어제 사용자에게 보이는 부분만 렌더링 하는 기술인 Virtual을 프로젝트에 도입해보려다가 실패했었다.
많은 자료도 없었고, Docs도 엄청 친절하다고 느끼진 않았었다..(내가 부족해서)
대체 무슨 원리길래 이렇게 되는 걸까?
선택부터 예제, 예제를 톺아보는 원리, 적용까지 이어 나가 보겠다.
스포하자면 적용 실패했다. 다음 편에 이어서 할 것
라이브러리 선택
npm의 트렌딩을 먼저 살펴 보았다.
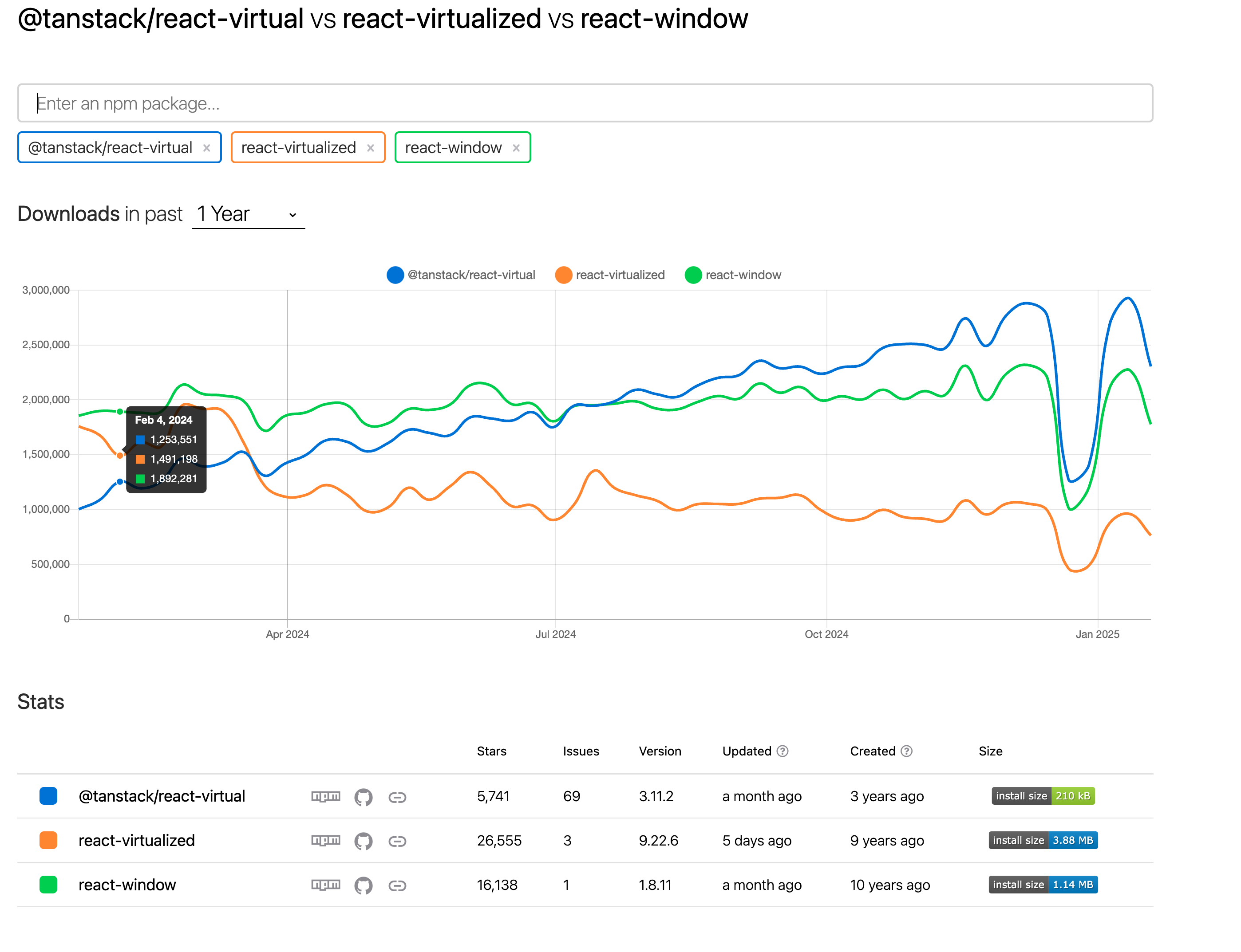
tanstack사의 @tanstack/react-virtaul이 생긴지는 얼마 안됐지만, 용량이 가장 적고(1/5, 1/15수준.. ㄷㄷ)
유지보수도 요즘 잘 되고 있고, 트렌딩에서도 설치 비중이 가장 높길래 선택했다.
설치
pnpm add -D @tanstack/react-virtual간단하다, 아이고 쉽다.
예제
간단하게 0~9999까지 하나씩 담겨 있는 배열을 만들어서 List에 출력해보자
const count = 10000;
const divHeight = 25;
function App() {
const array = Array.from({ length: count }, (value, idx) => idx);
//길이는 count만큼 현재 idx에 idx값을 넣는다. value는 _로도 생략가능.
return (
<div
style={{
height: "400px",
overflow: "auto",
}}
>
{array.map((each) => (
<div
key={each}
style={{
height: `${divHeight}px`,
borderBottom: "1px solid #ddd",
}}
>
Row {each}
</div>
))}
</div>
);
}
export default App;
짜잔 400px의 height를 가진 div안에 25px의 div를 10000개 출력한다.
아래는 @tanstack/react-virtual에 들어가서 가장 처음에 보이는 예제이다
위와 같은 역할을 하지만 List에서 보이는 부분만을 계산해 렌더링을 진행하는 예제이다.
import { useVirtualizer } from '@tanstack/react-virtual';
function App() {
// The scrollable element for your list
const parentRef = React.useRef(null)
// The virtualizer
const rowVirtualizer = useVirtualizer({
count: 10000,
getScrollElement: () => parentRef.current,
estimateSize: () => 35,
})
return (
<>
{/* The scrollable element for your list */}
<div
ref={parentRef}
style={{
height: `400px`,
overflow: 'auto', // Make it scroll!
}}
>
{/* The large inner element to hold all of the items */}
<div
style={{
height: `${rowVirtualizer.getTotalSize()}px`,
width: '100%',
position: 'relative',
}}
>
{/* Only the visible items in the virtualizer, manually positioned to be in view */}
{rowVirtualizer.getVirtualItems().map((virtualItem) => (
<div
key={virtualItem.key}
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: 0,
left: 0,
width: '100%',
height: `${virtualItem.size}px`,
transform: `translateY(${virtualItem.start}px)`,
}}
>
Row {virtualItem.index}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
</>
)
}와.. 정리해볼까?
위 내용을 정리했을때 처음에 나는 이렇게 생각했다. 틀린 생각이니 참고하지 말 것!
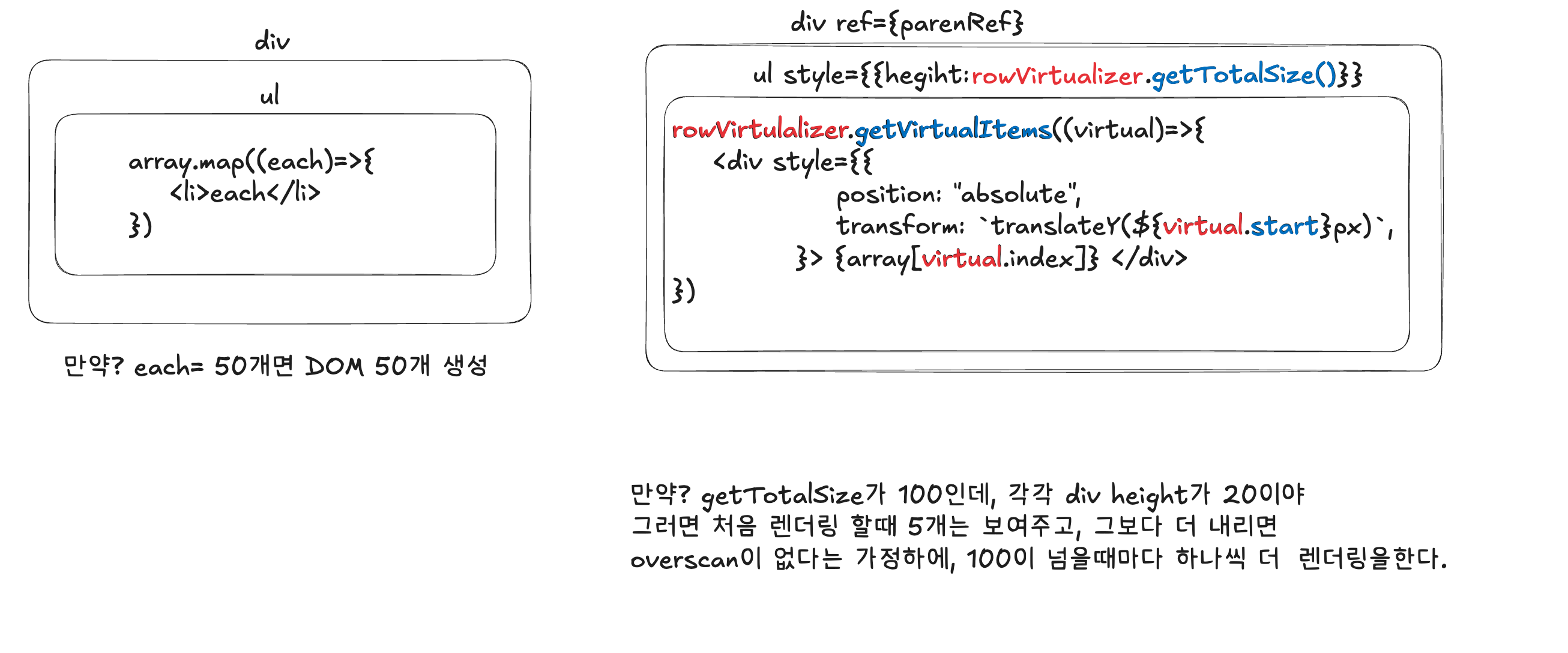
어제 이렇게 생각하고 실제로 프로젝트에 적용해보려다가 안돼서 포기했다. (내 5시간...)
원리
이럴 때마다 LLM이 그립긴 하지만, 머리가 너무 지끈지끈한 나머지 도입을 포기하고 어제 침대에 누웠는데 불 꺼놓고 핸드폰도 안키고 멍하니 천장을 바라보며, 머리속으로 코드를 계속 작성했다.
새벽까지도 잘 모르다가 아침에 일어나자마자 Docs를 다시 켰고, 예제가 저렇게 나와 있고, Docs에서도 설명을 해주길래 이해했다. 모든 답은 공식 Docs에 있다.
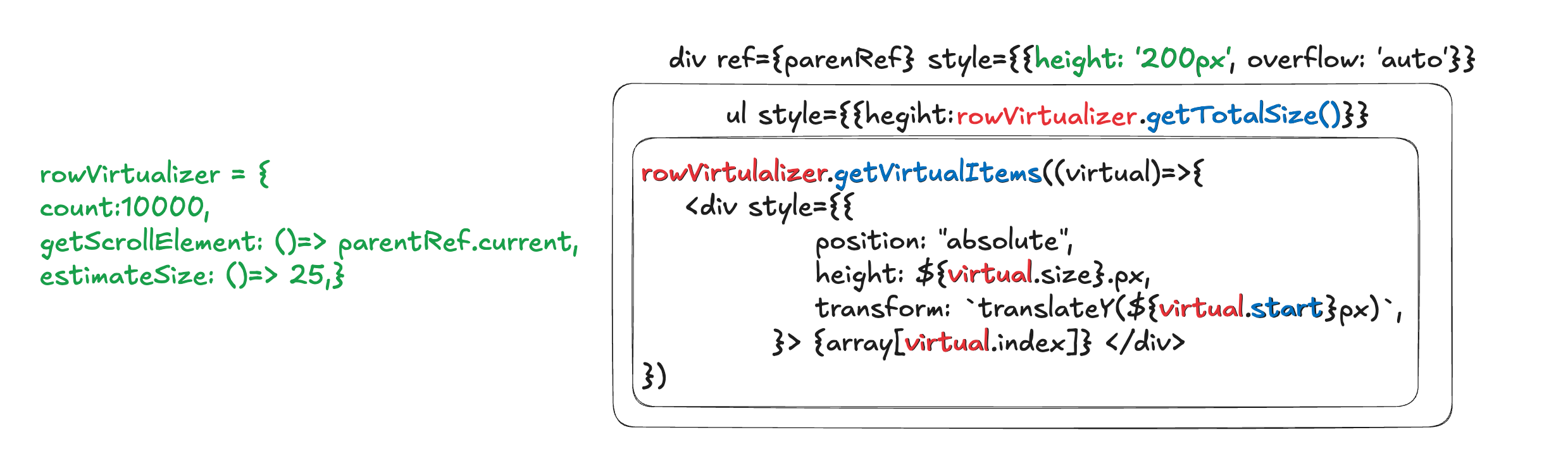
약식으로 표현한 코드니, 갖다 보고 사용하지는 말 것
정리해보겠다.
-
Virtualizer 선언부 - const rowVirtualizer = useVirtualizer()
count: 리스트 안에 들어갈 listItem의, 총 개수 10000개로 지정했다.getScrollElement: scroll이 있다고 지정한 요소, 가장 상위 부모가 될 것estimateSize: listItem 개별 요소의 높이(px), 25px로 지정했다.
-
List상 가장 상위 부모인 div
ref= 길이 참고를 위해 쓰임height= 유저가 보는 Viewport, 위에선 200px이다.
-
ListItem이 들어갈 ul
- height:
rowVirtualizer.getTotalSize()= estimateSize(25px) * count(10,000) = 250,000 하지만 상위 height가 200px이기에, 스크롤링을 통해 볼 수 있다. - position: 'relative' = 상대적인 배치
- height:
-
rowVirtualizer는 배열로 이루어져 있으며, 각 배열의 요소들은 선언부의 영향을 받는다
- ListItem 요소 div
- virtual.size = estimateSize : 25px -> height에 지정한다.
- virtaul.index = 부모에서 스크롤을 얼마나 내렸는지에 따라 바뀐다.
- virtual.start = 항목의 시작 offset, css 조정시에 사용한다.
- ListItem 요소 div
하지만 내 프로젝트는 useInfiniteQuery를 사용해, parameter마다 다른 데이터를 fetching해와야 하기 때문에 추가적인 작업이 더 필요하다.
왜냐하면 count의 개수가 가변적이기 때문이다.
아래는 무한스크롤을 사용하는 예시이다.
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import {
QueryClient,
QueryClientProvider,
useInfiniteQuery,
} from '@tanstack/react-query'
import './index.css'
import { useVirtualizer } from '@tanstack/react-virtual'
const queryClient = new QueryClient()
async function fetchServerPage(
limit: number,
offset: number = 0,
): Promise<{ rows: Array<string>; nextOffset: number }> {
const rows = new Array(limit)
.fill(0)
.map((_, i) => `Async loaded row #${i + offset * limit}`)
await new Promise((r) => setTimeout(r, 500))
return { rows, nextOffset: offset + 1 }
}
function App() {
const {
status,
data,
error,
isFetching,
isFetchingNextPage,
fetchNextPage,
hasNextPage,
} = useInfiniteQuery({
queryKey: ['projects'],
queryFn: (ctx) => fetchServerPage(10, ctx.pageParam),
getNextPageParam: (lastGroup) => lastGroup.nextOffset,
initialPageParam: 0,
})
const allRows = data ? data.pages.flatMap((d) => d.rows) : []
const parentRef = React.useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null)
const rowVirtualizer = useVirtualizer({
count: hasNextPage ? allRows.length + 1 : allRows.length,
getScrollElement: () => parentRef.current,
estimateSize: () => 100,
overscan: 5,
})
React.useEffect(() => {
const [lastItem] = [...rowVirtualizer.getVirtualItems()].reverse()
if (!lastItem) {
return
}
if (
lastItem.index >= allRows.length - 1 &&
hasNextPage &&
!isFetchingNextPage
) {
fetchNextPage()
}
}, [
hasNextPage,
fetchNextPage,
allRows.length,
isFetchingNextPage,
rowVirtualizer.getVirtualItems(),
])
return (
<div>
<p>
This infinite scroll example uses React Query's useInfiniteScroll hook
to fetch infinite data from a posts endpoint and then a rowVirtualizer
is used along with a loader-row placed at the bottom of the list to
trigger the next page to load.
</p>
<br />
<br />
{status === 'pending' ? (
<p>Loading...</p>
) : status === 'error' ? (
<span>Error: {error.message}</span>
) : (
<div
ref={parentRef}
className="List"
style={{
height: `500px`,
width: `100%`,
overflow: 'auto',
}}
>
<div
style={{
height: `${rowVirtualizer.getTotalSize()}px`,
width: '100%',
position: 'relative',
}}
>
{rowVirtualizer.getVirtualItems().map((virtualRow) => {
const isLoaderRow = virtualRow.index > allRows.length - 1
const post = allRows[virtualRow.index]
return (
<div
key={virtualRow.index}
className={
virtualRow.index % 2 ? 'ListItemOdd' : 'ListItemEven'
}
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: 0,
left: 0,
width: '100%',
height: `${virtualRow.size}px`,
transform: `translateY(${virtualRow.start}px)`,
}}
>
{isLoaderRow
? hasNextPage
? 'Loading more...'
: 'Nothing more to load'
: post}
</div>
)
})}
</div>
</div>
)}
<div>
{isFetching && !isFetchingNextPage ? 'Background Updating...' : null}
</div>
<br />
<br />
{process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? (
<p>
<strong>Notice:</strong> You are currently running React in
development mode. Rendering performance will be slightly degraded
until this application is build for production.
</p>
) : null}
</div>
)
}
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}>
<App />
</QueryClientProvider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root'),
)잘 안보이시는 분들은
https://tanstack.com/virtual/latest/docs/framework/react/examples/infinite-scroll
그래서 내 프로젝트에 적용을 해봤다. 결과는?
스크롤을 내리면, 바로 엄청난 ReRendereing이 된다. state에 관여하는 모든 로직도 주석처리 해보고, docs도 눈빠지게 쳐다보고, 바꿔보고 하면서 현재 12시간 넘게 사투중, 실마리를 겨우 하나 찾아냈다.
- Virtualizer 선언부 - const rowVirtualizer = useVirtualizer()
getScrollElement: scroll이 있다고 지정한 요소, 가장 상위 부모가 될 것
이라고 위에 써놨었는데, scroll이 있다고 지정한 요소 이놈이 문제인 것 같다.
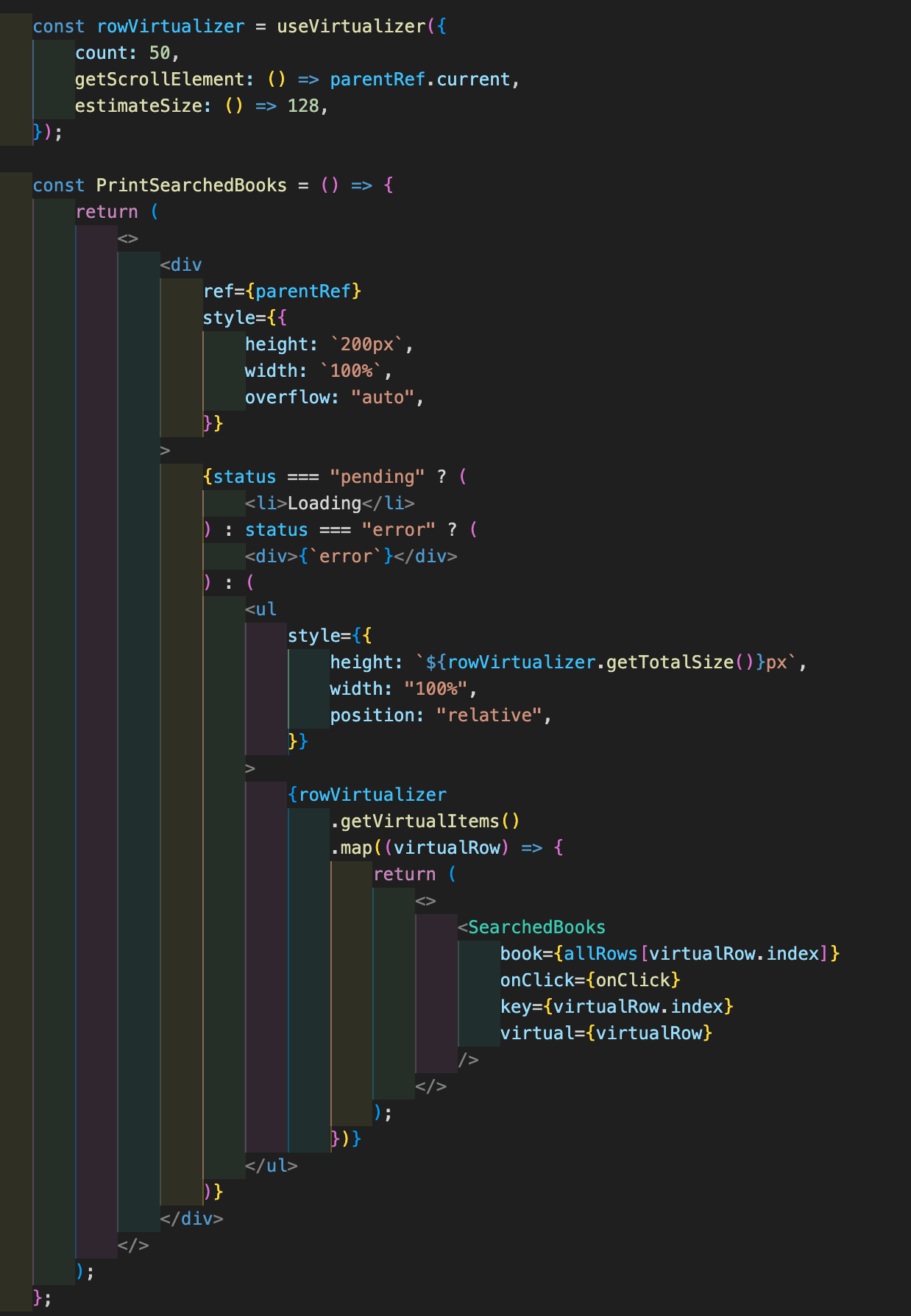
- div가 가장 상위: scroll이 있는 곳
- ul: 모든 아이템을 담을 곳, 실제론 50개의 렌더링이 될 위치이다.
- SearchedBooks: 정보를 담아낸 li 요소를 출력한다. li로 봐도 무방하다.
순서상, 이론상 문제가 없다. overflow:"scroll"을 없애면 어떻게 될까?
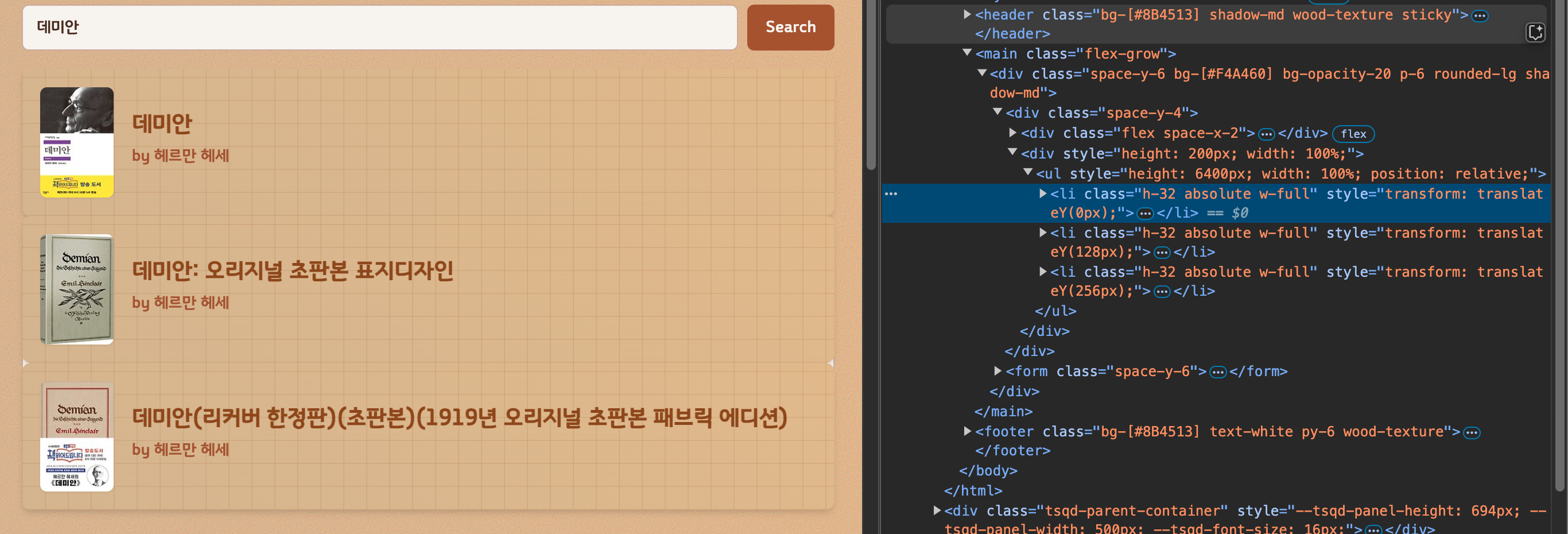
ul은 height는 count*estimateSize인 6400px이 되었지만, scrolling이 없기 때문에 그보다 더 많은 내용이 렌더링되지 않았다.
실마리는 겨우 찾았으니, 이걸 이용해서 한번 고쳐보자..
고치고 돌아오겠다. 24시간정도 투자하면 고쳐지겠지?
