Catalog-service
프로젝트 생성
기능 추가
- 상품 목록 조회
📌 프로젝트 생성
-
Dependency추가
➡ DevTools, Lombok, Web, Eureka Discovery Client, H2 Database,
ModelMapper, Spring Data JPA -
pom.xml 수정
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<version>2.2.224</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.modelmapper</groupId>
<artifactId>modelmapper</artifactId>
<version>2.3.8</version>
</dependency>📌 소스코드
- application.yml 수정
spring:
application:
name: catalog-service
h2:
console:
enabled: true
settings:
web-allow-others: true
path: /h2-console
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create-drop
show-sql: true
generate-ddl: true
database: h2
defer-datasource-initialization: true
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
url: jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
server:
port: 0
eureka:
instance:
instance-id: ${spring.application.name}:${spring.application.instance_id:${random.value}}
client:
fetch-registry: true
register-with-eureka: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:8761/eureka
logging:
level:
com.example.catalogservice: DEBUG #option💡 추가 설명
- ddl-auto: create-drop
테이블에 초기 기본 데이터를 미리 저장해두는 설정- defer-datasource-initialization: true
SPRING 2.5부터data.sql스크립트가Hibernate초기화 되기 전 실행이 되지 않아,
테이블이 자동으로 생성되지 못해서 INSERT 구문의 오류 발생으로 인해 설정 추가
- data.sql 생성
insert into catalog(product_id, product_name, stock, unit_price)
values ('CATALOG-001', 'Berlin', 100, 1500);
insert into catalog(product_id, product_name, stock, unit_price)
values ('CATALOG-002', 'Tokyo', 110, 1000);
insert into catalog(product_id, product_name, stock, unit_price)
values ('CATALOG-003', 'Stockholm', 120, 2000);- Entity.java 생성
package com.example.catalogservice.jpa;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Data;
import org.hibernate.annotations.ColumnDefault;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@Entity
@Table(name="catalog")
public class CatalogEntity implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, length = 120, unique = true)
private String productId;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String productName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Integer stock;
@Column(nullable = false)
private Integer unitPrice;
@Column(nullable = false, updatable = false, insertable = false)
@ColumnDefault(value = "CURRENT_TIMESTAMP")
private Date createdAt;
}Serializable (=직렬화)
자바에서 직렬화란 어떤 객체(Class)를 Byte로 변환하는 것
(cf. 역직렬화: 직렬화한 Byte를 다시 객체(Class)로 변환하여 JVM 메모리에 들고 있는 것)
➡ JAVA 객체를 JVM에서 뽑아내서 데이터를 파일과 같은 형태로 저장할 수 있게 됨
➡ 자바 시스템 내부에서 사용되는 Object 또는 Data를 외부의 자바 시스템에서도 사용할 수 있게 됨
🔗 출처: [Java] Serializable. 직렬화란 무엇일까?
🔗 출처: JAVA 직렬화(Serializable)란?
- CatalogRepository.java 생성
package com.example.catalogservice.jpa;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface CatalogRepository extends CrudRepository<CatalogEntity, Long> {
CatalogEntity findByProductId(String productId);
}- CatalogDto.java 생성
package com.example.catalogservice.dto;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
public class CatalogDto implements Serializable {
private String productId;
private Integer qty;
private Integer unitPrice;
private Integer totalPrice;
private String orderId;
private String userId;
}- ResponseCatalog.java 생성
package com.example.catalogservice.vo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@JsonInclude(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL) //NUll값 반환하지 않음
public class ResponseCatalog {
private String productId;
private String productName;
private Integer unitPrice;
private Integer stock;
private Date createdAt;
}📌 상품 목록 조회 기능
- CatalogService.java 인터페이스 생성
package com.example.catalogservice.service;
import com.example.catalogservice.jpa.CatalogEntity;
public interface CatalogService {
Iterable<CatalogEntity> getAllCatalogs();
}- CatalogServiceImpl.java 생성
package com.example.catalogservice.service;
import com.example.catalogservice.jpa.CatalogEntity;
import com.example.catalogservice.jpa.CatalogRepository;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Data
@Slf4j
@Service
public class CatalogServiceImpl implements CatalogService {
CatalogRepository catalogRepository;
@Autowired
public CatalogServiceImpl(CatalogRepository catalogRepository) {
this.catalogRepository = catalogRepository;
}
@Override
public Iterable<CatalogEntity> getAllCatalogs() {
return catalogRepository.findAll();
}
}- CatalogController.java 생성
package com.example.catalogservice.controller;
import com.example.catalogservice.jpa.CatalogEntity;
import com.example.catalogservice.service.CatalogService;
import com.example.catalogservice.vo.ResponseCatalog;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/catalog-service")
public class CatalogController {
Environment env;
CatalogService catalogService;
@Autowired
public CatalogController(Environment env, CatalogService catalogService) {
this.env = env;
this.catalogService = catalogService;
}
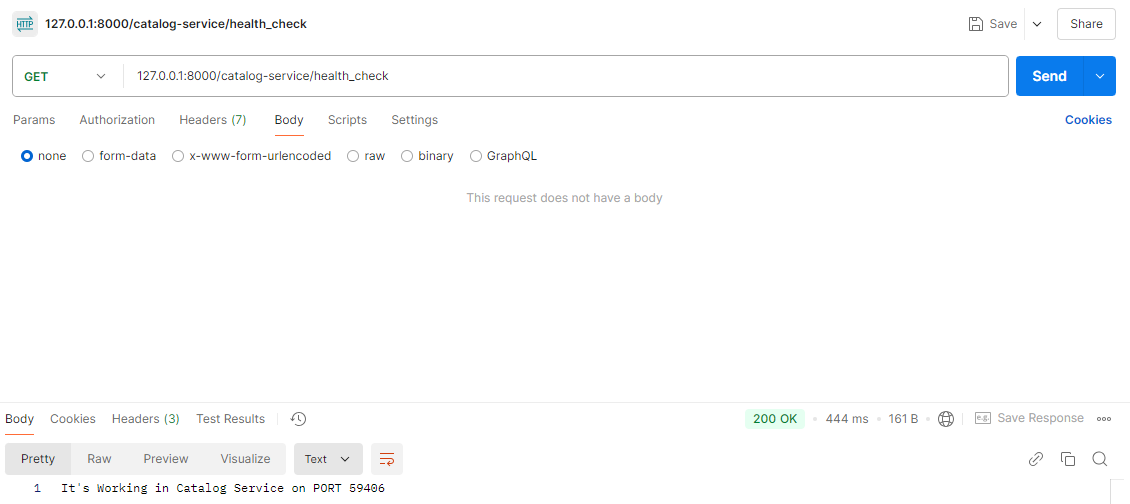
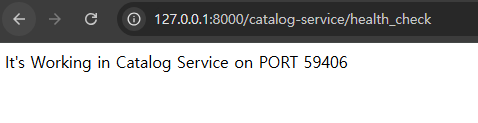
@GetMapping("/health_check")
public String status(){
return String.format("It's Working in Catalog Service on PORT %s",
env.getProperty("local.server.port"));
}
@GetMapping("/catalogs")
public ResponseEntity<List<ResponseCatalog>> getCatalogs(){
Iterable<CatalogEntity> catalogList = catalogService.getAllCatalogs();
List<ResponseCatalog> result = new ArrayList<>();
catalogList.forEach(v -> {
result.add(new ModelMapper().map(v, ResponseCatalog.class));
});
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(result);
}
}- API Gateway의 application.yml 수정
spring:
application:
name: apigateway-service
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: catalog-service
uri: lb://CATALOG-SERVICE
predicates:
- Path=/catalog-service/**- 실행결과
(1) 콘솔 로그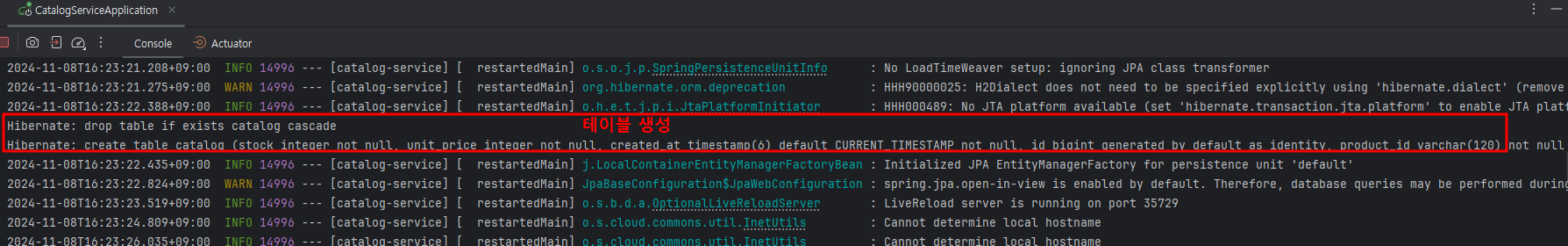 ➡
➡ data.sql을 통해 테이블 미리 생성됨 확인
(2) 데이터베이스 조회 결과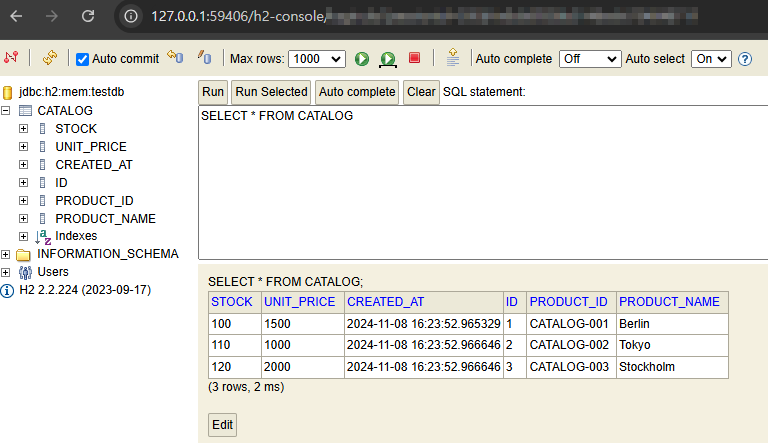
(3) 실행결과