문제
Programmers 거리두기 확인하기
핵심
- 입력의 크기가 작아 구현에 초점을 맞춘다.
- 5개의 대기실에 응시자가 자리에 앉아 있다. 거리두기로 인해 맨해튼 거리(2) 이하로 앉지 않아야 한다. 단, 응시자 사이에 파티션이 있다면 붙어서 앉을 수 있다. 거리두기 준수 여부를 배열로 반환해야 한다.
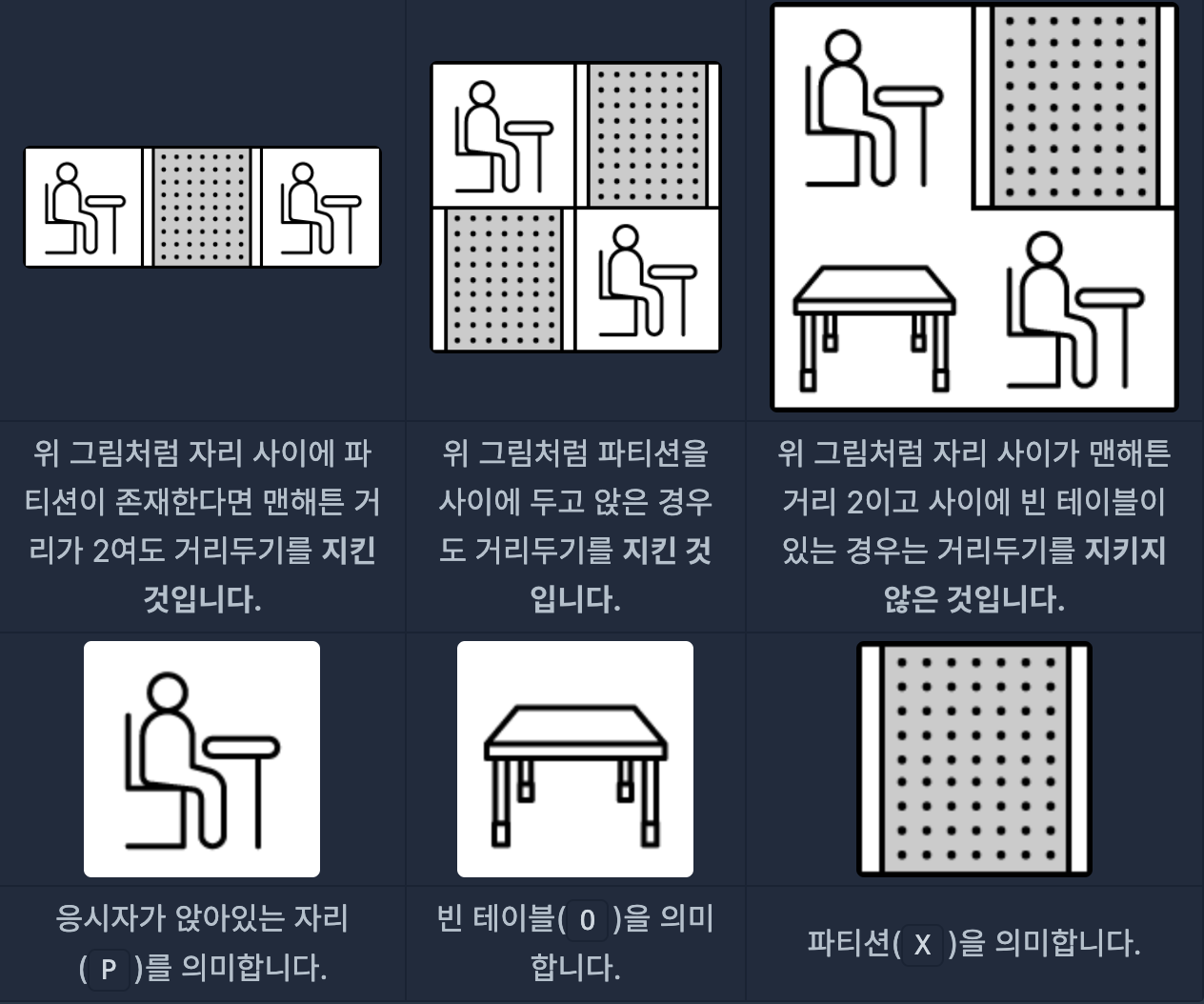
- 직관적으로 접근할 수 있다. BFS나 DFS 탐색으로 접근할 수도 있고, 문제 조건 자체가 간단하기 때문에 2중 반복문으로도 해결할 수 있다. 후자는 조건 처리 부분에서 실수할 여지가 있기 때문에 BFS로 구현하였다.
- String[][] places로 격자판이 주어지기 때문에 접근할 때 조금 헷갈렸었다. 차례대로 접근하는 코드는 아래와 같다.
for (int j = 0; j < places[i].length; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < places[i][j].length(); ++k) {
if (places[i][j].charat(k) == 'p') {
par.add(new int[]{j, k});
}
}
}
- 사용자가 앉은 자리를 기준으로 BFS 탐색을 시작한다. 큐에 넣고 빼기를 반복하면서 이동 거리가 2 이상 탐색하지 않기 위해 거리 2부터는 더 이상 큐에 넣지 않는다. 사용자의 초기 자리가 아닌 곳에서 P(다른 사용자)를 만났다면 거리두기를 지키지 않은 것으로 본다.
boolean bfs(int i, int y, int x, String[][] places) {
int start_y = y;
int start_x = x;
isVisited[y][x] = true;
q.offer(new int[]{y, x, 0});
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
var e = q.poll();
y = e[0];
x = e[1];
int move = e[2];
if (!(start_y == y && start_x == x) && places[i][y].charAt(x) == 'P') return false;
for (int dir = 0; dir < 4; ++dir) {
int ny = y + dy[dir];
int nx = x + dx[dir];
if (ny < 0 || ny >= r || nx < 0 || nx >= c) continue;
if (places[i][ny].charAt(nx) == 'X' || isVisited[ny][nx] == true) continue;
if (move > 1) continue;
q.offer(new int[]{ny, nx, move + 1});
}
}
return true;
}
개선
- 답을 구하는 과정에서 stream을 쓰게 되면, stream 연산 비용과 unboxing 비용으로 속도가 많이 느려진다. 입력의 크기가 작은데도 10배가량 차이가 난다.
int[] answer = ans.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
시간복잡도
O(5∗r∗c∗r∗c)
- r*c는 방 내부 탐색과 BFS 시간복잡도를 의미한다.
코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
int dy[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
List<int[]> par = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] solution(String[][] places) {
for (int i = 0; i < places.length; ++i) {
par.clear();
q.clear();
for (int j = 0; j < places[i].length; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < places[i][j].length(); ++k) {
if (places[i][j].charAt(k) == 'P') {
par.add(new int[]{j, k});
}
}
}
boolean isSafe = true;
for (var e : par) {
if (!bfs(i, e[0], e[1], places)) {
isSafe = false;
ans.add(0);
break;
}
}
if (isSafe) ans.add(1);
}
int[] answer = new int[ans.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
answer[i] = ans.get(i);
}
return answer;
}
boolean bfs(int i, int y, int x, String[][] places) {
int r = places[i].length;
int c = places[i][0].length();
boolean [][]isVisited = new boolean[r][c];
int start_y = y;
int start_x = x;
isVisited[y][x] = true;
q.offer(new int[]{y, x, 0});
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
var e = q.poll();
y = e[0];
x = e[1];
int move = e[2];
if (!(start_y == y && start_x == x) && places[i][y].charAt(x) == 'P') return false;
for (int dir = 0; dir < 4; ++dir) {
int ny = y + dy[dir];
int nx = x + dx[dir];
if (ny < 0 || ny >= r || nx < 0 || nx >= c) continue;
if (places[i][ny].charAt(nx) == 'X' || isVisited[ny][nx] == true) continue;
if (move > 1) continue;
q.offer(new int[]{ny, nx, move + 1});
}
}
return true;
}
}



