23.11.2 (목) 31일차
영상처리 비전 (C++ 기반)
C++ 장점이 무엇인가?
다형성 (Polymorphism)
다양한 형태를 만들 수 있음.
1. 추상화
"virtual"
명시적으로 구현했지만 실체가 없는 상태. 흔히 interface라고 함.
무엇을 위해 만들었을까?
2. 상속
참고)
오버로딩 : 생긴 건 똑같은데 꼴이 다름. 10, 20, 30cm는 하고자 하는 역할은 똑같음. 선택적으로 사용 가능.
오버라이딩 : 거리를 측정할 때 누구는 줄자, 레이저 자, 3차원 자... 기능은 하난데 구현을 하기 위한 실체가 다른 것.
부모 클래스가 선언을 하고 정의했을 때 다시 내 것으로 대체하는 것.
pointer가 무엇인가?
가리키는 것. 어떤 자원이든 다 가리킬 수 있음.
주소, 주소값이라고 정의를 한다면 address라고 하지 왜 굳이 pointer라는 이름을 붙였을까?
함수도 포인터다
누군가 물었을 때 다 알려줄 수도 있지만 가리킴으로써 나타낼 수도 있음.
-> 전원을 켰을 때 컴퓨터의 모든 자원을 사용할 수 있는 것처럼
* : 택배를 시켰을 때 비밀번호를 알려주지 않고 문 앞까지만 알려주는 것. 포인터도 문 앞까지만 알려주는 것인데, *가 비밀번호 역할을 해서 접근할 수 있게 되는 것.
C에서와 C++에서 포인터 차이?
C는 포인터를 보호할 수 있는 장치가 없어서 내 프로그램이 죽거나 시스템이 죽을 수 있음. (양날의 검) 하지만 자원을 보호할 줄 아는 것도 프로그래밍 덕목 중 하나.
자원을 생성과 해제할 때 프로그램 중간부에서는 생성과 소멸이 됨. 이때 exception이 발생해서 소멸하지 않는다면 메모리가 점점 가득 차서 시스템이 나갈 수 있음.
C++에서 스마트 포인터 나옴. 미처 자원이 소멸되지 않고 나왔을 때도 안정적으로 관리됨. 자원이 효율적으로 관리되는 것이 중요한 패러다임 중 하나.
포인터 사이즈의 크기는? 컴퓨터에 따라 다름. (32bit, 64bit..)
한국에서는 32bit로 주소를 표현할 수 있었지만, 미국에서는 사용이 불가. 주소 체계를 더 키워줘야 잉여 땅을 없앨 수 있음.
물리적인 현재 자원 중 최대 접근할 수 있는 표현을 몇 bit로 할 것인지에 대한 것.
void pointer? 명확한 걸 좋아함. 명시적이지 않은 것이 void pointer.
type casting할 때 포인터도 casting할 수 있음. 형태를 무한히 바꿀 수 있음.
void는 4bit를 가리키고 있는데 그때그때마다 형태가 바뀌어서 사용됨.
순수 가상 함수와 가상 함수의 차이?
-
순수 가상 함수는 인터페이스(Interface)를 자식 클래스에게 전달하기 위해 사용하는 함수입니다.
-
일반(단순) 가상 함수는 인터페이스(Interface) + 함수의 선언(내부 구현) 까지 자식 클래스에게 전달하기 위해 사용하는 함수입니다.
순수 가상 함수는 자식에게 '아들아 너는 A기능이 꼭 있어야 해! 근데 그것은 너가 알아서 선언해!, 이거 선언 안 하면 아들아 너의 클래스는 돌아가지 않는단다.'
일반(단순) 가상 함수는 '아들아 B기능을 물려줄건데, 니가 선언 안 해도 내가 기본적으로 기능이 돌아가게 해줄게' 이런것입니다.
a = 1과 b(2)의 차이
int a = 1;
// int ctor -> instance -> operator '=' -> 1
int b(2);
// int ctor -> instance -> 2b(2) : int type의 메모리 공간을 만들어놓고 객체화(instance화)시킨다. 2라는 값으로 동시에 초기화됨.
a는 객체가 만들어진 후 대입연산자를 활용해 값을 초기화한다.
객체를 생성과 동시에 초기화한다.
class Shape
{
public:
Shape()
:a(1) // member initialize
,b(10)
{
// copy operator
a = 1;
b = 2;
cout << "Ctor" << endl;
}
~Shape();
private:
int a;
int b = 0;
};생성자 생성 및 소멸
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
public:
Shape()
:a(1) // member initialize
,b(10)
,pA(nullptr)
{
// copy operator
a = 1;
b = 2;
cout << "Ctor" << endl;
}
~Shape();
private:
int a;
int b = 0;
int* pA;
};
enum EShape {
eCircle,
eRectangle,
eTriangle,
ePoly,
eShapeMax
};
int main()
{
int a = 1;
// int ctor -> instance -> operator = -> 1
int b(2);
// int ctor -> instance -> 2
int c = a + b;
cout << c << "\t=\t" << a << "\t+\t" << b << endl;
int* pA = nullptr;
cout << "size of pointer pA = " << sizeof(pA) << endl;
EShape _eShape = EShape::eCircle;
int* pShape = new int[EShape::eShapeMax];
// init and managment
memset((void*)pShape, 0, sizeof(int)* EShape::eShapeMax);
// destroy
if (pShape != nullptr)
{
delete[] pShape;
pShape = nullptr;
}
vector<int> vShape(EShape::eShapeMax, 0);
vShape[0] = 1;
vShape[1] = 2;
vShape[2] = 3;
vShape[3] = 4;
return 1;
}구구단 세로로 출력
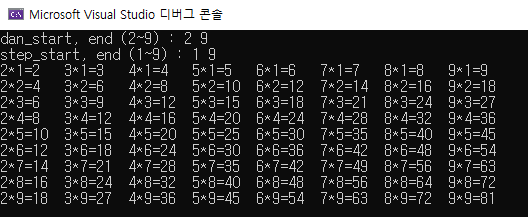
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int dStart, dEnd;
int sStart, sEnd;
cout << "dan_start, end (2~9) : ";
cin >> dStart >> dEnd;
cout << "step_start, end (1~9) : ";
cin >> sStart >> sEnd;
if (dStart < 2 || dEnd > 9 || sStart < 1 || sEnd > 9) {
cout << "wrong number!";
return 0;
}
for (size_t step = sStart; step <= sEnd; step++)
{
string msg = "";
for (size_t dan = dStart; dan <= dEnd; dan++)
{
size_t result = dan * step;
string str = "";
str = to_string(dan);
str += "*";
str += to_string(step);
str += "=";
str += to_string(result);
msg += str + "\t";
}
cout << msg << endl;
}
return 1;
}반복문에서 i, j 쓰는 거 지양하기! (i, j가 무엇을 가리키는지 애매하기 때문)
클래스화 하기
// GuGuDan.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class GuGuDan
{
public:
GuGuDan();
~GuGuDan();
void SetParams(size_t DanS = 0, size_t DanE = 0, size_t StepS = 0, size_t StepE = 0);
int Proc();
void Display();
private:
size_t _DanS, _DanE, _StepS, _StepE;
vector<string> vMsg;
};// GuGuDan.cpp
#include <string>
#include "GuGuDan.h"
using namespace std;
GuGuDan::GuGuDan()
: _DanS(0)
, _DanE(0)
, _StepS(0)
, _StepE(0)
{
cout << "GuGuDan::Ctor" << endl;
}
GuGuDan::~GuGuDan()
{
cout << "GuGuDan::Dtor" << endl;
}
void GuGuDan::SetParams(size_t DanS, size_t DanE, size_t StepS, size_t StepE)
{
this->_DanS = DanS;
this->_DanE = DanE;
this->_StepS = StepS;
this->_StepE = StepE;
_DanS = DanS;
_DanE = DanE;
_StepS = StepS;
_StepE = StepE;
}
int GuGuDan::Proc()
{
vMsg.clear();
for (size_t step = _StepS; step <= _StepE; step++)
{
string msg = "";
for (size_t dan = _DanS; dan <= _DanE; dan++)
{
size_t result = dan * step;
string str = "";
str = to_string(dan);
str += "*";
str += to_string(step);
str += "=";
str += to_string(result);
msg += str + "\t";
}
vMsg.push_back(msg);
//cout << msg << endl;
}
return 0;
}
void GuGuDan::Display()
{
// for basic
for (size_t i = 0; i < vMsg.size(); i++)
{
cout << vMsg[i] << endl;
}
// for range with iter
for (auto iter = vMsg.begin(); iter != vMsg.end(); iter++)
{
cout << (*iter) << endl;
}
// for auto range
for (const auto& msg : vMsg)
{
cout << msg << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
GuGuDan ggd;
int DanS = 2, DanE = 9, StepS = 1, StepE = 9;
ggd.SetParams(DanS, DanE, StepS, StepE);
ggd.Proc();
ggd.Display();
return 1;
}