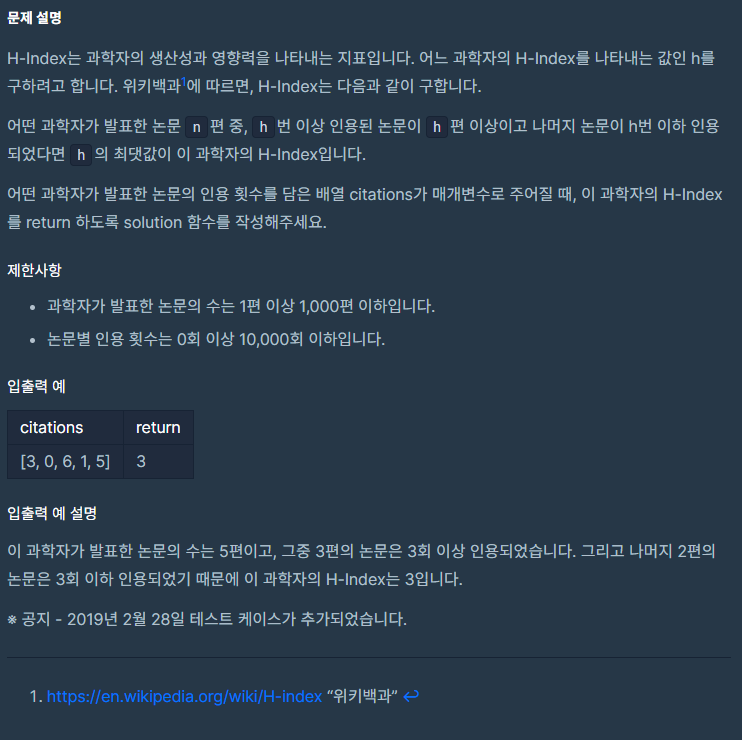
코드
def solution(citations):
answer = 0
# index가 인용 횟수인 리스트 생성
res=[0]*(max(citations)+1)
# 인용 횟수가 c번인 논문의 개수 확인
for c in range(max(citations)+1):
cnt=0
for i in citations:
if i>=c:
cnt+=1
res[c]=cnt
for idx, val in enumerate(res):
if idx<=val:
answer=idx
return answerO(n^2)으로 속도면에서 좋지 않은 코드
다른 사람의 풀이
def solution(citations):
citations = sorted(citations)
l = len(citations)
for i in range(l):
if citations[i] >= l-i:
return l-i
return 0l-i가 도대체 뭔지 한참을 고민했다.
if citations[i] >= l-i는 주어진 h번 이상 인용된 논문이 h편 이상이라는 조건을 그대로 풀어쓴 것이었다.
citations[i]는 i번 논문이 인용된 횟수이고 l-i는 인용된 논문의 개수를 최댓값부터 하나씩 줄여나간 것이다. (최댓값을 찾아야 하므로 가장 큰 값부터 시작)
그리고 리스트는 오름차순 정렬된 상태이므로 i번째 이후는 모두 i번째보다 큰 값을 가질 것이다.
