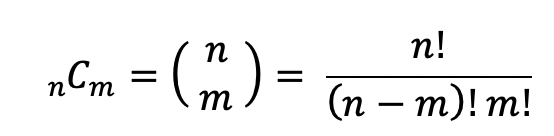Baekjoon Online Judge
algorithm practice
- 단계별 문제풀기
17. 정수론 및 조합론
정수론과 조합론을 배워 봅시다.
Java / Python
12. 조합 0의 개수
위와 비슷한데 N! 대신 이항계수가 들어간 문제
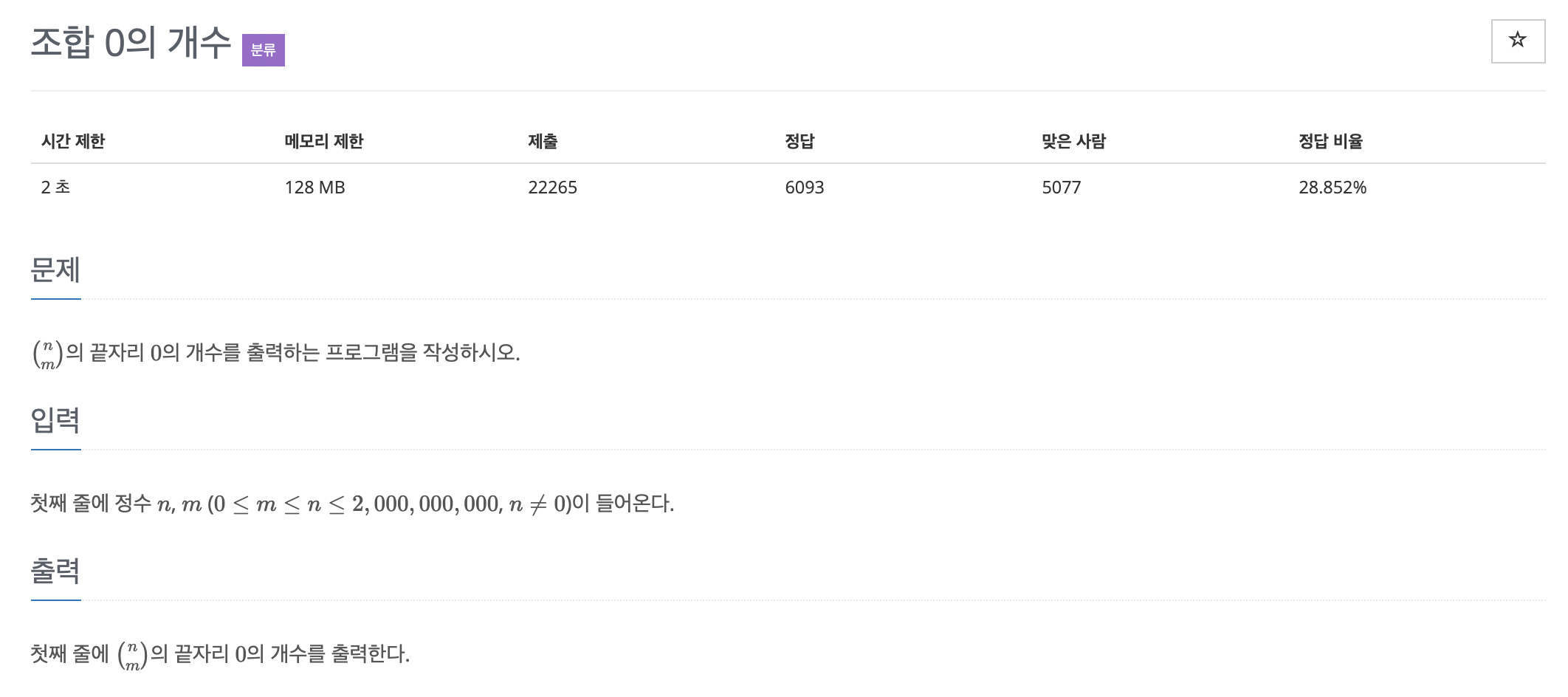
이번 문제는 저번 문제와 유사한데, N!이 아닌 조합에서 끝자리 0의 개수를 구하는 문제입니다.
이항 계수를 구하는 공식입니다.
여기서도 0의 개수는 2, 5의 겹치는 제곱 값과 같기 때문에, n!, (n-m)!, m1!의 2와 5의 제곱을 구합니다. nCm 내에 있는 2와 5 중 최소값이 무엇인지 알아낸 뒤 출력하면 됩니다.
- Java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine(), " ");
long N = Long.parseLong(st.nextToken());
long M = Long.parseLong(st.nextToken());
long five = FiveCount(N) - FiveCount(N - M) - FiveCount(M);
long two = TwoCount(N) - TwoCount(N - M) - TwoCount(M);
System.out.println(Math.min(five, two));
}
static long FiveCount(long num) { // 5 개수 세는 함수
int cnt = 0;
while (num >= 5) {
cnt += (num / 5);
num /= 5;
}
return cnt;
}
static long TwoCount(long num) { // 2 개수 세는 함수
int cnt = 0;
while (num >= 2) {
cnt += (num / 2);
num /= 2;
}
return cnt;
}
}- Python
import sys
n, m = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
# 5 개수 세는 함수
def five_count(n):
cnt = 0
while n != 0:
n = n // 5
cnt += n
return cnt
# 2 개수 세는 함수
def two_count(n):
cnt = 0
while n != 0:
n = n // 2
cnt += n
return cnt
if m == 0:
print(0)
else:
print(min(two_count(n)-two_count(m)-two_count(n-m), five_count(n)-five_count(m)-five_count(n-m)))