../contexts/UserContext'
function UserList() {
const { state, dispatch } = useContext(UserContext)
const [userInput, setUserInput] = useState({
id: '',
name: '',
email: '',
})
const userInputHandler = (e) => {
const { name, value } = e.target
setUserInput({ ...userInput, [name]: value })
}
return (
<div>
{state.map((user) => (
<div key={user.id}>
<p>{user.name}</p>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'UPDATE', data: { id: user.id, name: '변경되었습니다.' } })}>이름 변경</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'DELETE', id: user.id })}>삭제하기</button>
</div>
))}
<br></br>
<input name="id" onChange={userInputHandler} />
<input name="name" onChange={userInputHandler} />
<input name="email" onChange={userInputHandler} />
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'ADD', data: userInput })}>디스패치</button>
</div>
)
}
export default UserList
state와 dispatch만 불러와서 사용하니까 코드가 조금 단순해졌다.
유저 정보를 표시하는 부분을 분리해서 불러오는지 확인해보자
UserList.jsx
function UserList() {
const { state: users } = useContext(UserContext)
return (
<div>
{}
<h1>리스트</h1>
{users.map((user) => (
<UserDetail key={user.id} user={user} />
))}
</div>
)
}userDetail.jsx
import React, { useContext } from 'react'
import { UserContext } from '../contexts/UserContext'
function UserDetail({ user }) {
const { dispatch } = useContext(UserContext)
return (
<div key={user.id}>
<p>{user.name}</p>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'UPDATE', data: { id: user.id, name: '변경됨' } })}>이름 바꾸기</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'REMOVE', data: { id: user.id } })}>삭제하기</button>
</div>
)
}
export default UserDetail
props로 내려주지 않았는데도 sate와 dispatch를 각각 잘 불러온다!

Axios와 Reducer(날씨 이용해보기)
1) 날씨 api사용하기
axios를 통한 응답처리방식을 useReducer를 통해서 구현해보기로 한다.
https://open-meteo.com/en/docs#api_form
여기로 들어가면 다양한 정보를 선택하고, api요청을 보내기 위한 주소를 만들어준다.
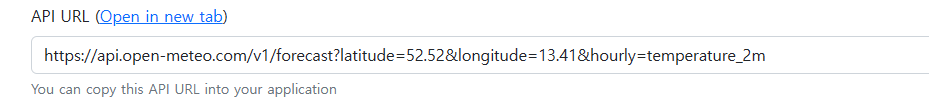
간단히 실시간 날씨만 표시하도록 아래와 같은 url을 사용해서 요청을 보낼것이다.
`https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude=${latitude}&longitude=${longitude}¤t_weather=true&timezone=auto`먼저 axios를 설치한다
yarn add axios
2) axios와 useState사용해서 요청 다루기
먼저 useState만 사용해서 진행한다.
아래와 같이, 상수 형태로 위도, 경도및 날씨 상태를 선언
constants/weather.js
export const GEOLOCATION = {
'서울': {latitude: 37.55, longitude: 127},
'런던': {latitude: 51.51, longitude: 0},
'뉴욕': {latitude: 40.71, longitude: -74.01},
}
export const GRADE = {
0: '매우 맑음',
1: '맑음',
2: '약간 흐림',
3: '흐림'
}그리고 Weather컴포넌트 생성
1) getWeather 메소드 작성
- location값을 바탕으로 latitude, longitude를 constants의 weather로부터 가져와서 api 요청 url의 경도의 위도값에 집어 넣는다.
그리고 해당 response.data 를 리턴한다.
2) setWeatherByResponse 메소드 작성
location 값을 사용해서 getWeather(location)을 호출한 data를 사용해서 setWeather(data)를 호출하여 weather데이터를 변경한다.
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
import { GEOLOCATION, GRADE } from '../constants/weather'
import axios from 'axios'
function Weather() {
const [weather, setWeather] = useState()
const getWeather = async (location) => {
const { latitude, longitude } = GEOLOCATION[location]
const response = await axios.get(
`https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude=${latitude}&longitude=${longitude}¤t_weather=true&timezone=auto`,
)
return response.data
}
const setWeatherByResponse = async (location) => {
const data = await getWeather(location)
setWeather(data)
}
useEffect(() => {
setWeatherByResponse('서울')
}, [])
return (
<div>
<h1>날씨</h1>
<p>{weather && weather.current_weather.temperature} 도</p>
<p>{weather && GRADE[weather.current_weather.weathercode]}</p>
</div>
)
}
export default Weather
axios 는 단순히 데이터를 보여주기만 한다고 끝이 아니고,error나 loading 관리도 해줘야한다.
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react'
import { GEOLOCATION, GRADE } from '../constatnts/weather'
import axios from 'axios'
import Loading from './../../../seventhApp/src/components/Common/Loading/index'
function Weather() {
const [weather, setWeather] = useState()
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState()
const [error, setError] = useState(null)
const getWeather = async (location) => {
try {
setIsLoading(true)
const { latitude, longitude } = GEOLOCATION[location]
const response = await axios.get(
`https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude=${latitude}&longitude=${longitude}¤t_weather=true&timezone=auto`,
)
return response.data
} catch (err) {
setError(err)
setIsLoading(false)
}
}
const setWeatherByResponse = async (location) => {
const data = await getWeather(location)
setWeather(data)
setIsLoading(false)
}
useEffect(() => {
setWeatherByResponse('서울')
}, [])
if (isLoading)
return (
<div>
<Loading />
</div>
)
if (error) return <div>{error.message}</div>
return (
<div>
<h1>날씨</h1>
<p>{weather && weather.current_weather.temperature} 도</p>
<p>{weather && GRADE[weather.current_weather.weathercode]}</p>
</div>
)
}
export default Weather
- isLoading useState()생성
- error useState()생성
- try catch 문을 사용해서 try에는 이전에 작성한 호출 내용을작성하고 오류가 발생했을때 동작하는 내용을 catch 에 작성한다.
- 로딩중일 때는 이전에 만든 로딩 컴포넌트를 사용했다.

3) useReducer 및 useContext로 처리
axios를 useReducer 로 처리하는 것이 유용한 이유는 바로 에러와 로딩 관리를 조금 더 효율적으로 할 수 있기 때문이다.
에러, 로딩, 데이터를 하나의 객체로 만들어놓고 한번에 관리하는 방식으로 코드를 작성한다.
- 단순히 useReducer만 쓰기
weatherReducer.js
우선 LOADING / SUCCESS / ERROR 총 3가지 경우만 존재한다고 생각하고 가정하고 진행한다.
export function weatherReducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'LOADING':
return {
loading: true,
data: null,
error: null,
}
case 'SUCCESS':
return {
loading: false,
data: action.data,
error: null,
}
case 'ERROR':
return {
loading: false,
data: null,
error: action.error,
}
default:
throw new Error(`Unhandled action type: ${action.type}`)
}
}
Weather.jsx
데이터의 초기값을 아래와 같이 정의하고 useReducer를 통해서 상태관리를 한다.
{
loading: false,
data: null,
error: null,
} const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(weatherReducer, {
loading: false,
data: null,
error: null,
})weatherReducer.js
export function weatherReducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'LOADING':
return {
loading: true,
data: null,
error: null,
}
case 'SUCCESS':
return {
loading: false,
data: action.data,
error: null,
}
case 'ERROR':
return {
loading: false,
data: null,
error: action.error,
}
default:
throw new Error(`Unhandled action type: ${action.type}`)
}
}이제 요청보내는 부분을 아래처럼 작성한다.
function Weather() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(weatherReducer, {
loading: false,
data: null,
error: null,
})
const { loading, data: weather, error } = state
const getWeather = async (location) => {
const { latitude, longitude } = GEOLOCATION[location]
const response = await axios.get(
`https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude=${latitude}&longitude=${longitude}¤t_weather=true&timezone=auto`,
)
return response.data
}
const fetchWeather = async (location) => {
try {
dispatch({ type: 'LOADING' })
const data = await getWeather(location)
dispatch({ type: 'SUCCESS', data })
} catch (error) {
dispatch({ type: 'ERROR', error })
}
}
/* const setWeatherByResponse = async (location) => {
const data = await getWeather(location)
setWeather(data)
setIsLoading(false)
} */
useEffect(() => {
/* setWeatherByResponse('서울') */
fetchWeather('서울')
}, [])
if (loading)
return (
<div>
<Loading />
</div>
)
if (error) return <div>{error.message}</div>
return (
<div>
<h1>날씨</h1>
<p>{weather && weather.current_weather.temperature} 도</p>
<p>{weather && GRADE[weather.current_weather.weathercode]}</p>
</div>
)
}
export default Weather
- loading과 data, error 데이터를 weatherReducer 에서 가져온다.
- loading 상태관리는 reducer가 담당하므로 useState는 제거한다.
- loading 이 true일 동안 로딩 애니메이션을 보여준다.
- setWeatherByResponse 대신에 fetchWeather메소드를 작성했다. try 로 LOADING 타입을 dispatch하고 getWeather를 호출해서 얻은 data를 생성하고 SUCCESS type을 dispatch해서 api 호출을 통해 얻은 data를 state 에 있는 data로 업데이트한다.
- useContext와 함께 써보고싶어(날씨가 한 컴포넌트에서 필요한게 아니라 다른 곳에서도 필요하다면 어떻게 해야할까?)
간단하다. context를 생성해서 다른 컴포넌트와 공유하고 싶은 props들을 작성한다!
- weatherReducer의 state와 dispatch를 다른 컴포넌트에도 공유해야지
그렇게 하려면 context를 만들어야겠네
WeatherContext.jsx
import React, { createContext, useReducer } from 'react'
import { weatherReducer } from '../reducers/weatherReducer'
export const WeatherContext = createContext(null)
const initialState = {
loading: false,
data: null,
error: null,
}
export function WeatherProvider({ children }) {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(weatherReducer, initialState)
return <WeatherContext.Provider value={{ state, dispatch }}>{children}</WeatherContext.Provider>
}Provider 내부의 value에 state, dispatch 를 넣어서 사용할거야
- App.js에서 전달하고자 하는 컴포넌트의 바깥에
WeatherProvider를 사용하여 덮는다.
import { WeatherProvider } from './contexts/WeatherContext'
import Weather from './components/Weather'
function App() {
return (
<WeatherProvider>
<Weather />
</WeatherProvider>
)
}
export default App- 마지막으로 Weather에서 사용하는 state,dispatch내용을 수정해주면 끗!
const { state, dispatch } = useContext(WeatherContext) // 이 부분만 달라졌음!