Baekjoon Online Judge
algorithm practice
- 단계별 문제풀기
24. DFS와 BFS
그래프를 순회하는 알고리즘을 배워 봅시다.
Java / Python
7. 토마토
위 문제의 3차원 버전
(토마토 7576번 문제의 3차원 버전)
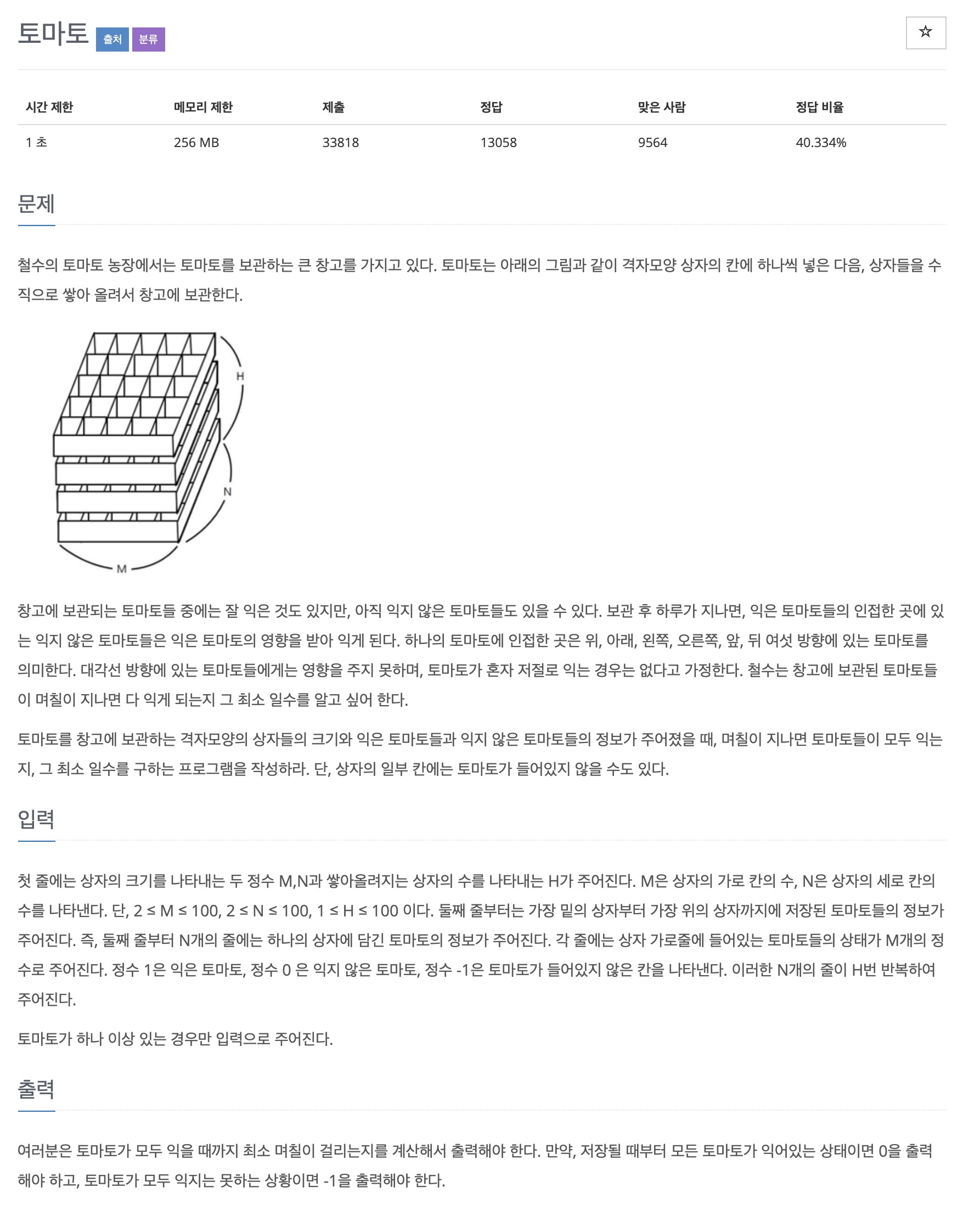
이번 문제는 토마토를 창고에 보관하는 격자모양의 상자들의 크기와 익은 토마토들과 익지 않은 토마토들의 정보가 주어졌을 때, 며칠이 지나면 토마토들이 모두 익는지, 그 최소 일수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하는 문제입니다. (단, 상자의 일부 칸에는 토마토가 들어있지 않을 수도 있다.)
BFS 탐색을 이용했습니다.
- Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class PointXYZ{
int row;
int col;
int height;
public PointXYZ(int height, int row, int col){
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.height = height;
}
}
public class Main {
// 6방향을 나타내기 위한 배열
static int rowArr[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0};
static int colArr[] = {0, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0};
static int heightArr[] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 1, -1};
static int M, N, H;
static int tomato[][][];
static int result;
static Queue<PointXYZ> queue = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
H = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
tomato = new int[H + 1][N + 1][M + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= H; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++){
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for(int k = 1; k <= M; k++){
tomato[i][j][k] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(tomato[i][j][k] == 1) queue.add(new PointXYZ(i, j, k));
}
}
}
bw.write(bfs() + "\n");
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
public static int bfs() {
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
PointXYZ point = queue.poll();
int row = point.row;
int col = point.col;
int height = point.height;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 6; i++){
int newHeight = height + heightArr[i];
int newRow = row + rowArr[i];
int newCol = col + colArr[i];
// 6방향으로 토마토가 익을 수 있는지 여부 확인
if(checkPoint(newHeight, newRow, newCol)){
// 익은 토마토를 큐에 추가
queue.add(new PointXYZ(newHeight, newRow, newCol));
// 익은 토마토의 값 = 이전에 익은 토마토의 값 + 1
tomato[newHeight][newRow][newCol] = tomato[height][row][col] + 1;
}
}
}
// 최대 값을 구하기 위한 변수 (결과값)
int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 1; i <= H; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++){
for(int k = 1; k <= M; k++){
if(tomato[i][j][k] == 0){ // 하나라도 익지 않은 토마토
return -1;
}
// 토마토가 익는데 걸리는 시간을 구함
result = Math.max(result, tomato[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
if(result == 1) {
return 0;
}else {
return result - 1;
}
}
public static boolean checkPoint(int height, int row, int col){
// 주어진 범위 밖인지 검사
if(height < 1 || height > H || row < 1 || row > N || col < 1 || col > M) return false;
// 아직 익지 않은 토마토라면 true 반환
if(tomato[height][row][col] == 0) return true;
// 이미 익어있거나 빈 자리라면 false 반한
else return false;
}
}- Python
from collections import deque
import sys
M, N, H = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())
tomato = [[list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())) for _ in range(N)] for depth in range(H)]
# queue 방식 사용 (deque 필수 X)
queue = deque()
for i in range(H):
for j in range(N):
for k in range(M):
if tomato[i][j][k] == 1:
queue.append([i, j, k])
dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
dy = [0, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0]
dz = [0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 1]
# bfs 경로 탐색
def bfs():
while queue:
z, x, y = queue.popleft()
for i in range(6):
nx = x + dx[i]
ny = y + dy[i]
nz = z + dz[i]
if 0 <= nx < N and 0 <= ny < M and 0 <= nz < H and tomato[nz][nx][ny] == 0:
tomato[nz][nx][ny] = tomato[z][x][y] + 1
queue.append([nz, nx, ny])
bfs()
result = -1
check = False
for i in tomato:
for j in i:
for k in j:
if k == 0:
check = True
result = max(result, k)
if check:
print(-1)
elif result == 1:
print(0)
else:
print(result - 1)