Baekjoon Online Judge
algorithm practice
- 단계별 문제풀기
27. 동적 계획법과 최단거리 역추적
지금까지는 최솟값, 최댓값, 최단거리만 찾았습니다. 이번에는 실제 최적해와 최단경로를 찾아 봅시다.
Java / Python
8. 최소비용 구하기 2
간선에 가중치가 있을 때 최단경로를 출력하는 문제
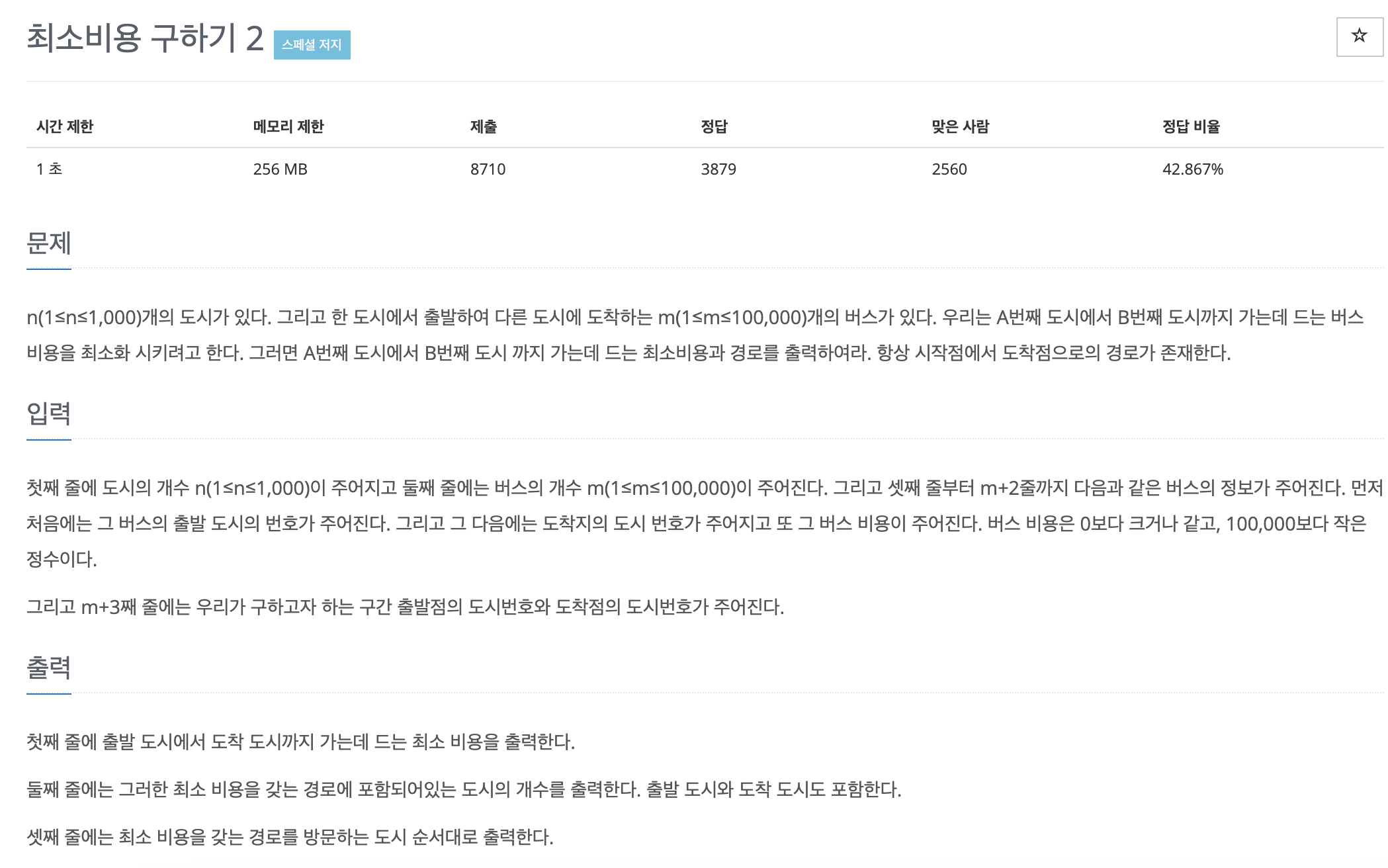
이번 문제는 A번째 도시에서 B번째 도시 까지 가는데 드는 최소비용과 경로를 출력하는 문제입니다.
다익스트라 알고리즘을 활용하는 문제입니다.
(최단거리 문제에, 경로추적을 하는 문제이고, 경로의 가중치가 양수이기 때문에 다익스트라 알고리즘을 활용했습니다.)
- Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static class Bus implements Comparable<Bus> {
public int end, cost;
public Bus(int end, int cost) {
this.end = end;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Bus o) {
return cost - o.cost;
}
}
static int INF = 100000000;
static ArrayList<Bus>[] graph;
static int N, M, cnt, s, e;
static int[] dist, pcity;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
M = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
graph = new ArrayList[N + 1];
pcity = new int[N + 1];
// 인접리스트 초기화
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int start = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int end = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int cost = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
graph[start].add(new Bus(end, cost));
}
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
s = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
e = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
dist = new int[N + 1];
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dijkstra();
Stack<Integer> stack = searchPath();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int city = stack.pop();
sb.append(city + " ");
}
bw.write(dist[e] + "\n");
bw.write(cnt + "\n");
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.flush();
br.close();
bw.close();
}
static void dijkstra() {
PriorityQueue<Bus> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
boolean[] visit = new boolean[N + 1];
pq.add(new Bus(s, 0));
dist[s] = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Bus curBus = pq.poll();
int cur = curBus.end;
if (visit[cur] == true)
continue;
visit[cur] = true;
for (Bus bus : graph[cur]) {
if (dist[bus.end] > dist[cur] + bus.cost) {
dist[bus.end] = dist[cur] + bus.cost;
pq.add(new Bus(bus.end, dist[bus.end]));
pcity[bus.end] = cur;
}
}
}
}
public static Stack<Integer> searchPath() {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int cur = e;
while (cur != s) {
stack.push(cur);
cnt++;
cur = pcity[cur];
}
stack.push(cur);
cnt++;
return stack;
}
}- Python
import sys
from heapq import heappop, heappush
import copy
input = sys.stdin.readline
INF = int(1e9)
# 다익스트라 함수
def dijkstra(start):
dis = [INF] * (N + 1)
dis[start] = 0
que = []
heappush(que, (0, start))
while que:
now_cost, now_way = heappop(que)
if dis[now_way] < now_cost:
continue
path[now_way].append(now_way)
if now_way == end:
return dis[end]
# 최단 거리 수정
for new_cost, new_way in graph[now_way]:
if dis[new_way] > new_cost + now_cost:
dis[new_way] = new_cost + now_cost
heappush(que, (dis[new_way], new_way))
# 최단 거리 수정으로 인해 최단 경로 수정
path[new_way] = copy.deepcopy(path[now_way])
N = int(input())
M = int(input())
graph = [[] for _ in range(N + 1)] # 인접 리스트
path = [[] for _ in range(N + 1)] # 경로 저장
# 그래프
for _ in range(M):
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append((c, b))
start, end = map(int, input().split())
print(dijkstra(start)) # 최소 비용 출력
print(len(path[end])) # 경로 길이
print(*path[end]) # 경로 출력