Baekjoon Online Judge
algorithm practice
- 단계별 문제풀기
24. DFS와 BFS
그래프를 순회하는 알고리즘을 배워 봅시다.
Java / Python
5. 미로 탐색
BFS의 특징은 각 정점을 최단경로로 방문한다는 것입니다. 이 점을 활용해 최단거리를 구해 봅시다.
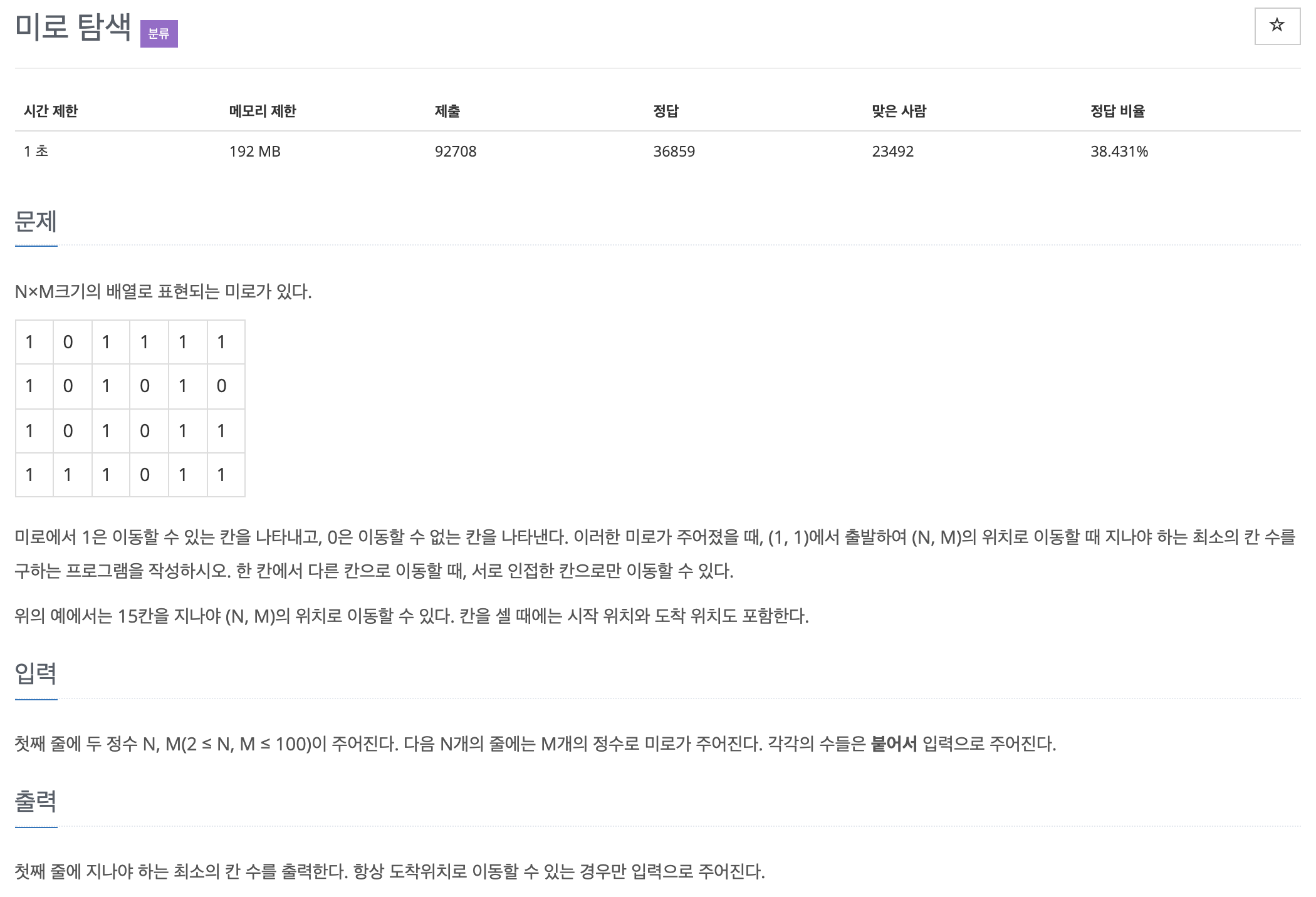
이번 문제는 미로에서 1은 이동할 수 있는 칸을 나타내고, 0은 이동할 수 없는 칸을 나타내는 미로가 주어졌을 때, (1, 1)에서 출발하여 (N, M)의 위치로 이동할 때 지나야 하는 최소의 칸 수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하는 문제입니다. 한 칸에서 다른 칸으로 이동할 때, 서로 인접한 칸으로만 이동할 수 있습니다. (BFS 이용했습니다.)
- Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int[] dr = {1, -1, 0, 0};
static int[] dc = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static int N, M;
static int[][] map;
static boolean[][] check; // 방문 여부
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[N][M];
check = new boolean[N][M];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
String str = st.nextToken();
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++){
map[i][j] = str.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
bfs(0,0);
bw.write(map[N-1][M-1] + "\n");
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
public static void bfs(int x, int y){
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new int[] {x, y});
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int temp[] = queue.poll();
check[x][y] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int r = temp[0] + dr[i];
int c = temp[1] + dc[i];
if(r >= 0 && c >= 0 && r < N && c < M) {
if(map[r][c] != 0 && !check[r][c]){
queue.offer(new int[] {r,c});
check[r][c] = true;
map[r][c] = map[temp[0]][temp[1]] + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}- Python
import sys
N, M = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
matrix = [sys.stdin.readline().rstrip() for _ in range(N)]
check = [[0]*M for _ in range(N)]
dx, dy = [-1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, -1, 1]
# BFS 경로 탐색
# queue 방식 사용
queue = [(0,0)]
check[0][0] = 1
while queue:
x, y = queue.pop(0)
if x == N-1 and y == M-1:
print(check[x][y]) # 최종 경로 도착
break
for i in range(4):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
if 0 <= nx < N and 0 <= ny < M:
if check[nx][ny] == 0 and matrix[nx][ny] == '1':
check[nx][ny] = check[x][y] + 1
queue.append((nx,ny))