지난 글에 이어 자바스크립트의 비동기 처리와 관련된 함수를 알아보고자 한다.
In Javascript?-2
1. Promise
Promise는 말 그대로 미래에 대한 약속이다. 이 약속은 지켜질 수도, 지켜지지 않을 수도 있다. 우선 프로미스는 객체로, 3가지 상태를 가지고 있다.
- Pending: 초기 상태
- Resolved: 프로미스가 완료된 상태
- Rejected: 프로미스가 실패한 상태
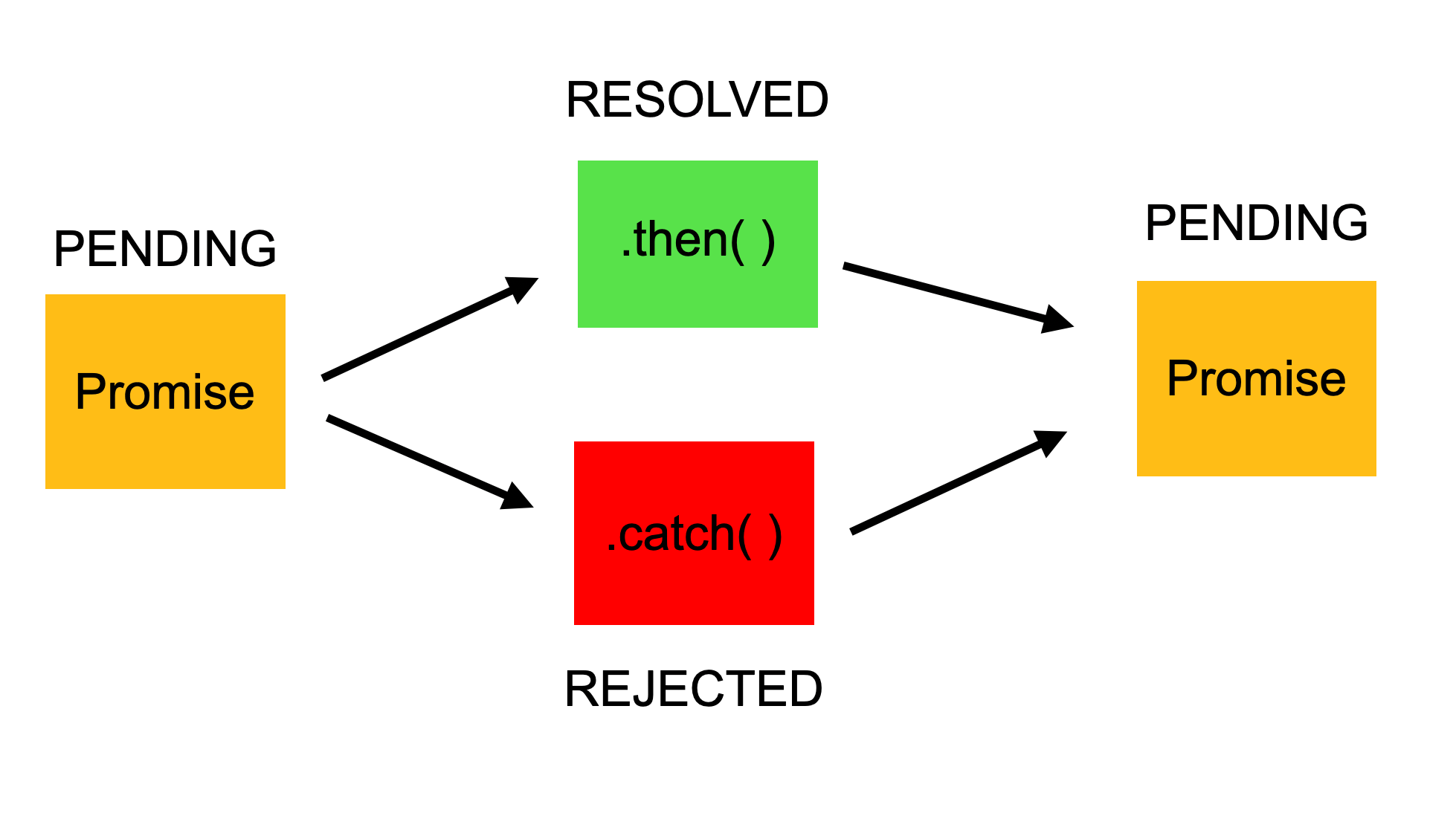
위 그림처럼 완료되었을 경우에는 .then()메소드로 실행하고, 실패했을 경우 .catch()로 예외처리를 해줄 수 있다.(물론 .then(undefined, func)등으로 then()을 사용해 똑같이 예외처리를 해줄 수도 있지만 읽기가 불편하다)
var promise = new Promise( (resolve, reject) => {
// 뭔가 비동기 작업을 만들고
if (/* 참일 때 */) {
resolve("Stuff worked!");
}
else {
reject(Error("It broke"));
}
});프로미스 객체는 기본적으로 위와 같이 생성한다. 이제 생성된 객체에서 성공했으면 .then()으로, 실패했으면 .catch()로 가서 그 다음에 할 작업을 만들어 주면 된다.
promise.then(result => {
console.log("Success!", result); // "Stuff worked!"
}).catch(err => {
console.log("Failed!", err); // Error: "It broke"
});위에서 볼 수 있듯, then과 catch는 서로 붙일 수 있는데 여기서 then에 then을 더 붙이는 것도, catch를 한번 써주고 또 몇개 밑에 다시 별도의 catch를 쓰는 것도 가능하다. 이를 chaining 이라고 하며 체이닝을 통해 여러 작업을 생성해 주는 것이 가능해진다.
function processImage(imageName, domNode) {
return loadImage(imageName)
.then(function(image) {
return scaleToFit(150, 225, image);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log('Error in loadImage() or scaleToFit()', error);
console.log('Using fallback image');
return fallbackImage();
})
.then(function(image) {
return watermark('Google Chrome', image);
})
.then(function(image) {
showImage(image);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log('We had a problem with watermark() or showImage()', error);
});
}2. async/await
비동기처리와 관련하여 자바스크립트에 내장된 가장 최신 기술(?)이 async/await이다. ECMA2017에서 추가되었으니 나름 최근이라면 최근이라 할 수 있겠다. Promise도 콜백에 비하면 선녀같지만, async/await은 프로미스보다 훨씬 동기적으로(?)생겨서 한눈에 알아보기가 편해졌다.
function who() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('🤡');
}, 200);
});
}
function what() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('lurks');
}, 300);
});
}
function where() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('in the shadows');
}, 500);
});
}
async function msg() {
const a = await who();
const b = await what();
const c = await where();
console.log(`${ a } ${ b } ${ c }`);
}
msg(); // 🤡 lurks in the shadows <- 1초 후 나타남다만 위의 코드는 a->b->c 순차적으로(sequentially) 처리되므로 a가 끝나야 b가 시작되는 식이다. 그래서 병렬적(parallel)으로 처리하고 싶다면 Promise.all을 사용해야 한다.
그리고 async함수를 실행한 결과는 항상 프로미스 객체를 리턴한다는 특징이 있다.
예외처리에 있어서도 Promise는 then()/catch()를 사용했지만 async함수는 try/catch로 예외처리를 실행한다.
