function
// function
// 이름이 hello1 인 함수를 선언
function hello1() {
console.log("hello1")
}
console.log(hello1, typeof hello1);
// 함수의 매개변수
// 함수를 호출할 때 값을 지정
function hello2(name) {
console.log('hello', name);
}
hello2("yeongchan")
// 함수의 리턴
// 함수를 실행하면 얻어지는 값
function hello3(name) {
return `hello3 ${name}`;
}
console.log(hello3('YeongChan'))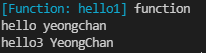
const
//function
// 이름이 hello1 인 함수 선언
const hello1 = function () {
console.log('hello1');
}
console.log(hello1, typeof hello1)
const hello2 = function (name) {
console.log('hello1', name);
}
hello2('yeongchan')
const hello3 = function (name) {
return `hello3 ${name}`
}
console.log(hello3('yeongchan'))선언적 function과 익명 함수를 만들어 변수에 할당 하는 방법의 차이점
hello1();
hello2();
hello3();
function hello1() {
console.log('hello1');
}
var hello2 = function () {
console.log('hello2'); // TypeError: hello2 is not a function
}
const hello3 = function () {
console.log('hello3'); // ReferenceError: Cannot access 'hello3' before initialization
}-
hello1같은 경우는 function 으로 선언이 되었기 때문에 function이라는 타입이 선언되므로 선언 위치와 상관없이 배치가 가능하다(호이스팅 참조)
-
var,const 같은 경우는 저번의 호이스팅과 같은 원리를 적용하면 이해가 쉽다
- var같은 경우는 선언됨과 동시에 초기화가 진행되어 undefined로 초기화가 되었다.- 따라서 hello2는 초기화가 된 상태에서 hello2()를 호출하라니 오류가 발생하는 것
- const의 경우는 선언만 됐지 초기화가 되지 않았기 때문에 즉, 변수를 위한 메모리 공간이 아직 확보되지 않았기 때문에 변수로 사용할 수가 없다. 따라서 애초에 hello3 자체가 정의되지 않은것! (변수는 "선언" - "초기화" - "할당" 을 거쳐서 정의가 된다라고 생각하면 이해가 잘 된다. )
-
호이스팅은 정말 중요한 항목이므로 헷갈린다 싶으면 다시 복습하자
생성자 함수로 함수를 만드는 방법
// newFuntionc(/* 인자1, 인자1,...., 함수의 바디 */);
const sum = new Function('a', 'b', 'c', 'return a+b+c');
console.log(sum(1, 2, 3))function 과 new function 의 차이점
{
const a = 1;
const test = new Function('return a');
console.log(test); // ReferenceError: a is not defined
}
{
const a = 2;
const test = function () {
return a;
};
console.log(test()); //제대로 작동함
}- new function()으로 만든 함수는 외부 변수가 아니라 전역변수를 참조하기 때문에 오류가 발생한다. {}밖에서 a를 정의하면 오류는 사라진다.
()=>{} (arrow function)
const hello1 = () => {
console.log('hello1');
}
hello1();
//매개변수가 하나일 때, 괄호 생략 가능
const hello2 = name => {
console.log('hello2', name);
}
hello2("yeongchan")
const hello3 = (name, age) => {
console.log('hello3', name, age);
};
hello3('yeongcahn', 20)
const hello4 = name => {
return `hello4 ${name}`;
};
console.log(hello4('yeongchan'));
const hello5 = name => `hello5 ${name}`;
console.log(hello5('yeongchan'));new 함수(); - 생성자 함수
//생성자 함수를 이용하여 새로운 객체 생성
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
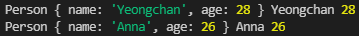
const p = new Person('Yeongchan', 28)
console.log(p, p.name, p.age);
const a = new Person('Anna', 26);
console.log(a, a.name, a.age);
const Cat = (name, age) => {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
const c = new Cat('냥이', 1); //오류 발생arrow function 은 this 에 대한 바인딩이 없고 생성자로 사용할 수 없기 때문이다.
함수 안에 함수를 만들어서 리턴
//함수 안에서 함수를 만들어 리턴
function plus(base) {
return function (num) {
return base + num;
}
}
const plus5 = plus(5);
console.log(plus5(10));
const plus8 = plus(8);
console.log(plus8(7));
//함수를 인자로 하여 함수를 호출
function hello(c) {
console.log('hello');
c();
}
//hello를 실행하면 console.log('hello')를 실행하고 c() 함수를 실행한다.
hello(function () {
console.log('콜백');
});
//c함수 정의