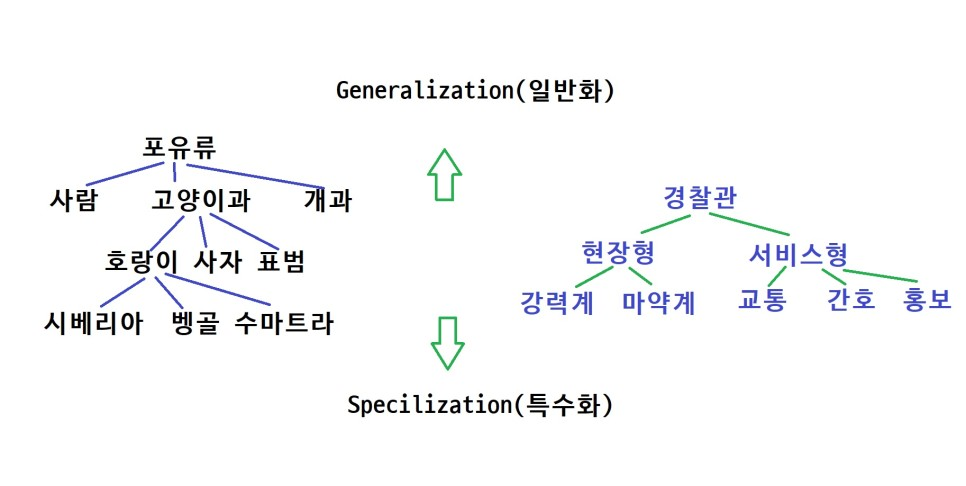
이렇게 종속관계가 명확할 때 상속을 사용해야 한다.
package ex03.inheritance.extends00;
//상속
//1. 클래스를 잘 설계해 놓는다
//2. 상속만 받아도 그대로 물려받는다
//3. 물려받은 모든 기능을 사용할 수 있다
public class ExtendsMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GrandFather gFather = new GrandFather();
gFather.handsome();
Father father = new Father();
father.handsome();
father.wealth();
Child child = new Child();
child.handsome();
child.wealth();
child.play();
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends00;
//java의 모든 클래스는 컴파일 되는 순간
//자동으로 java.lang.object 클래스의 상속을 받는다.
public class GrandFather {
public void handsome() {
System.out.println("잘 생겼다~");
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends00;
public class Father extends GrandFather{
public void wealth() {
System.out.println("부유하다~");
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends00;
public class Child extends Father{
public void play() {
System.out.println("인생을 즐긴다~");
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends02;
/*
자식객체가 생성될 때
내부적으로 부모 객체가 먼저 생성된다
부모 객체가 자식 내부에 생성되기 때문에
자식은 부모의 기능을 사용할 수 있게 된다
*/
public class ExtendsMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Child child = new Child();
Child child = new Child(50,10000000L,20);
child.play(); // Child
child.wealth(); // Father
child.handsome(); // GrandFather
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends02;
//java의 모든 클래스는 컴파일되는 순간
//자동으로 java.lang.object 클래스의 상속을 받는다
public class GrandFather {
int handsomeScore=100;
public GrandFather() {
System.out.println("GrandFather 생성자");
}
public GrandFather(int handsome) {
this.handsomeScore = handsome;
System.out.println("GrandFather 매개변수 생성자");
}
public void handsome() {
System.out.println("점수: " + handsomeScore + " 잘 생겼다~");
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends02;
public class Father extends GrandFather {
long money = 9999999999999L;
public Father() {
System.out.println("Father 생성자");
}
public Father(long money) {
this.money = money;
System.out.println("Father 매개변수 1개 생성자");
}
public Father(int handsome, long money) {
super(handsome); //GrandFather 생성
this.money = money;
System.out.println("Father 매개변수 2개 생성자");
}
public void wealth() {
System.out.println("재산 : " + money + "부유하다~");
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends02;
public class Child extends Father{
int duration=365;
public Child() {
System.out.println("Child 생성자");
}
public Child(int duration) {
this.duration = duration;
System.out.println("Child 매개변수 1개 생성자");
}
public Child(int handsome, long money, int duration) {
super(handsome, money); //Father 생성자
this.duration = duration;
System.out.println("Child 매개변수 3개 생성자");
}
public void play() {
System.out.println(duration + "일 동안 인생을 즐긴다~");
}
}메서드 기능
package ex03.inheritance.extends03;
public class ExtendsMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child child = new Child();
child.play();
child.wealth();
child.handsome();
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends03;
public class Grandfather {
public Grandfather() {
System.out.println("Grandfather 생성자");
}
public void handsome() {
System.out.println("잘생겼다~ ");
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends03;
public class Father extends Grandfather{
public Father() {
System.out.println("Father 생성자 ");
}
public void wealth() {
System.out.println("부유하다~ ");
}
}package ex03.inheritance.extends03;
public class Child extends Father{
public Child() {
System.out.println("Child 생성자 ");
}
//물려 받은 메서드를 덮어쓴다
public void handsome() {
System.out.println("뺀질거리게 생겼다~");
}
// 물려받은 메서드의 기능을 확장했다
public void wealth() {
super.wealth(); //Father의 wealth
System.out.println("돈을 많이 썼다! ");
}
//물려받지 않은 새롭게 정의한 메서드
public void play() {
System.out.println("인생을 즐긴다~ ");
}
}