
1. 데이터 구조
- 어떤 데이터를 효과적으로 사용, 관리하기 위한 구조
1. 자료구조
- 각 데이터의 효율적인 저장, 관리를 위한 구조를 나눠 놓은 것
- 대량의 데이터를 효율적으로 관리할수 있는 구조
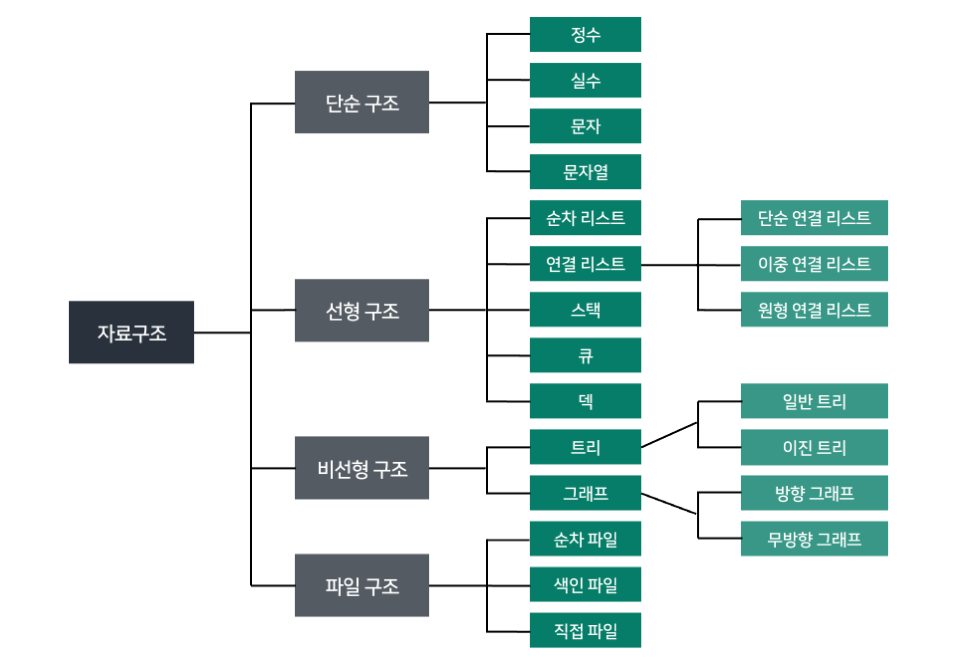
[출처]https://cheris8.github.io/python/DS-Overview/
- 구조 활용
- 문자열, 리스트, 딕셔너리 등 각 데이터 구조의 메서드를 호출하여 다양한 기능을 활용하기
2. 메서드
- 객체에 속한 함수
- 객체의 상태를 조작하거나 동작을 수행
- 특징
- 메서드는 클래스 내부에 정의되는 함수
- 클래스는 파이썬에서 '타입을 표현하는 방법'이며 이미 은연중에 사용해 왔음
- 예를 들어 help 함수를 통해 str을 호출해보면 class 였다는 것을 확인 가능
2. 비시퀀스 구조
1. set
- 고유한 항목들의 정렬되지 않은 컬렉션
- 순서가 존재하지 않는다
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| s.add(x) | 세트 s에 항목 x를 추가. 이미 x가 있다면 변화 없음 |
| s.clear() | 세트 s의 모든 항목을 제거 |
| s.remove(x) | 세트 s에서 항목 x를 제거. 항목 x가 없을 경우 key error |
| s.pop() | 세트 s에서 랜덤하게 항목을 반환하고, 해당 항목을 제거 |
| s.discard(x) | 세트 s에서 항목 x를 제거 |
| s.update(iterable) | 세트 s에 다른 iterable 요소를 추가 |
-
s.add(x)
- 세트에 x 를 추가
my_set = {'a', 'b', 'c', 1, 2, 3} my_set.add(d) print(my_set) #{1, 'b', 3, 2, 'c', 'd', 'a'} my_set.add(d) print(my_set) #{1, 'b', 3, 2, 'c', 'd', 'a'} -
s.clear()
- 세트의 모든 항목을 제거
my_set = {'a', 'b', 'c', 1, 2, 3} my_set.clear() print(my_set) -
s.remove(x)
- 세트에서 항목 x를 제거
my_set = {'a', 'b', 'c', 1, 2, 3} my_set.remove(2) print(my_set) # {'b', 1, 3, 'c', 'a'} my_set.remove(10) print(my_set) # key error -
s.dicard()
- 세트 s에서 항목 x를 제거. remove와 달리 에러 없음
my_set = {1, 2, 3} my_set.discard(2) print(my_set) # {1, 3, 'a', 'c', 'b'} my_set.discard(10) -
s.pop()
- 세트에서 임의의 요소를 제거하고 반환
my_set = {'a', 'b', 'c', 1, 2, 3} element = my_set.pop() print(element) # 1 print(my_set) # {2, 3, 'b', 'a', 'c'} -
s.update()
- 세트에 다른 iterable 요소를 추가
my_set = {'a', 'b', 'c', 1, 2, 3} my_set.update([1, 4, 5]) print(my_set) # {1, 2, 3, 'c', 4, 5, 'b', 'a' }
| 메서드 | 설명 | 연산자 |
|---|---|---|
| set1.difference(set2) | set1에는들어 있지만 set2에는 없는 항목으로 세트를 생성후 반환 | set1 - set2 |
| set1.intersection(set2) | set1과 set2 모두 들어 있는 항목으로 세트를 생성후 반환 | set1 & set2 |
| set1.issubset(set2) | set1의 항목이 모두 set2에 들어있으면 True를 반환 | set1 <= set2 |
| set1.issuperset(set2) | set1 가 set2의 항목을 모두 포함하면 True를 반환 | set1 >= set2 |
| set1.union(set2) | set1 또는 set2에 들어있는 항목으로 세트를 생성 후 반환 | set1\set2 |
set1 = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}
set2 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}
print(set1.difference(set2)) # {0, 2, 4}
print(set1.intersection(set2)) # {1, 3}
print(set1.issubset(set2)) # False
print(set1.issuperset(set2)) # False
print(set1.union(set2)) # {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}2. dictionary
- 고유한 항목들의 정렬되지 않은 컬렉션
| 메서드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| D.clear() | 딕셔너리 D의 코든 키/값 쌍을 제거 |
| D.get(k) | 키 k에 연결된 값을 반환 (키가 없으면 None을 반환) |
| D.get(k,v) | 키 k에 연결된 값을 반환하거나 키가 없으면 기본 값으로 v를 반환 |
| D.keys() | 딕셔너리 D의 키를 모은 객체를 반환 |
| D.values() | 딕셔너리 D의 값을 모은 객체를 반환 |
| D.items() | 딕셔너리 D의 키/값 쌍을 모은 객체를 반환 |
| D.pop(k) | 딕셔너리 D에서 키 k를 제거하고 연결됬던 값을 반환 (없으면 오류) |
| D.pop(k, v) | 딕셔너리 D에서 키 k를 제거하고 연결됬던 값을 반환 ( 없으면 v를 반환) |
| D.setdefault(k) | 딕셔너리 D에서 키 k 와 연결된 값을 반환 |
| D.setdefault(k, v) | 딕셔너리 D에서 키 k와 연결된 값을 반환 k가 D의 키가 아니면 값 v와 연결한 키 k를 D에 추가하고 v를 반환 |
| D.update(other) | other 내 각 키에 대해 D에 있는 키면 D에 있는 그 키의 값을 other에 있는 값으로 대체 other에 있는 각 키에 대해 D에 없는 키면 키/값 쌍을 D에 추가 |
-
D.clear()
- 딕셔너리 D의 모든 키/값 쌍을 제거
-
D.get(key[,default])
- 키 연결된 값을 반환하거나 키가 없으면 None 혹은 기본 값을 반환
person = {'name':'Alice', 'age':25} print(person.get('name')) # Alice print(person.get('country')) # None print(person.get('country', 'Unknown')) # Unknown -
D.keys()
- 딕셔너리 키를 모은 객체를 반환
-
D.values()
- 딕셔너리 값을 모은 객체를 반환
person = {'name' : 'Alice', 'age' : 25} print(person.keys()) # dict_keys(['name', 'age']) for v in person.values(): print(v) """ Alice 25 """ -
D.items()
- 딕셔너리 키/값 쌍을 모은 객체를 반환
person = {'name': 'Alice', 'age':25} print(person.itmes()) # dict_items([('name', 'Alice'), ('age', 25)]) for k, v in person.items(): print(k, v) """ name Alice age 25 """ -
D.pop(key[,default])
- 키를 제거하고 연결됬던 값을 반환
- 없으면 에러나 default를 반환
-
D.setdefault(key[,default])
- 키와 연결된 값을 반환
- 키가 없다면 default와 연결한 키를 딕셔너리에 추가하고 default를 반환
person = {'name':'Alice', 'age':25} print(pseron.setdefault('country', 'KOREA')) # KOREA print(persion) # {'name': 'Alice', 'age':25, 'country': 'KOREA'} -
D.update()
- other 가 제공하는 키/값 쌍으로 딕셔너리르 갱신
- 기촌 키는 덮어 씀
3. 해시 테이블
- 해시 함수를 사용하여 변환한 값을 색인(index)으로 삼아 키(key)와 데이터(value)를 저장하는 자료구조
- 데이터를 효율적으로 저장하고 검색하기 위해 사용
- 해시테이블 원리
- 키를 해시 함수를 통해 해시 값으로 변환하고, 이 해시 값을 인덱스로 사용하여 데이터를 저장하거나 검색
- 데이터 검색이 매우
빠르게이루어짐
- 변수를 비교 할 때, 먼저 Hash 값을 비교하고 이후 Hash 값이 같다면 그 변수가 같은지 확인한다.
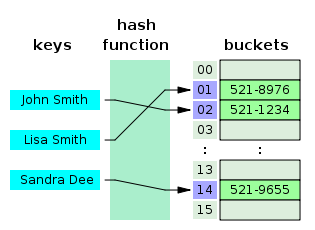
[출처]https://mangkyu.tistory.com/102
4. 해시(Hash)
-
임의의 크기를 가진 데이터를 고정된 크기의 고유한 값으로 변환하는 것
-
이렇게 생성된 고유한 값은 주로 해당 데이터를 식별하는 데 사용될 수 있음
- 일종의 "지문"과 같은 역할
- 데이터를 고유하게 식별
-
파이썬에서는 해시 함수를 사용하여 데이터를 해시 값으로 변환하며, 이 해시 값은 정수로 표현됨
-
해시 함수
- 임의의 길이의 데이터를 입력 받아 고정된 길이의 데이터(해시 값)를 출력하는 함수
- 주로 해시 테이블 자료구조에 사용되며, 매우 빠른 데이터 검색을 위한 컴퓨터 소프테웨어에서 유용하게 사용
5. set의 요소 & dictionary의 키와 해시테이블의 관계
- 파이썬에서 세트의 요소와 딕셔너리의 키는 해시 테이블을 이용하여 중복되지 않는 고유한 값을 저장함
- 세트 내의 각 요소는 해시 함수를 통해 해시 값으로 변환되고, 이 해시 값을 기반으로 해시 테이블에 저장됨.
- 마찬가지로 딕셔너리의 키는 고유해야 하므로, 키를 해시 함수를 통해 해시 값으로 변환하여 해시 테이블에 저장
- 따라서 딕셔너리의 키는 매우 빠른 탐색 속도를 제공하며, 중복된 값을 허용하지 않음
- 반환 값이 매번 다름
파이썬에서의 해시 함수
- 파이썬에서 해시 함수의 동작 방식은 객체의 타입에 따라 달라짐
- 정수와 문자열은 서로 다른 타입이며, 이들의 해시 값을 계산하는 방식도 다름
1. 정수 일 때
- 같은 정수는 항상 같은 해시 값을 가짐
- 해시 테이블에 정수를 저장할 때 효율적인 방법
- 예를 들어, hash(1)과 hash(2)는 항상 서로 다른 해시 값을 갖지만, hash(1)은 항상 동일한 해시 값을 갖게 됨.
2. 문자열 일 때
- 문자열은 가변적인 길이를 갖고 있고, 문자열에 포함된 각 문자들의 유니코드 코드 포인트 등을 기반으로 해시 값을 계산
- 이로 인해 문자열의 해시 값은 실행 시마다 다르게 계산됨
print(hash(1)) # 1
print(hash(1)) # 1
print(hash('a')) # 실행시마다 다름
print(hash('a')) # 실행시마다 다름3. hashable
- hash() 함수의 인자로 전달해서 결과를 반환 받을 수 있는 객체를 hashdable이라고 함
- 대부분의 불변형 데이터 타입은 hashable
- 단, tuple의 경우 불변형이지만 해시 불가능한 객체를 참조 할 때는 tuple 자체도 해시 불가능해지는 경우가 있음
print(hash(1))
print(hash(1.0))
print(hash('1'))
print(hash((1,2,3)))
# TypeError : unhashable type: 'list
print(hash((1, 2, [3, 4])))4. hashable과 불변성의 관계
- 해시 테이블의 키는 불변해야 함
- 객체가 생성된 후에 그 값을 변경할 수 없어야 함
- 불변 객체는 해시 값이 변하지 않으므로 동일한 값에 대해 일관된 해시 값을 유지할 수 있음
- 단, "hash 가능하다 != 불변하다 "
5. 가변형 객체가 hashable 하지 않는 이유
- 값이 변경될 수 있기 때문에 동일한 객체에 대한 해시 값이 변경될 가능성이 있음 (해시 테이블의 무결성 유지 불가)
- 가변형 객체가 변경되면 해시 값이 변경되기 때문에, 같은 객체에 대한 서로 다른 해시 값이 반환될 수 있음
# TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
print(hash([1, 2, 3]))
# TypeError: unhashable type : 'list'
my_set = {[1, 2, 3], 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
# TypeError: unhashable type : 'set'
my_dict = {{3, 2}: 'a'}6. hashable 객체가 필요한 이유
- 해시 테이블 기반 자료 구조 사용
- set와 dict의 키
- 중복 값 방지
- 빠른 검색과 조회
- 불변성을 통한 일관된 해시 값
- 안전성과 예측 가능성 유지