알고리즘에서 트리를 탐색할 때 BFS를 활용할 수 있다.
BFS를 사용하면 레벨을 기준으로 트리를 탐색할 수 있다. 아래 사진을 살펴보자.
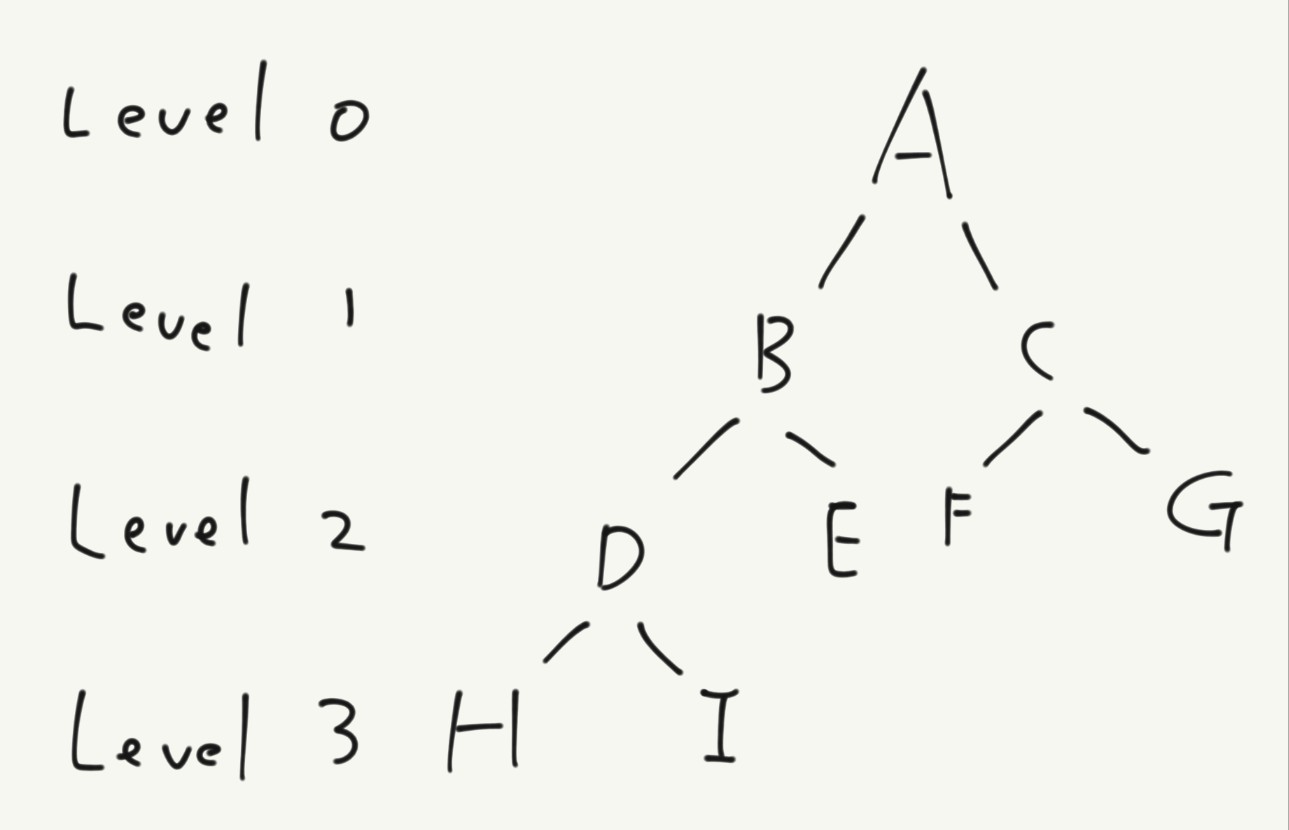
BFS를 사용하면 Level 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 순으로 트리를 탐색할 수 있다.
이를 구현한 코드는 아래와 같다. BFS는 큐를 사용한다.
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Queue;
class CompleteBinaryTree<T> {
private static int SIZE;
private static Object[] nodes;
private int lastIndex;
public CompleteBinaryTree (int size) {
SIZE = size;
nodes = new Object[size+1];
}
private boolean isFull() {
return lastIndex == SIZE;
}
public void add(T e) {
if (isFull()) {
return;
}
nodes[++lastIndex] = e;
}
public void bfs() {
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(1);
int current = 0;
int size;
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
size = queue.size();
System.out.print("level " + level + " : ");
while (--size >= 0) {
current = queue.poll();
System.out.print(nodes[current] + " ");
if (current * 2 <= lastIndex) {
queue.offer(current * 2);
}
if ((current * 2 + 1) <= lastIndex) {
queue.offer((current * 2 + 1));
}
}
level++;
System.out.println();
}
}
}
public class CompleteBinaryTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 9;
CompleteBinaryTree<Character> tree = new CompleteBinaryTree<> (size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
tree.add((char)(65 + i));
}
tree.bfs();
}
}실행 결과는 아래와 같다.
level 0 : A
level 1 : B C
level 2 : D E F G
level 3 : H I
알고리즘에서 트리를 탐색할 때 DFS를 활용할 수 있다.
트리의 노드들을 체계적으로 방문하는 것을 순회라고 한다.
순회에는 아래 3가지 방법이 있다.
- 전위 순회 : 자신 -> 왼쪽 자식 -> 오른쪽 자식 순으로 방문한다.
- 중위 순회 : 왼쪽 자식 -> 자신 -> 오른쪽 자식 순으로 방문한다.
- 후위 순회 : 왼쪽 자식 -> 오른쪽 자식 -> 자신 순으로 방문한다.
실제로 트리를 순회해보자. 아래 트리를 3개의 순회 방법으로 순회해보자.
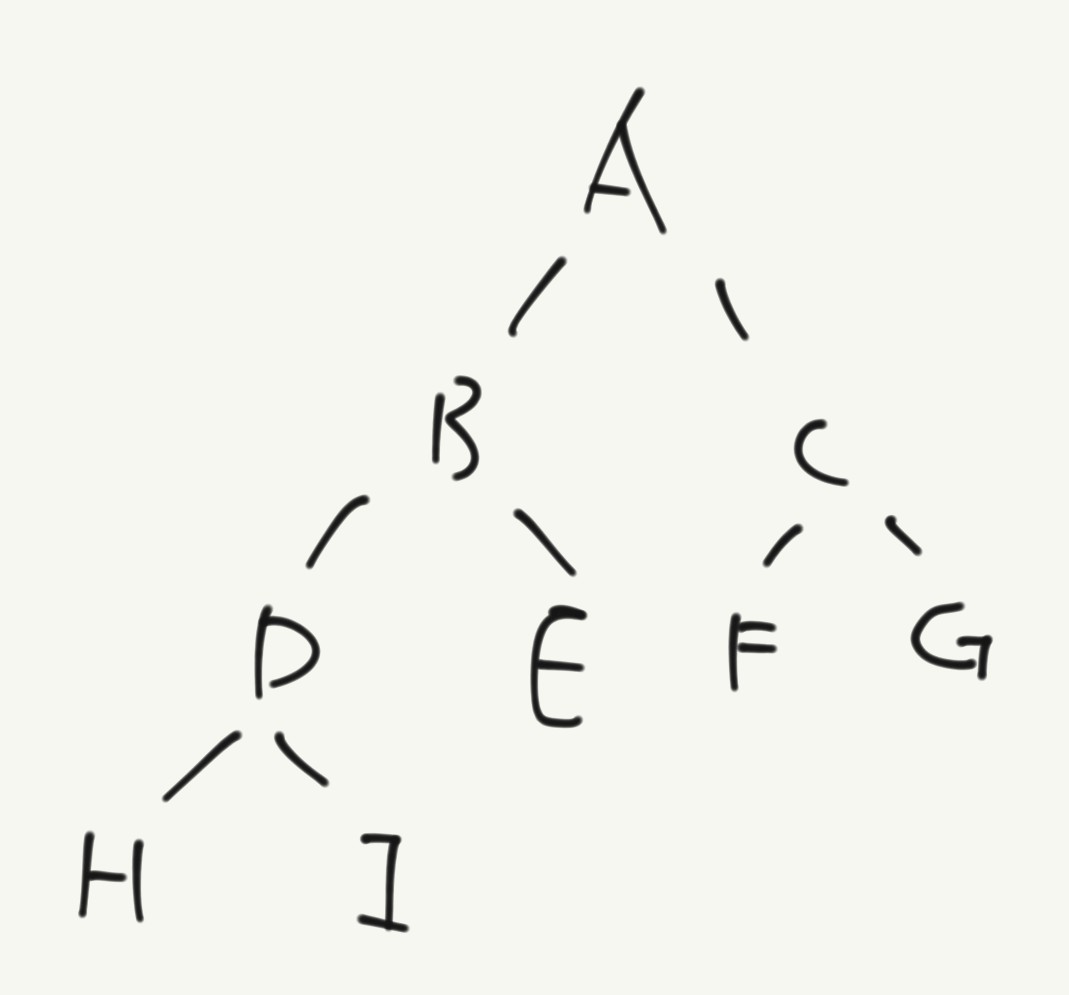
먼저 전위 순회이다. 전위 순회를 구현한 코드는 아래와 같다.
...
public void dfsByPreOrder() {
System.out.print("PreOrder : ");
dfsByPreOrder(1);
System.out.println();
}
private void dfsByPreOrder(int current) {
System.out.print(nodes[current] + " ");
if (current*2 <= lastIndex) {
dfsByPreOrder(current * 2);
}
if ((current*2 + 1) <= lastIndex) {
dfsByPreOrder(current * 2 + 1);
}
}
...실행 결과는 아래와 같다.
A B D H I E C F G
다음으로 중위 순회이다. 중위 순회를 구현한 코드는 아래와 같다.
...
public void dfsByInOrder() {
System.out.print("InOrder : ");
dfsByInOrder(1);
System.out.println();
}
private void dfsByInOrder(int current) {
if (current*2 <= lastIndex) {
dfsByInOrder(current * 2);
}
System.out.print(nodes[current] + " ");
if ((current*2 + 1) <= lastIndex) {
dfsByInOrder(current * 2 + 1);
}
}
...실행 결과는 아래와 같다.
H D I B E A F C G
다음으로 후위 순회이다. 후위 순회를 구현한 코드는 아래와 같다.
public void dfsByPostOrder() {
System.out.print("PostOrder : ");
dfsByPostOrder(1);
System.out.println();
}
private void dfsByPostOrder(int current) {
if (current*2 <= lastIndex) {
dfsByPostOrder(current * 2);
}
if ((current*2 + 1) <= lastIndex) {
dfsByPostOrder(current * 2 + 1);
}
System.out.print(nodes[current] + " ");
}실행 결과는 아래와 같다.
H I D E B F G C A
전위 순회는 재귀가 아닌 스택으로도 구현이 가능하다. 아래 코드는 이를 보여준다.
public void dfsByPreOrderUseStack() {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
int current = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
current = stack.pop();
System.out.print(nodes[current] + " ");
if ((current*2 + 1) <= lastIndex) {
stack.push(current * 2 + 1);
}
if (current*2 <= lastIndex) {
stack.push(current * 2);
}
}
}이 때는 오른쪽 자식, 왼쪽 자식 순으로 넣어줌으로써 재귀 출력 순서와 동일하게 출력된다.
출력 결과는 아래와 같다.
A B D H I E C F G
알고리즘에서 힙을 활용할 수 있다.
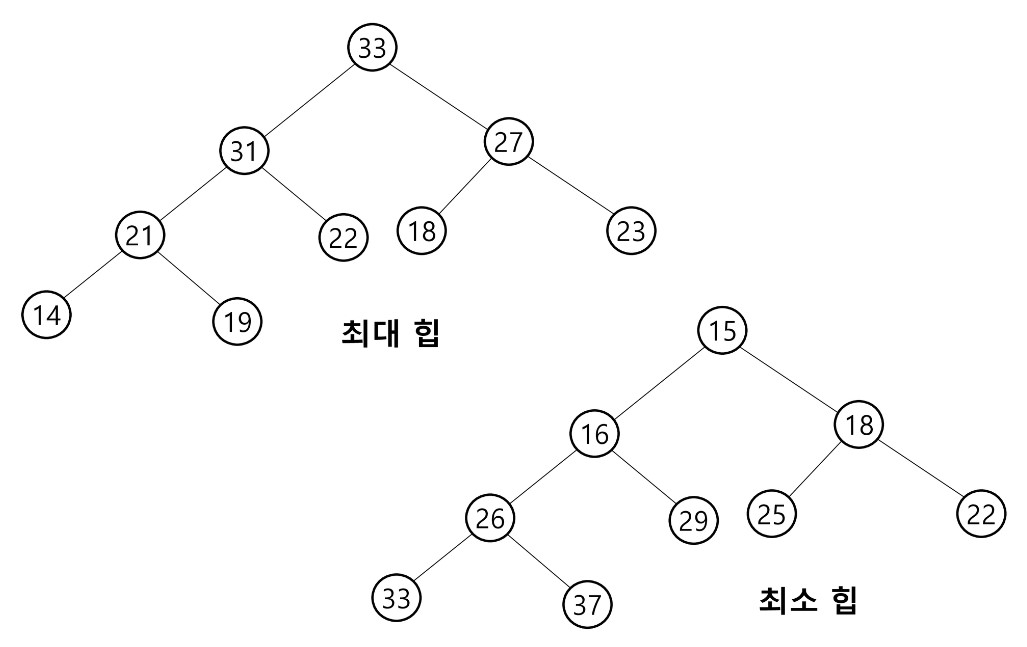
힙은 최대 힙, 최소 힙 두 가지가 있다. 최대 힙의 특징은 아래와 같다.
- 키 값이 가장 큰 노드를 찾기 위한 완전 이진 트리이다.
- 부모 노드의 키 값 >= 자식 노드의 키 값이 모든 서브 트리에서 성립한다.
- 2번 논리에 따라 키 값이 가장 큰 노드는 루트 노드가 된다.
최소 힙은 최대 힙과 반대되는 개념이다.
아래 사진은 최대 힙과 최소 힙의 예시이다.