구현 / 시뮬레이션
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/14499›
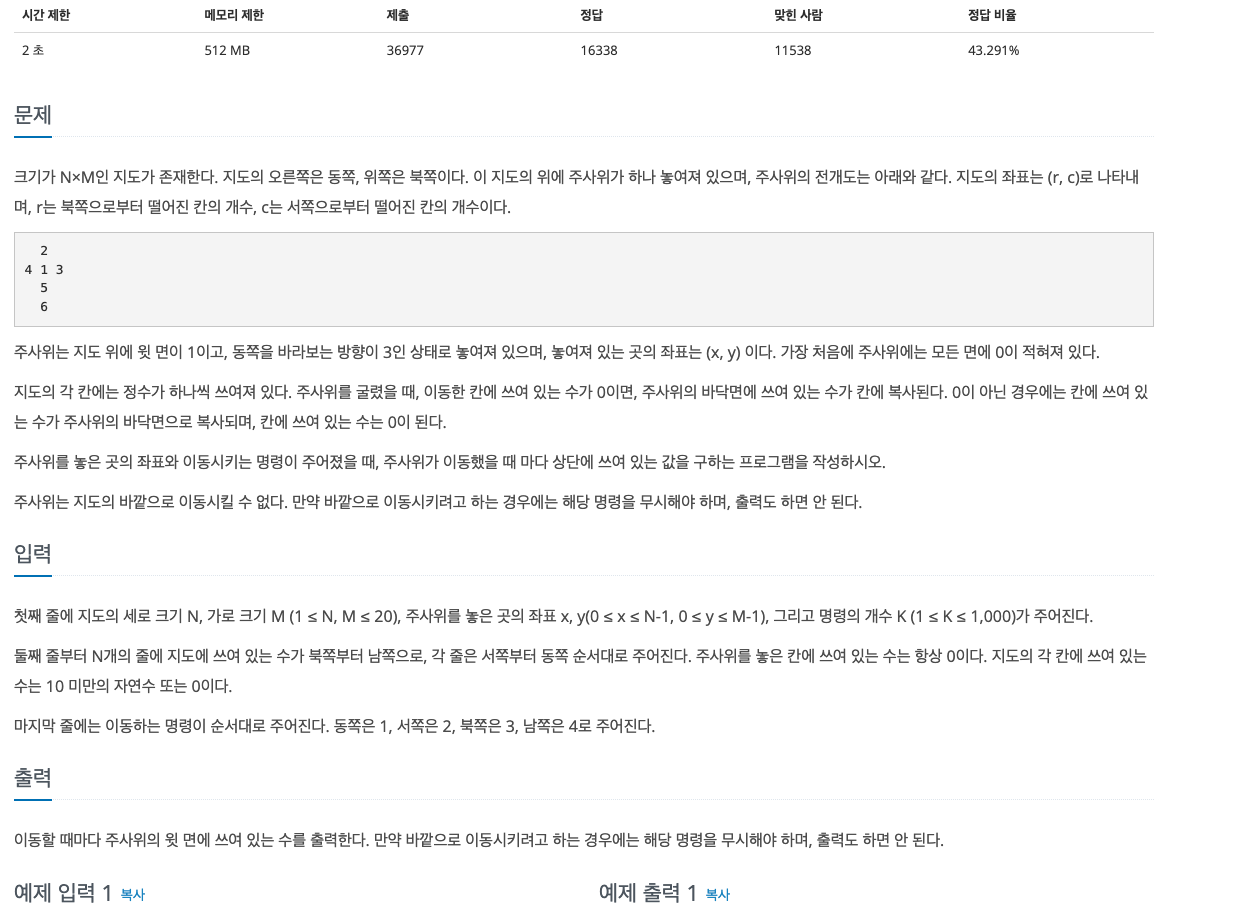
- 가장 처음에 주사위에는 모든 면에 0이 적혀져 있다.
- 주사위를 굴렸을 때, 이동한 칸에 쓰여 있는 수가 0이면, 주사위의 바닥면에 쓰여 있는 수가 칸에 복사된다.
- 0이 아닌 경우에는 칸에 쓰여 있는 수가 주사위의 바닥면으로 복사되며, 칸에 쓰여 있는 수는 0이 된다.
주사위가 4방향으로 이동하면 어떻게 변하는지 함수를 작성하고 그에 따라서 1~3 순서대로 구현하면 된다.
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
n, m, x, y, k = map(int, input().split())
board = []
dice = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
for _ in range(n):
board.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
dir = list(map(int, input().split()))
# 서 동 남 북
dx = [0, 0, -1, 1]
dy = [1, -1, 0, 0]
nx, ny = x, y
def turn(dir):
a, b, c, d, e, f = dice[0], dice[1], dice[2], dice[3], dice[4], dice[5]
if dir == 1: # 동
dice[0], dice[1], dice[2], dice[3], dice[4], dice[5] = e, b, a, d, f, c
elif dir == 2: # 서
dice[0], dice[1], dice[2], dice[3], dice[4], dice[5] = c, b, f, d, a, e
elif dir == 3: # 북
dice[0], dice[1], dice[2], dice[3], dice[4], dice[5] = d, a, c, f, e, b
elif dir == 4: # 남
dice[0], dice[1], dice[2], dice[3], dice[4], dice[5] = b, f, c, a, e, d
for i in dir:
nx += dx[i-1]
ny += dy[i-1]
if nx < 0 or ny < 0 or nx >= n or ny >= m:
nx -= dx[i-1]
ny -= dy[i-1]
continue
turn(i)
if board[nx][ny] == 0:
board[nx][ny] = dice[-1]
else:
dice[-1] = board[nx][ny]
board[nx][ny] = 0
print(dice[0])