Intro
Operating System
is a software that operates a computer system.
Computer
is a machine that processes the information.
Information
can be defined as a quantitative representation that measures the uncertainty.
-
정보의 최소 단위: bit(binary digit)
-
정보의 처리: 정보의 상태 변환 (0에서 1로, 1에서 0으로)
-
부울 대수(Boolean Algebra):
NOT,AND,OR -
논리 게이트:
NOT,AND,OR,XOR,NAND,NOR -
논리 회로 :
IC,LSI,VLSI,ULSI,SoC, ..., 무어의 법칙, 황의 법칙 -
정보의 저장과 전송 : 플립-플롭, 데이터 버스
컴퓨터가 정보를 처리하는 방법
-
덧셈은? 반가산기, 전가산기
-
뺄셈은? 2의 보수 표현법
-
곱셈과 나눗셈은? 덧셈과 뺄셈의 반복
-
실수 연산은? 부동 소수점 표현법
-
함수는? GOTO
-
삼각함수, 미분, 적분, 사진 촬영, 동영상 재생 ...
컴퓨터의 범용성(Universality)
-
NOT,AND,OR게이트만으로 모든 계산을 할 수 있다. -
NAND게이트만으로 모든 계산을 할 수 있다. -
범용 컴퓨터(general-purpose computer)
컴퓨터의 계산가능성(Computability)
-
Turing-computable: 튜링 머신으로 계산 가능한 것.
-
정지 문제(Halting Problem): 튜링 머신으로 풀 수 없는 문제
컴퓨터는 누가 만들었는가?
-
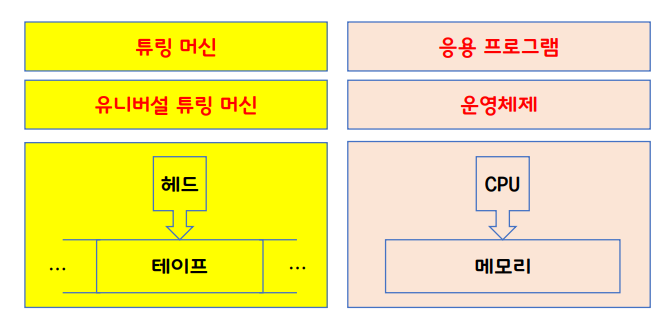
컴퓨터의 할아버지: Alan Turing-Turing Machine
-
컴퓨터의 아버지: John von Neumann-ISA: Instruction Set Architecture
앨런 튜링에 대해
현대 컴퓨터의 모형(CPU, RAM, Application Programs, Operating System)을 설계
- Head와 Tape를 활용하여 목적성을 가진 Turing Machine을 만들 수 있음
- Turing Machine을 엮어 Universal Turing Machine을 만들 수 있음
폰 노이만에 대해
명령을 끌어와서(fetch) 실행하는(execute) 사이클을 가진 내장형 프로그램 컴퓨터를 최초로 설계
A stored-program computer is a computer that stores programs in a memory.
Program
is a set of instructions that tells a computer's hardware to perform a task. 
Operating System
-
is a program running at all times on the computer
-
to provide system services to application programs
-
to manage processes, resources, user interfaces, and so on.
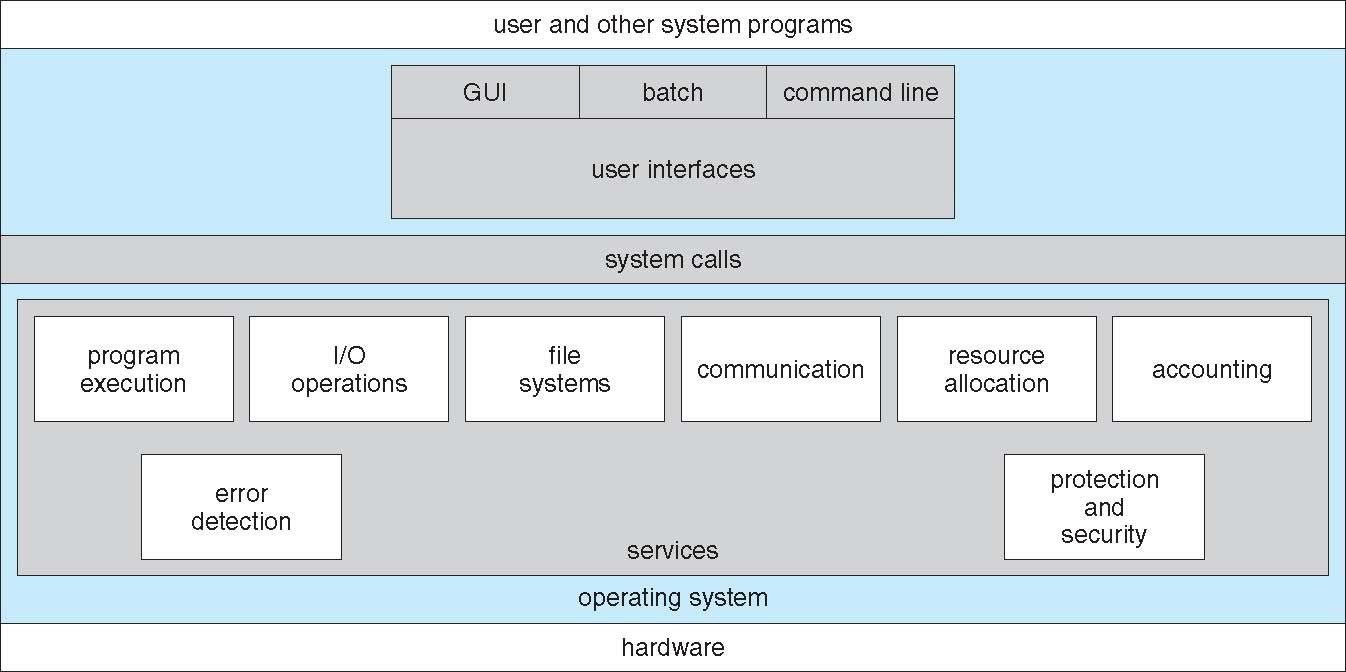
1.1 What Operating Systems Do
⭐ Operating system
-
is a software that managers a computer's hardware.
-
It also provides a basis for application programs
-
and acts as an intermediary between the computer user and the computer hardware.
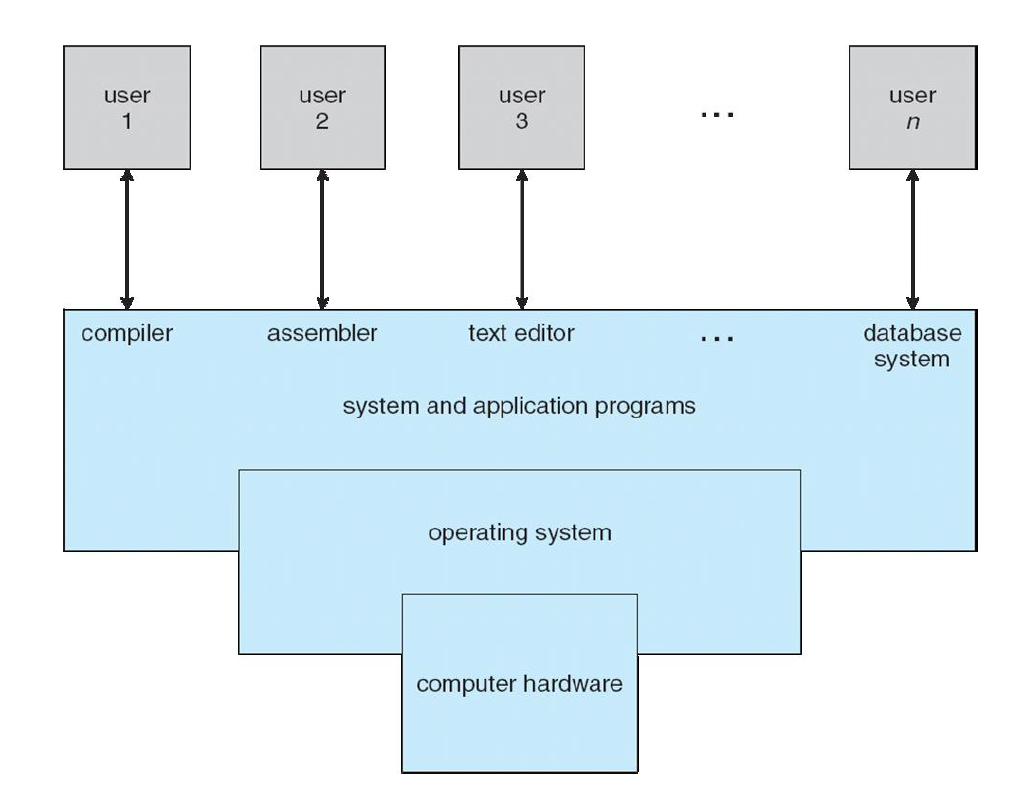
Computer system
can be divided roughly into four components
| [1] hardware | [2] operating system | [3] application programs | [4] user |
|---|
Defining Operating Systems
There are NO universally accepted definition of an operating system.
A more common definition is that "the one program running at all times on the computer", usually called the kernel.
Along with the kernel, there are two other types of programs
-
⭐ system programs
-
⭐ application programs
1.2 Computer-System Organization
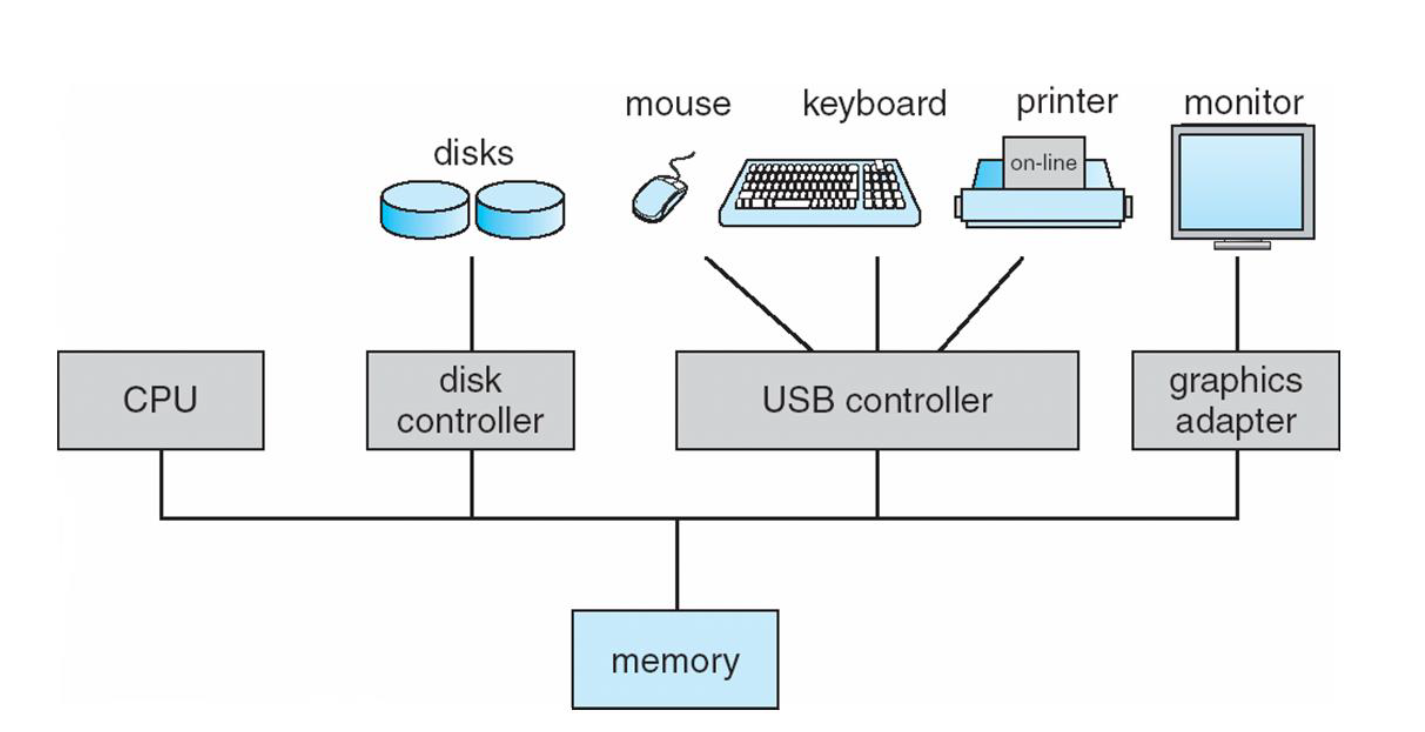
Classical Computer System
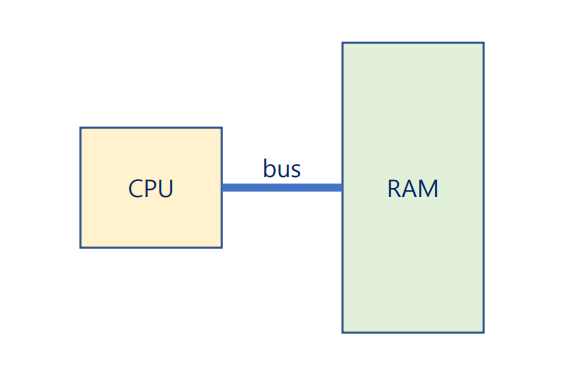
One or more CPUs and a number of device controllers connected through a common bus
⭐ Bootstrap Program
is the first program to run on computer power-on and then loads the operating system.
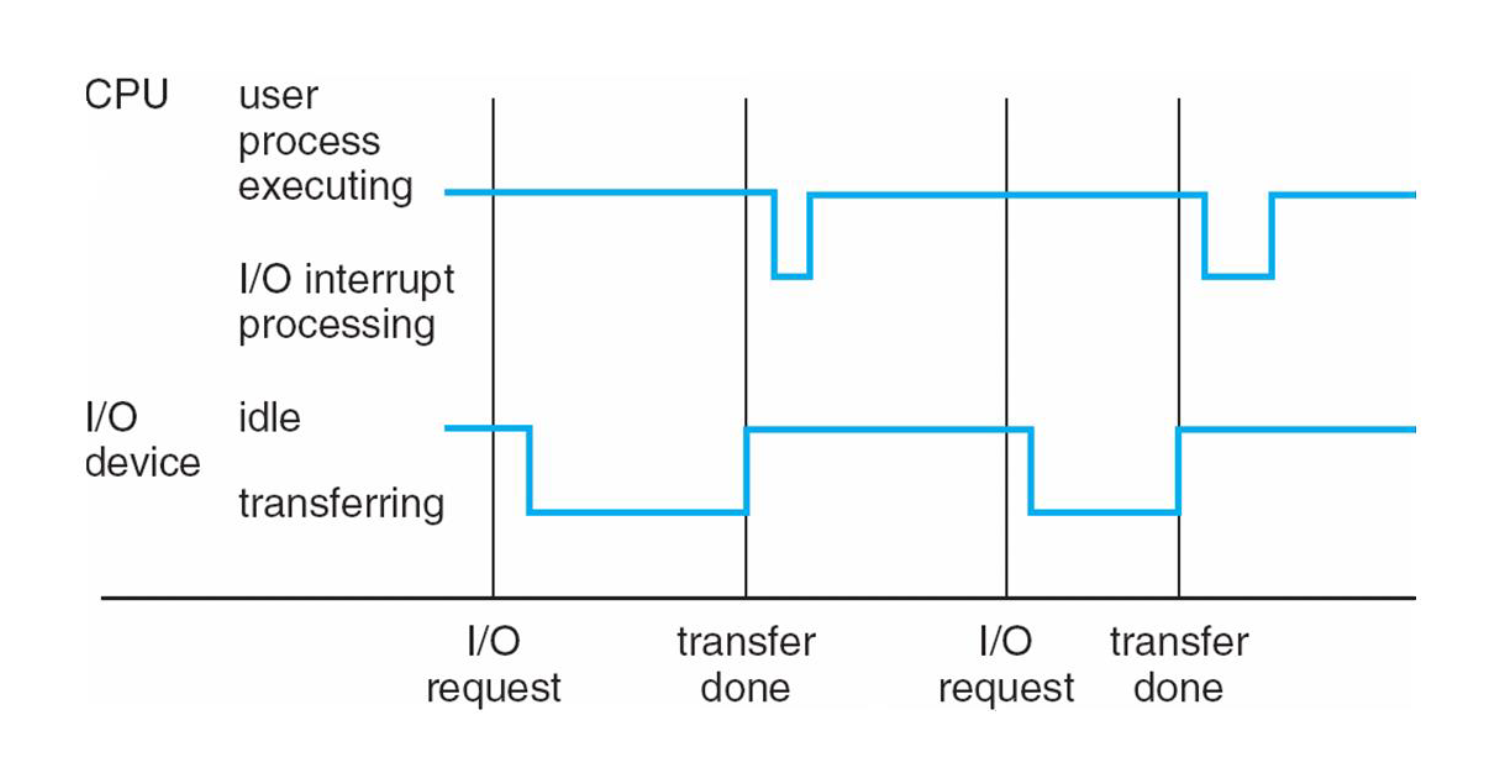
Interrupts
Hardware may trigger an interrupt at any time by sending a signal to the CPU, usually by way of the system bus.
⭐ von Neumann architecture
A typical instruction-execution cycle
-
first fetches an instruction from memory
-
and stores that instruction in the instruction register.
The instruction is then decoded
-
and may cause operands to be fetched from memory
-
and stored in some internal register.
After the instruction on the operands
-
has been executed,
-
the result may be stored back in memory.
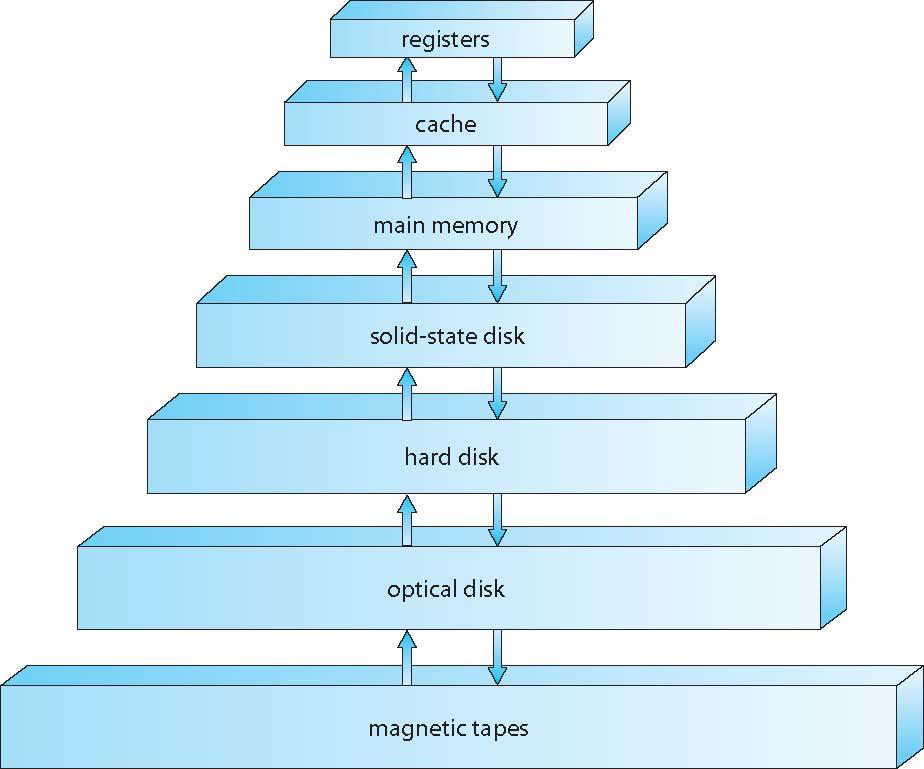
⭐ Storage System
The wide variety of storage systems can be organized in a hierarchy according to storage capacity, and access time.
I/O Structure
A large portion of OS code is dedicated to managing I/O
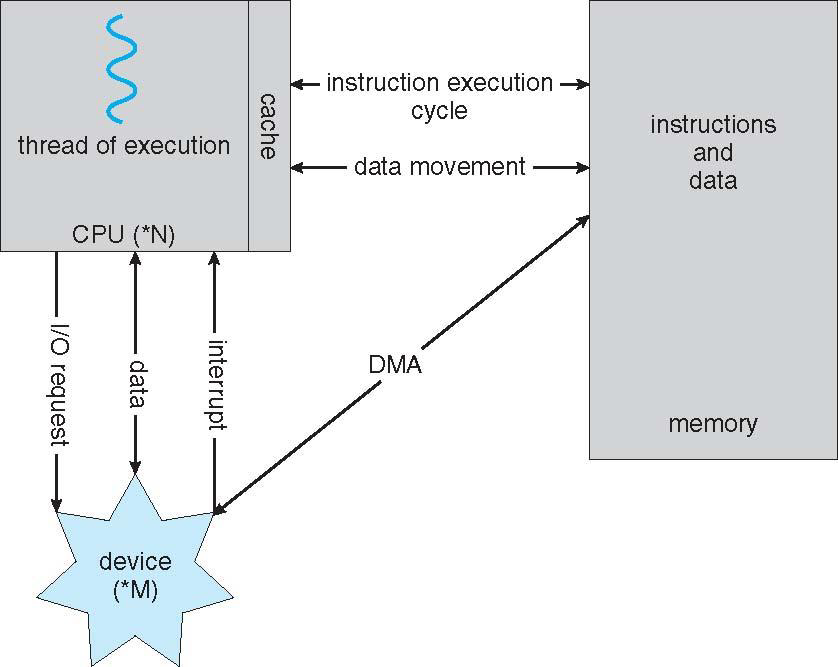 * DMA(Direct Message Access)
* DMA(Direct Message Access)
1.3 Computer System Architecture
⭐ Definition of Computer System Components
-
CPU - The hardware that executes instructions.
-
Processor - A physical chip that contains on or more CPUs.
-
Core - The back computatino unit of the CPU.
-
Multicore - Including multiple computing cores on the same CPU.
-
Multiprocessor - Including multiple processors.
⭐ Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP)
The most common multiprocessor systems, in which each peer CPU processor performs all tasks. / ⭐ Asymmetric multiprocessing each processor is assigned a specific task.
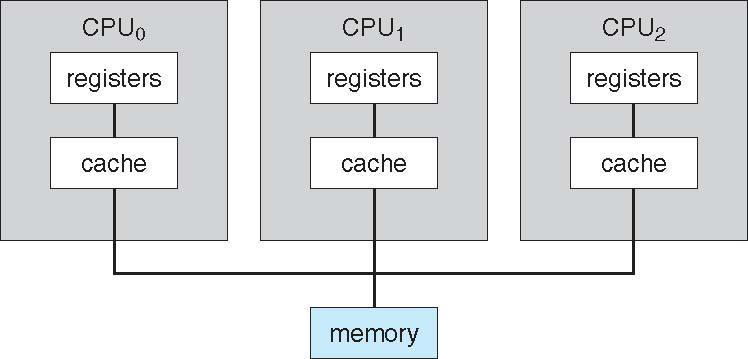
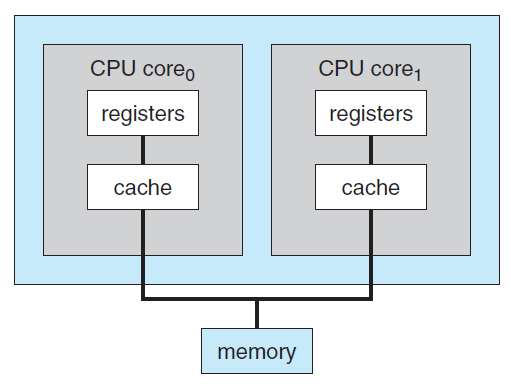
Multi-core design
Muti-core design with several cores on the same processor chip.
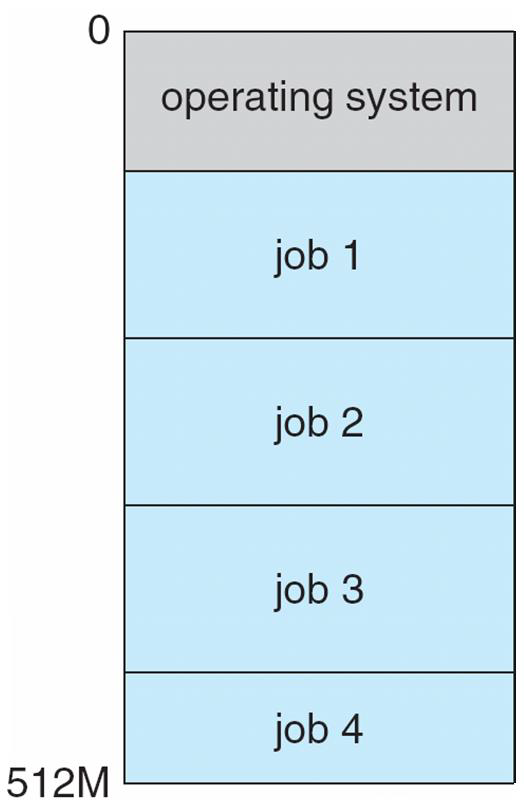
⭐ Multiprogramming
-
runs more than one program at a time.
-
keeps several processes in memory simultaneously to increase CPU utilization.
Multiprogramming → Multitasking
is a logical extension of multiprogramming in which CPU switches jobs so frequently that users can interact with each job while it it running.
파워포인트 작업하면서 유튜브 동영상 시청할 때 CPU가 여러 작업을 빠르게 번갈아가며 수행하는데, 사용자는 이를 자연스러운 멀티태스킹으로 인지함.
⭐ CPU scheduling
If several processes are ready to run at the same time, the system must choose which process will run next.
1.4 Operating System Operations
⭐ User mode, Kernel mode
Two separate mode of operations to ensure that an incorrect program cannot cause other programs to execute incorrectly.
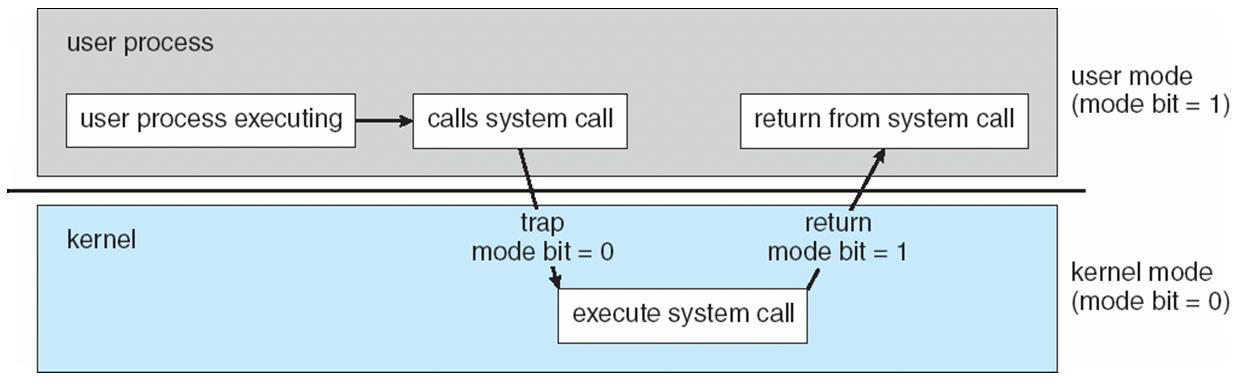 * 커널 모드 외에는 직접 하드웨어를 제어할 수 없기에 부적절한 명령이 방지됨.
* 커널 모드 외에는 직접 하드웨어를 제어할 수 없기에 부적절한 명령이 방지됨.
⭐ 1.7 Virtualization
Virtualization
is a technology that allow us to abstract the hardware of a single computer into several different execution environments.
⭐ VMM(Virtual MAchine Manager)
VMware, XEN, WSL, and so on.
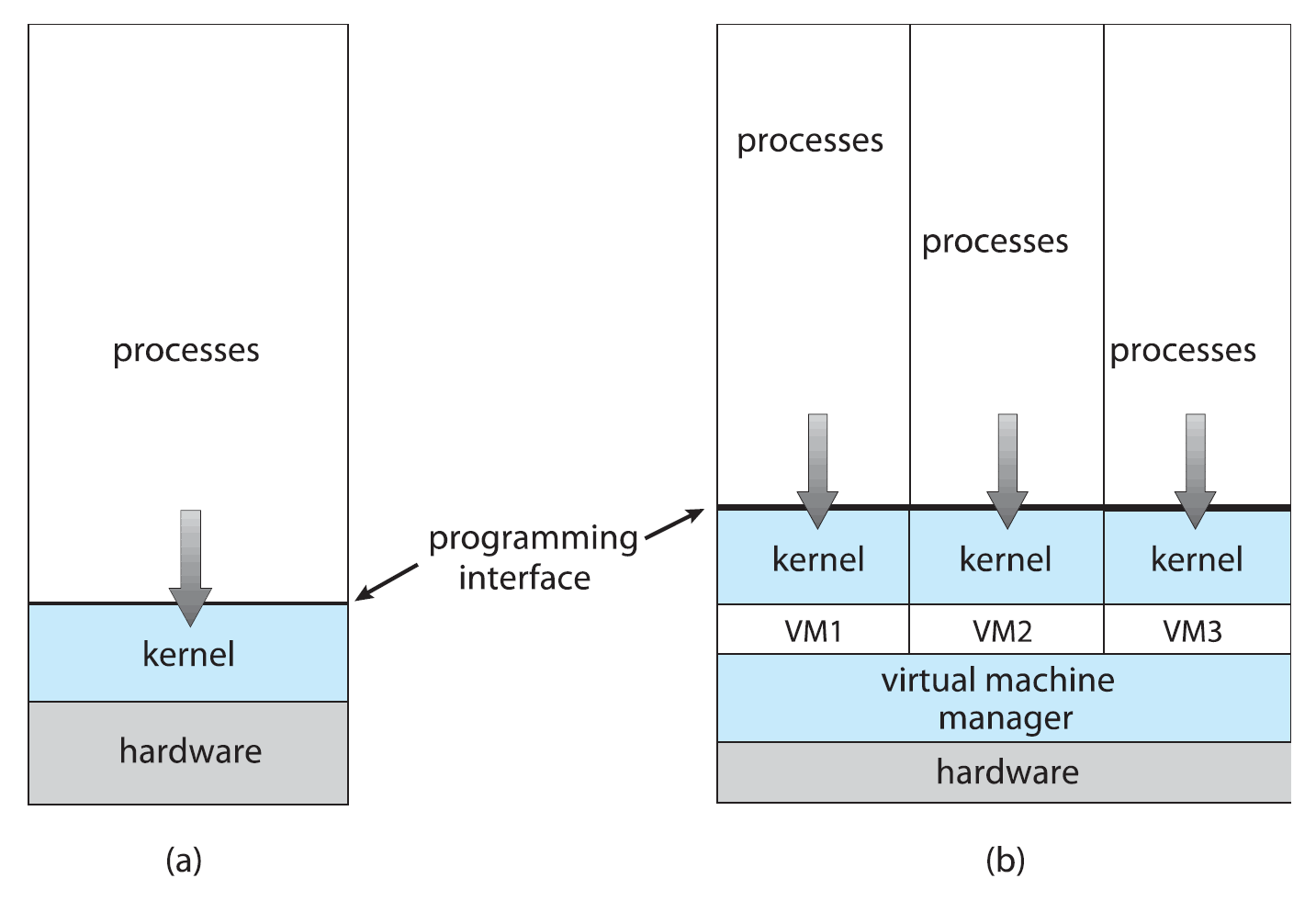 * (a) a single operating system and (b) three virtual machines.
* (a) a single operating system and (b) three virtual machines.
1.10 Computing Environments
Operating Systems in Variety of Computing Environments
-
Traditional Computing
-
Mobile Computing
-
Client-Server Computing (웹 클라이언트-서버 구조 etc)
-
Peer-to-peer Computing (음악/영화 공유, 토렌트 etc)
-
Cloud Computing (AWS, Azure, GCP etc)
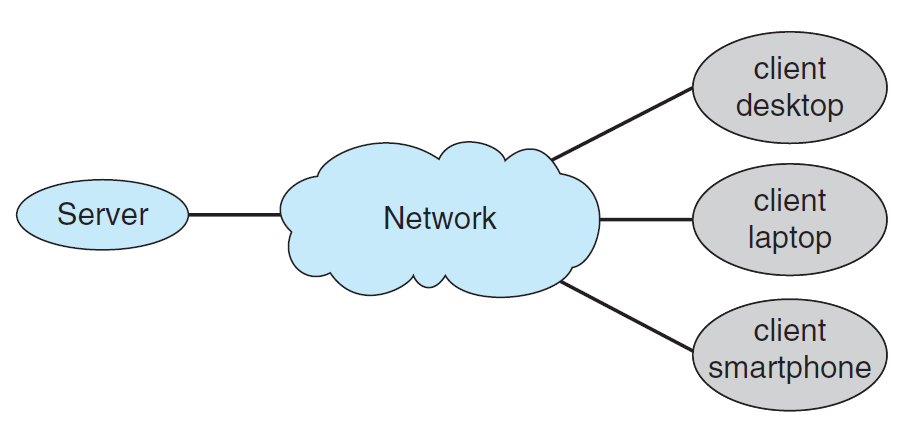 ▲ General Structure of a client-server system
▲ General Structure of a client-server system
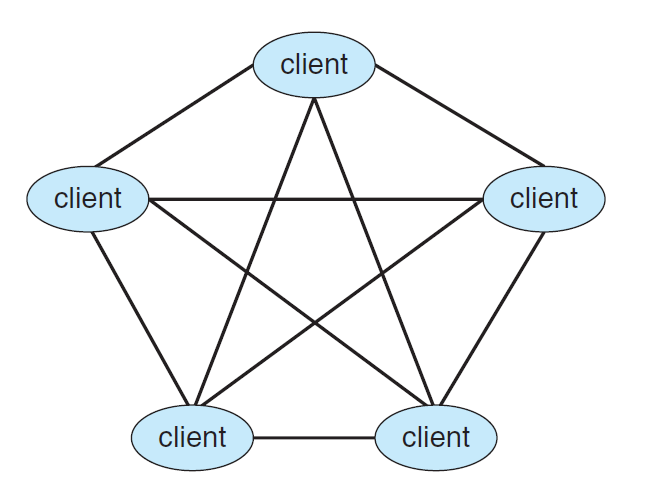 ▲ Peer-to-peer system with no centralized service
▲ Peer-to-peer system with no centralized service
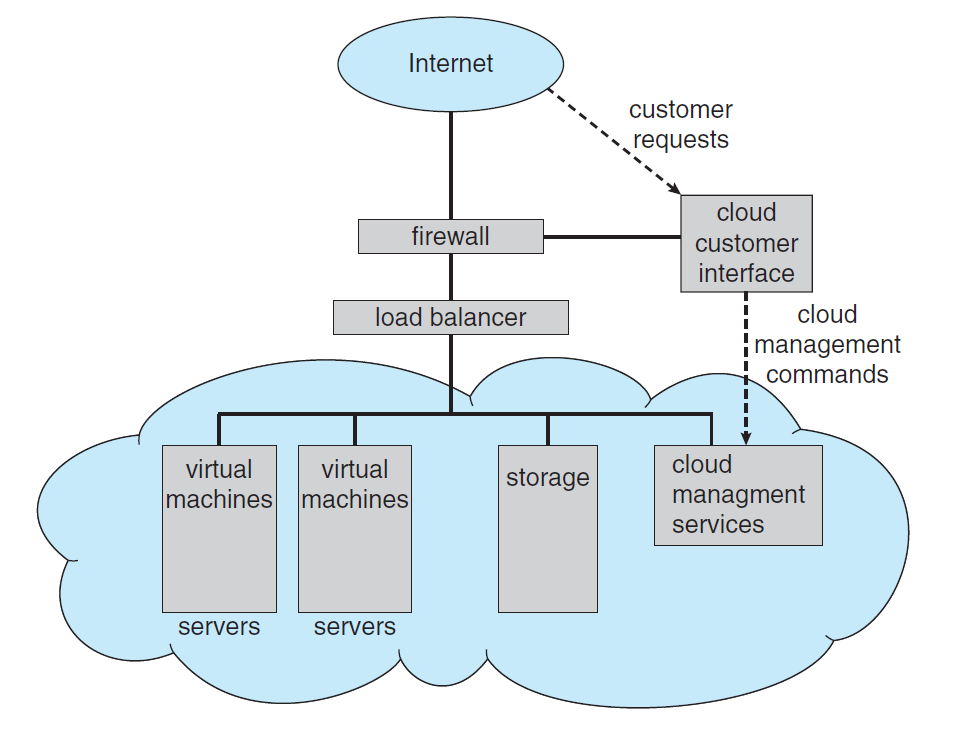 ▲ Cloud Computing
▲ Cloud Computing
2.1 Operating System Services
User Interface
Program execution
I/O operation
File-system manipulation
Communications
Error detection
Resource allocation
Logging
Protection and security
2.2 User and Operating - System Interface
Three fundamental ways for users to interface with the OS
-
CLI: command line interface, or command interpreter, known as shells, sh, bash, csh, tcsh, zsh, etc.
-
GUI: graphical user interface, Windows, Aqua for MacOS, KDE/GNOME for Linux, etc.
-
Touch-Screen Interface, Android UI, IPhone UI, etc.
2.3 System calls (aka. API of OS)
provides an interface to the services made available by the OS.
API(Application Programming Interface)
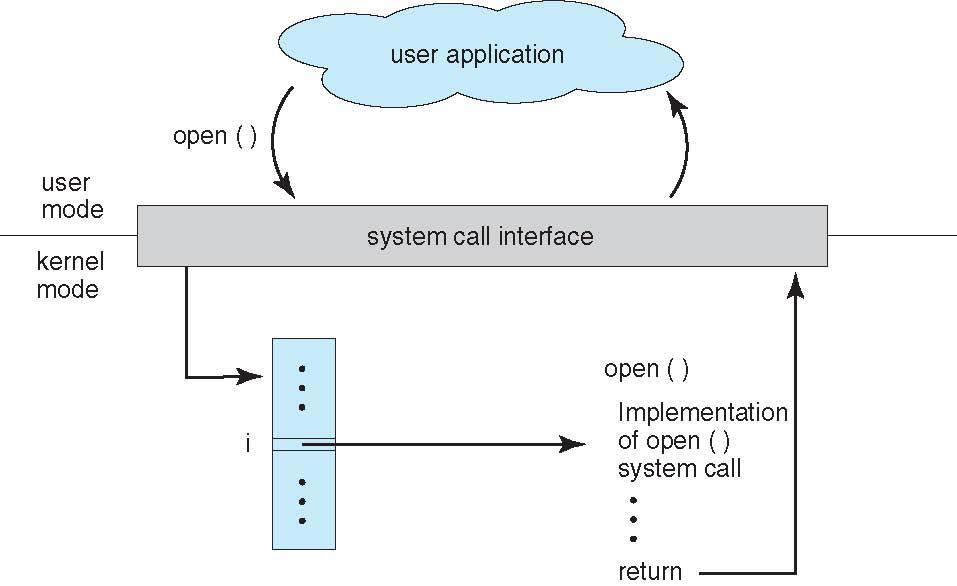
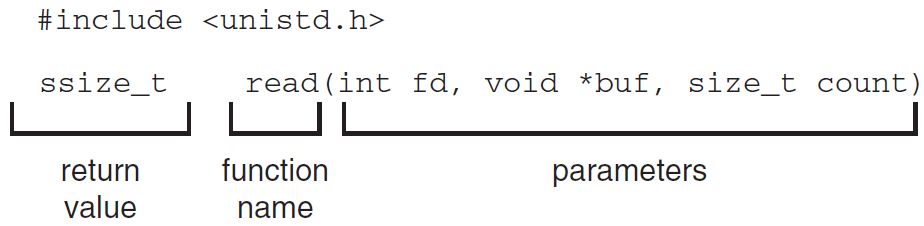 * The handling of a user application invoking the open() system call
* The handling of a user application invoking the open() system call
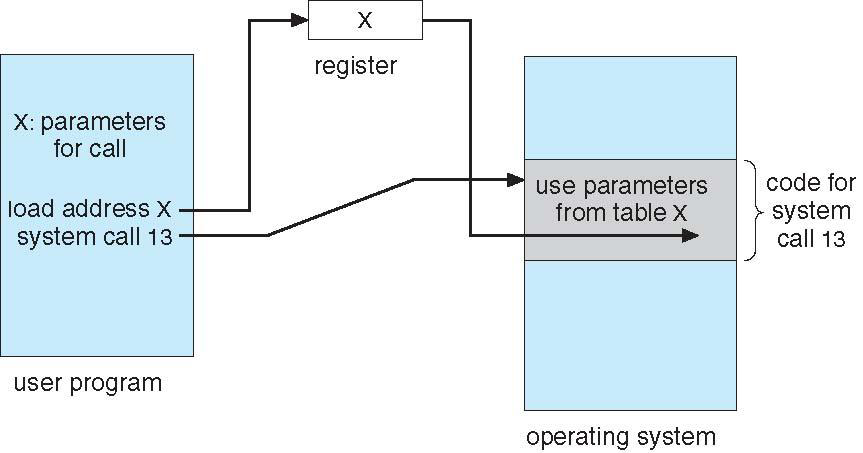
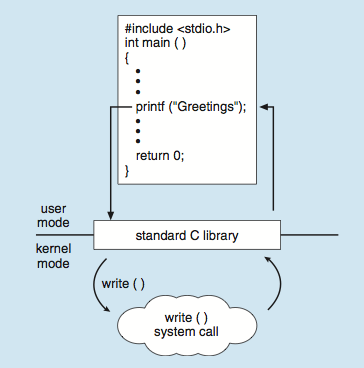 *
* printf (사용자가 open(), read(), write()하는 단계를 대신 함)
 * Examples of Windows and UNIX system calls
* Examples of Windows and UNIX system calls