Refresh token 개념 복습:
https://inpa.tistory.com/entry/WEB-%F0%9F%93%9A-Access-Token-Refresh-Token-%EC%9B%90%EB%A6%AC-feat-JWT
Redis
참고자료: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/why-when-use-redis-hamed-moayeri/
Redis is an open-source, NoSQL-based, in-memory databse. It can use caching to improve performance.
Why store the refresh token in a DB?
The refresh token can be stored in any DB or just be stored with the client. Storing the refresh token on a db allows the server to blacklist a certain refresh token if the access token has been attacked. The server can view who has been authenticated as currently has access to the system.
Connecting to Redis on Ubuntu
Connecting locally on Ubuntu:
redis-cliConnecting to Redis cloud on Ubuntu:
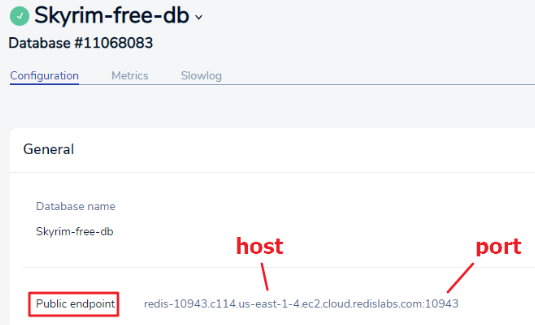
redis-cli -h <HOST> -p <PORT> -a <PASSWORD>Connecting to Redis on NodeJS
Install the Redis package:
npm i redisSetting up connection to Redis in the service layer:
const { createClient } = require('redis')
class RedisService {
constructor() {
this.client = createClient({
socket: {
host: process.env.REDIS_HOST,
port: process.env.REDIS_PORT
},
password: process.env.REDIS_PASSWORD
})
this.client.on('connect', () => console.log('Connected to Redis'))
this.client.on('error', (err) => console.log('Redis client error', err))
this.client.on('end', () => console.log('Disconnected from Redis'))
}
set = async ({ key, value, timeType, time }) => {
try {
await this.client.connect();
await this.client.set(key, value, timeType, time);
await this.client.disconnect();
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
}
}
get = async (key) => {
await this.client.connect();
const result = await this.client.get(key);
await this.client.disconnect();
return result;
}
del = async (key) => {
await this.client.connect()
await this.client.del(key)
await this.client.disconnect()
}
}
module.exports = RedisServiceSample code to store the refresh token on Redis. The key is the refresh token to easily get the key from Redis by reading the refresh token on the client.
await this.redisService.set({
key: refreshToken,
value: userInfo.userId,
timeType: "EX", // Time in seconds
time: process.env.JWT_REFRESH_TOKEN_TIME
})When logging out, the accessToken and refreshToken cookies are deleted as well as the key in Redis.
await this.redisService.del(refreshToken)
res.clearCookie('accessToken');
res.clearCookie('refreshToken')Edited code
Github commit with entire code
https://medium.com/@agutierrezt/a-node-implementation-for-refresh-token-with-redis-a062020bbec0
auth-middlewares.js
The auth-middlewares.js file was modified to consider the following cases:
- Access token and refresh tokens are both not expired => logged in
- Access token and refresh tokens are both expired => redirect to log in page
- Access token is valid but the refresh token is expired => verify the access token to reissue the refresh token
- Refresh token is valid but the access token is expired => verify the refresh token to reissue the access token
참고 자료
auth-middlewares.js snippets
const { accessToken, refreshToken } = req.signedCookies
// Check if refresh token exists on Redis
const redisRefreshToken = !refreshToken ? [] : await redisService.get(refreshToken)
console.log(redisRefreshToken)
// jwt.verify를 이용해 access 토큰값 인증
const accessDecoded = jwt.verify(accessToken, secretKey, function (err, decoded) {
if (err) {
return undefined
} else {
// 1. Access token not expired, refresh token expired => create new refresh token
if (redisRefreshToken.length === 0) {
const newRefreshToken = jwtService.createRefreshToken()
res.cookie('refreshToken', newRefreshToken, { httpOnly: true, signed: true })
redisService.set({
key: newRefreshToken,
value: decoded.userId,
timeType: "EX",
time: process.env.JWT_REFRESH_TOKEN_TIME
})
}
return decoded
}
})
// If access token expired or undefined
let checkRefreshToken
if (accessDecoded === undefined) {
// Verify refresh token
checkRefreshToken = jwt.verify(refreshToken, secretKey, function (err, decoded) {
if (err) {
return undefined
} else {
return decoded
}
})
if (!checkRefreshToken && redisRefreshToken.length === 0) {
// 2. If access token expired & refresh token expired => login again
res.clearCookie("accessToken")
res.clearCookie("refreshToken")
res.locals.user = {}
return next()
} else {
// 3. If access token expired and refresh token is not expired => create new access token
const newAccessToken = jwtService.createAccessToken(redisRefreshToken)
res.cookie("accessToken", newAccessToken, { httpOnly: true, signed: true })
}
}
// Log in if acess token not expired code ommittedlogin.controller.js
Assigning to cookies changed from res.cookie("accessToken", accessToken) to res.cookie("accessToken", accessToken, {httpOnly: true, signed: true}).
httpOnly: A tag that prevents scripts in the client from accessing data.signed: Creates a signature to detect if the client modified the cookie. It will give an error when read if the signature does not match the signature on the cookie. This requires to read the cookie usingreq.signedCookiesinstead ofreq.cookies.
Things to improve from current code
- Some examples have two middlewares: one for access token authorization and one for the refresh token. This seems to make the code more readable and allows one middleware to do one job. Currently,
auth-middlewares.jschecks if the access token and refresh token are available, but this can be separated into two for better readability. - Try using the Helmet package. To use, install using
npm i helmet, then apply usingconst helmet = require('helmet'); app.use(helmet()).
Helmet is an Express middleware package that automatically sets various HTTP headers to prevent important information from accidentally sending between the server and the client. - There are several places where the layered architecture has not been used.
auth-middleware.jsaccesses the service layer (to create jwt and get and set Redis keys) and model (to send information to ejs). It does several functions in one file, and it would be better to separate these functions into separate files.
