테스트 관련 용어는 이전 포스팅을 참고하자.
테스트를 어떻게 작성할까?
- 프로덕션 코드가 완성되고 나서 테스트 코드를 하나씩 작성한다는 건 꿈만 같은 일이다. 실제 서비스는 여러 기능이 복잡하게 얽혀 작동되기 때문에 중간에 어느 하나가 제대로 동작하지 않는다면 디버깅에 오랜 시간이 걸린다. 따라서 핵심 기능 단위로 테스트 코드가 작성되어 무결성을 보장해야 한다. 이는 개발 중간에 요구 사항이 변경되어 코드를 수정해야 할 때도 해당 기능이 제대로 동작하는지 이정표 역할을 한다.
테스트 주도 개발(Test-Driven Development, TDD)
-
이를 위한 테스트 주도 개발이 있다. 단순히 테스트를 기능 검사 체크리스트로 접근하는 것이 아닌 먼저 테스트를 만들고 해당 테스트를 통과하는 최소한의 코드 작성, 리팩토링을 반복하여 기능을 완성해 나가는 기법이다. 먼저 핵심 기능 테스트를 작성하여 의존관계를 파악하고, 필요한 코드만 작성하려고 노력하다 보면 코드 품질이 향상된다고 한다.
-
Spring Web MVC Framework를 이용해 기본적인 게시판 댓글 CRUD 기능을 테스트하며 구현해 본다. 웹 서비스는 외부 요청을 받아 처리하고 적절한 응답을 반환하는 Controller 계층, 비즈니스 로직을 구현하는 Service 계층, 데이터베이스를 조작하는 Repository 계층 구조를 가진다. 계층마다 책임이 다르기에 테스트해야 하는 부분이 다르다. 중요한 것부터 검증이 필요한 순서대로 테스트를 작성하면 되지만 개인적으로 핵심 의존 관계를 빠르게 파악하기 위해 Service 계층부터 작성해야 한다고 생각한다.
단위테스트 vs 통합테스트
- 굳이 계층마다 단위테스트를 작성할 필요가 있을까? 통합 테스트로 여러 기능을 한 번에 하면 되지 않을까? 사실 이 둘은 어느 하나를 선택해야 하는 배타적인 관계가 아니라 부족한 점을 보완하는 상호 보완적 관계에 있다.
- 단위 테스트는 환경을 격리하여 실행 속도가 빠르고, 해당 기능이 명세대로 동작하는지 쉽게 알아볼 수 있어 코드 수정이 쉽다. 반면 통합 테스트는 필요한 환경을 구성하는 데 오랜 시간이 걸리지만 실제 환경에서 여러 기능들이 복합적으로 동작할 때 제대로 동작하는지 확인할 수 있다.
Mockito
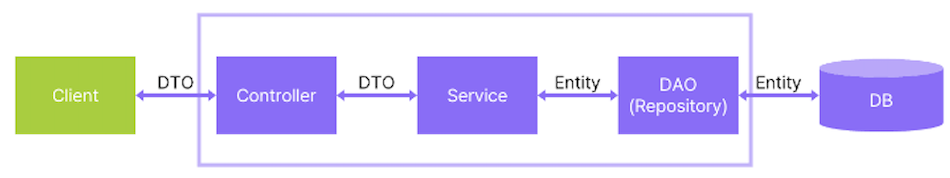
- Service 계층은 비즈니스 로직을 실행하며 필요한 경우 Repository 계층을 통해 데이터베이스에 접근한다. 데이터베이스 종속성을 제거하기 위해 Mokito를 사용한다.
1. Mocking
- Mocking, 모킹이란 실제 데이터베이스를 가짜 객체로 실제 행동을 모방(Mocking)하는 것을 말한다. 실제 데이터베이스에
@Mock으로 모방할 대상을 정하고,@InjectMocks는 Mocking 된 객체를 테스트 대상 객체(CommentService)에 주입하기 위해 사용한다. @ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)는 JUnit5에서 Mokito를 사용하겠다는 어노테이션이다.
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
public class CommentServiceTest {
@InjectMocks
private CommentService commentService;
@Mock
private CommentRepository commentRepository;
@Mock
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Mock
private ArticleRepository articleRepository;
}2. Stubbing
- Stubbing이란 가짜 객체의 행동을 지정하는 것을 말한다.
Mokito.when() ~ .thenReturn()을 통해 가짜 객체가 특정 메소드를 호출할 때 반환값을 지정할 수 있고,Mockito.when() ~ .thenThrow()를 통해 에러를 발생시킬 수도 있다.- 반환값이 없는 경우
Mokito.doThrow,Mokito.doNothing을 사용할 수 있다.
- 반환값이 없는 경우
when(articleRepository.findById(article.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(article));
Mockito.when(commentService.create(Mockito.eq(article.getId()), Mockito.any(RequestCreateComment.class)))
.thenThrow(new UserNotFoundException());3. Verification
- Verification이란 가짜 객체가 특정 메소드를 얼마나 호출했는지를 검증하는 것을 말한다.
Mokito.verify ~ times()를 통해 횟수 검증이 가능하다. times가 1인 경우 생략 가능하다.
Mockito.verify(commentRepository).delete(comment1);4. Argument Matcher
- Arguemnt Matcher(
any(), eq(), argThat(), ...)를 이용하여 메소드 호출 시 전달되는 인자를 유연하게 검증하는 것을 말한다.- any(): 어떤 타입이든 상관 없다.
- any(class type)
- anyInt(), anyString ...
- eq(): 인자가 지정된 값과 동일해야 한다.
- argThat(): 사용자 정의 조건에 만족해야 한다.
- any(): 어떤 타입이든 상관 없다.
when(commentRepository.save(any(Comment.class))).thenReturn(comment1);
verify(mock).someMethod(eq(1));댓글 서비스 CRUD 구현
1. 게시글 생성
@DisplayName("유효한 게시글, 유저로 댓글 생성한다")
@Test
void CreateComment_WithValidArticleAndUser_ReturnCreatedComment() {
//given
RequestCreateComment requestCreateComment = new RequestCreateComment(null, user2.getId(), "댓글 1");
when(articleRepository.findById(article.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(article));
when(userRepository.findById(user2.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(user2));
when(commentRepository.save(any(Comment.class))).thenReturn(comment1);
//when
ResponseCreateComment responseCreateComment = commentService.create(article.getId(), requestCreateComment);
//then
assertThat(responseCreateComment).isNotNull();
assertThat(responseCreateComment.id()).isEqualTo(1L);
assertThat(responseCreateComment.userId()).isEqualTo(user2.getId());
assertThat(responseCreateComment.content()).isEqualTo("댓글 1");
}
@DisplayName("존재하지 않는 게시글에 댓글 생성 시 CommentNotFoundException 발생한다")
@Test
void CreatedComment_WithNoneExistentArticle_ReturnCommentNotFoundException() {
//given
Long nonExistentArticleId = Long.MAX_VALUE;
RequestCreateComment requestCreateComment = new RequestCreateComment(null, user2.getId(), "댓글 1");
when(articleRepository.findById(nonExistentArticleId)).thenReturn(Optional.empty());
//when
//then
assertThatThrownBy(() -> {
commentService.create(nonExistentArticleId, requestCreateComment);
}).isInstanceOf(ArticleNotFoundException.class);
}
@DisplayName("존재하지 않는 유저가 댓글 생성 시 CommentNotFoundException 발생한다")
@Test
void CreatedComment_WithNoneExistentUser_ReturnCommentNotFoundException() {
//given
Long nonExistentUserId = Long.MAX_VALUE;
RequestCreateComment requestCreateComment = new RequestCreateComment(null, nonExistentUserId, "댓글 1");
when(articleRepository.findById(article.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(article));
when(userRepository.findById(nonExistentUserId)).thenReturn(Optional.empty());
//when
//then
assertThatThrownBy(() -> {
commentService.create(article.getId(), requestCreateComment);
}).isInstanceOf(UserNotFoundException.class);
}2. 게시글 조회
@DisplayName("유효한 댓글 아이디로 특정 댓글 조회시 해당 댓글을 반환한다")
@Test
void FindComment_WithValidId_ReturnComment() {
//given
ResponseComment expected = new ResponseComment(1L, 2L, "닉네임 2", 1L, "제목 1", "댓글 1");
when(commentRepository.findById(comment1.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(comment1));
//when
ResponseComment responseComment = commentService.findCommentById(comment1.getId());
//then
assertThat(responseComment).isNotNull();
assertThat(responseComment).usingRecursiveComparison().isEqualTo(expected);
}
@DisplayName("유효한 게시글 아이디에 해당하는 댓글 조회시 해당하는 모든 댓글을 반환한다")
@Test
void findComments_WithValidArticleId_ReturnComments() {
//given
List<Comment> comments = Arrays.asList(comment1, comment2);
List<ResponseComment> expected = mapper.commentsToResponseComments(comments);
when(articleRepository.findById(article.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(article));
when(commentRepository.findByArticleId(article.getId())).thenReturn(comments);
//when
List<ResponseComment> actual = commentService.findCommentsByArticleId(article.getId())
.stream()
.toList();
//then
assertThat(actual.size()).isEqualTo(2);
assertThat(actual).usingRecursiveComparison().isEqualTo(expected);
}
@DisplayName("모든 댓글 조회 시 모든 댓글을 반환한다")
@Test
void FindArticles_ReturnFoundArticles() {
//given
List<Comment> comments = Arrays.asList(comment1, comment2);
List<ResponseComment> expected = mapper.commentsToResponseComments(comments);
when(commentRepository.findAll()).thenReturn(comments);
//when
List<ResponseComment> actual = commentService.findAll()
.stream()
.toList();
//then
assertThat(actual.size()).isEqualTo(2);
assertThat(actual).usingRecursiveComparison().isEqualTo(expected);
}3. 댓글 수정
@DisplayName("유효한 정보로 댓글 수정 시 수정된 댓글을 반환한다")
@Test
void UpdateComment_ReturnUpdatedComment() {
//given
comment1 = new Comment(1L, user2, article, "댓글 수정 1");
ResponseComment expected = mapper.commentToResponseComment(comment1);
RequestUpdateComment requestUpdateComment = new RequestUpdateComment("댓글 수정 1", user2.getId());
when(commentRepository.findById(comment1.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(comment1));
when(commentRepository.save(any(Comment.class))).thenAnswer(invocation -> invocation.getArgument(0));
//when
ResponseComment updatedComment = commentService.update(comment1.getId(), requestUpdateComment);
//then
assertThat(updatedComment).isNotNull();
assertThat(updatedComment).usingRecursiveComparison().isEqualTo(expected);
}
@DisplayName("권한 없는 사용자가 댓글 수정 시 UnauthorizedAccessException 발생한다")
@Test
void UpdateComment_WithUnAuthorizedUser_ReturnUnauthorizedAccessException() {
//given
comment1 = new Comment(1L, user2, article, "댓글 수정 1");
ResponseComment expected = mapper.commentToResponseComment(comment1);
RequestUpdateComment requestUpdateComment = new RequestUpdateComment("댓글 수정 1", user1.getId());
when(commentRepository.findById(comment1.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(comment1));
//when
//then
assertThatThrownBy(() -> {
commentService.update(article.getId(), requestUpdateComment);
}).isInstanceOf(UserUnauthorizedAccessException.class);
}4. 게시글 삭제
@DisplayName("유효한 댓글 아이디로 댓글을 삭제한다")
@Test
void DeleteComment_WithValidId() {
//given
when(commentRepository.findById(comment1.getId())).thenReturn(Optional.of(comment1));
//when
commentService.delete(comment1.getId());
//then
Mockito.verify(commentRepository).delete(comment1);
}
@DisplayName("유효한 댓글 아이디가 아닐 경우 NotFoundExpcetion을 발생한다")
@Test
void DeleteComment_WithInvalidId_ReturnNotFoundException() {
//given
Long nonExistentArticleId = Long.MAX_VALUE;
when(commentRepository.findById(nonExistentArticleId)).thenReturn(Optional.empty());
//when
//then
assertThatThrownBy(() -> {
commentService.delete(nonExistentArticleId);
}).isInstanceOf(CommentNotFoundException.class);
}느낀 점
mapper (mapstruct)
- Service 계층에서 repository를 mocking하여 사용하고 있는데, 그렇게 중요하지 않은 mapper까지 mocking 로직을 사용하는 게 거부감이 들었다. Spring Bean을 로드하지 않기에
private CommentMapper mapper = Mappers.getMapper(CommentMapper.class);방법으로는 의존성을 주입할 수 없었다. 여러 해결 방법을 찾아보던 중 리플렉션으로 의존성을 주입하여 mapper에 대해서만 실제 객체를 사용할 수 있었다.
private CommentMapper mapper = Mappers.getMapper(CommentMapper.class);
ReflectionTestUtils.setField(commentService, "mapper", mapper);
Mockito 사용
- 복잡한 기능이 없지만 엄격한 스터빙 조건이라던든지 무엇을, 어떻게 Mocking하고 이게 의미가 있는 테스트인지 고민하는 시간이 많이 필요했다. 일정한 포멧으로 테스트 코드를 작성하려고 행위-상태-결과가 메서드 명에 포함되게끔 작성했다. 엔티티도 추가해야 할 요소들이 많아서 테스트 코드 수정도 불가피해 보인다. 부족한 점이 많지만, 습득의 영역이라는 생각이 들고 계속 고쳐나가야겠다.
