TL:DR;
Spring 의 Core technologies 로 가장 먼저 이야기 되는 IoC Container 에 대해 간단하게 정리해보고자 한다.
Spring Framework를 사용하면 @Autowired, @Bean, @Component, @Service, @Controller 등 다양한 annotation을 사용하게 된다.
이러한 작업들은 모두 IoC Container가 제대로 Object를 관리할 수 있도록 처리해주는 작업들이라 할 수 있다.
XML, Java Annotation 혹은 Java configuration 을 통해서 Bean을 등록할 수 있고 위에 언급한 @Component, @Repository, @Service, @Controller annotation을 통해서 Bean을 등록할 수 있다.
위 어노테이션으로 등록을 하게 되면 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 가 classpath를 조사하며 어노테이션을 filter 하여 Bean등록을 하게 된다.
public class ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner extends ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private BeanDefinitionDefaults beanDefinitionDefaults = new BeanDefinitionDefaults();
@Nullable
private String[] autowireCandidatePatterns;
private BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = AnnotationBeanNameGenerator.INSTANCE;
private ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = new AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver();
private boolean includeAnnotationConfig = true;
이렇게 Bean 등록을 하고 이를 IoC Container 가 관리하게 되는 것이다.
IoC Container 란?
IoC 는 Inversion of Control 이라는 뜻으로 직역하자면 제어의 역전이라 할 수 있다. 제어의 역전이란 말이 왜 붙게 됐냐 하면 일반적으로 객체의 관리를 사용자가 했던 관점에서 객체의 관리를 Spring 에 맡기게 되면서 관리하는 주체가 역전됐다는 의미에서 그런 이름이 붙여졌다.
제어의 주체가 사용자가 아닌 Spring?
단순히 글로만 이해하기 어려울 수 있어 간단한 예제를 들면 아래와 같다.
# 1 일반적인 객체 관리
public class MovieRecommender {
private final CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao;
public MovieRecommender() {
this.customerPreferenceDao = new customerPreferenceDao();
}
// ...
}
# 2 IoC 적용
public class MovieRecommender {
private final CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao;
@Inject
public MovieRecommender(CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao) {
this.customerPreferenceDao = customerPreferenceDao;
}
// ...
}
차이는 단순하다.
첫 번째 예시에는 MovieRecommender의 생성자에 직접 new 키워드를 사용하여 객체를 할당해주고 있다. 이렇게 되면 customerPreferenceDao 와 강하게 coupling 되게 된다.
또한 이러한 구성은 확장성도 갖기 힘들게 된다.
두 번째 예시는 외부에서 만들어진 객체를 인자로 받는 방식으로 soft 하게 두 객체의 관계를 유지할 수 있게 된다. 따라서 다형성을 확보하고 결합도 또한 낮출 수 있다.
위와 같은 방식이 DI ( Dependency Injection ) 와 유사하기 때문에 Spring docs 에서는 IoC == DI 로 정의하고 있다.
위 예시에서 Inject를 Autowired 로 바꾸면 Spring 방식의 DI 가 되는 것이다.
BeanFactory와 ApplicationContext
IoC 를 구현하는 기본이 되는 package가 BeanFactory Interface, Application Context interface 이다.
BeanFactory Interface는 모든 타입에 대한 Configuration 정보를 관리하고 ApplicationContext Interface는 BeanFactory 의 sub-interface 로 기능한다.
ApplicationContext Interface의 대표 기능은
- Spring's AOP featrue 통합
- Message resource handling
- 이벤트 생성
- web application 에 사용되는 Application Layer Context를 제공
Spring boot를 통한 Configuration metadata 설정은 보통 @Configuration 을 통해서 이루어진다.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityJavaConfig {
@Value("${jwt.secret}")
private String secret;
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable);
http.headers().frameOptions().disable();
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((requests) -> requests
.requestMatchers("/", "/home", "/h2-console", "/**", "/*").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.formLogin((form) -> form
.loginPage("/login")
.disable()
)
.addFilterBefore(new JwtAuthenticationFilter(jwtUtil()), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS);
return http.build();
}결론
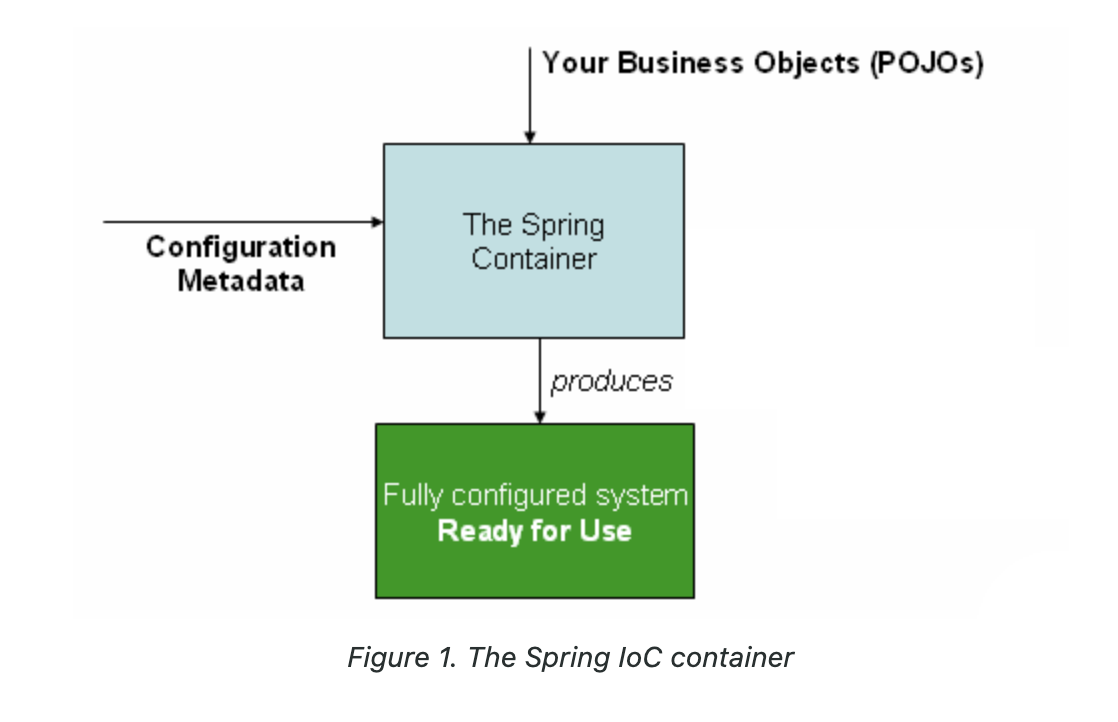
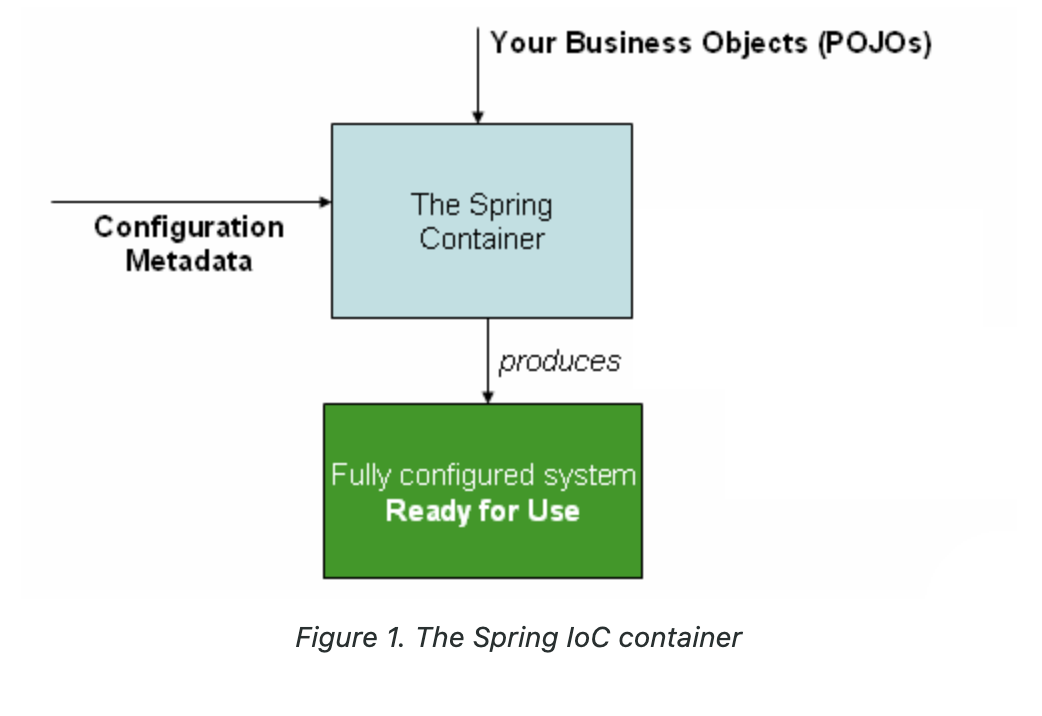
BeanFactory, ApplicationContext가 Configuration 정보를 가져와 ( XML, Java annotation, Java Configuration ) POJOS ( Plane Old Java Objects ) 를 결합해서 Bean을 만들고 이를 관리하는것이 IoC 컨테이너의 기본 동작 원리라 볼 수 있다.