ArrayList를 이용해서 stack 자료 구조 구현
stack를 구현할 때 ArrayList, LinkedList 중 어느 것을 선택하는 것이 좋을까?
스택(Stack)은 데이터를 저장하고 검색하는 데 사용되는 추상 자료형(ADT) 중 하나로, 후입선출(Last In, First Out; LIFO)의 원리를 따릅니다. 이는 가장 최근에 삽입된 요소가 가장 먼저 제거되는 구조를 말합니다. 스택은 주로 함수 호출이나 재귀 함수 호출과 같은 연산에서 유용하게 사용됩니다.
push(E Item) : 주어진 객체를 스텍에 넣음
peek() : 스택의 맨 위 객체를 가져옴, 객체를 스택에서 제거하지 않음
pop() : 스택의 맨 위 객체를 가져옴, 객체를 스택에서 제거
peak 구현
package chapter20230901.stack;
import java.util.*;
class MyStack {
private ArrayList<String> arrayStack = new ArrayList<String>();
public void push(String data) { // 스택의 맨 뒤에 요소를 추가
arrayStack.add(data);
}
public String pop() {
int len = arrayStack.size(); // 저장된 개수
if (len == 0) {
System.out.println("스택이 비었습니다.");
return null;
}
return(arrayStack.remove(len - 1)); // 맨 뒤에 있는 자료 반환하고 배열에서 제거
}
public String peek() {
int len = arrayStack.size(); // 저장된 개수
if (len == 0) {
System.out.println("스택이 비었습니다.");
return null;
}
return(arrayStack.get(len - 1)); // 맨 뒤에 있는 자료 반환
}
}
public class stack01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStack stack = new MyStack();
stack.push("A");
stack.push("B");
stack.push("C");
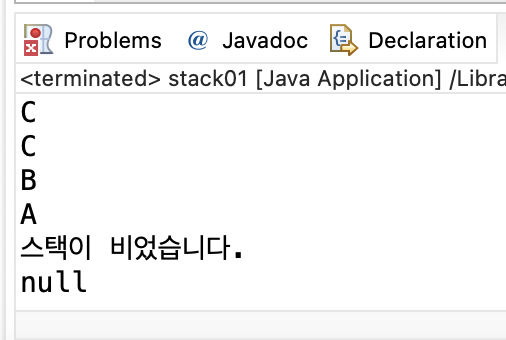
System.out.println(stack.peek()); // C
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // C
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // B
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // A
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // 스택이 비었습니다. , null
}
}