문제
가로 A(1≤A≤100), 세로 B(1≤B≤100) 크기의 땅이 있다. 이 땅 위에 로봇들이 N(1≤N≤100)개 있다.
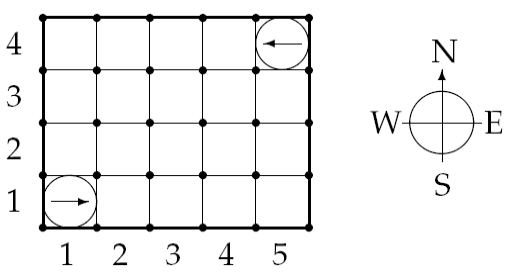
로봇들의 초기 위치는 x좌표와 y좌표로 나타난다. 위의 그림에서 보듯 x좌표는 왼쪽부터, y좌표는 아래쪽부터 순서가 매겨진다. 또한 각 로봇은 맨 처음에 NWES 중 하나의 방향을 향해 서 있다. 초기에 서 있는 로봇들의 위치는 서로 다르다.
이러한 로봇들에 M(1≤M≤100)개의 명령을 내리려고 한다. 각각의 명령은 순차적으로 실행된다. 즉, 하나의 명령을 한 로봇에서 내렸으면, 그 명령이 완수될 때까지 그 로봇과 다른 모든 로봇에게 다른 명령을 내릴 수 없다. 각각의 로봇에 대해 수행하는 명령은 다음의 세 가지가 있다.
- L: 로봇이 향하고 있는 방향을 기준으로 왼쪽으로 90도 회전한다.
- R: 로봇이 향하고 있는 방향을 기준으로 오른쪽으로 90도 회전한다.
- F: 로봇이 향하고 있는 방향을 기준으로 앞으로 한 칸 움직인다.
간혹 로봇들에게 내리는 명령이 잘못될 수도 있기 때문에, 당신은 로봇들에게 명령을 내리기 전에 한 번 시뮬레이션을 해 보면서 안전성을 검증하려 한다. 이를 도와주는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
잘못된 명령에는 다음의 두 가지가 있을 수 있다.
- Robot X crashes into the wall: X번 로봇이 벽에 충돌하는 경우이다. 즉, 주어진 땅의 밖으로 벗어나는 경우가 된다.
- Robot X crashes into robot Y: X번 로봇이 움직이다가 Y번 로봇에 충돌하는 경우이다.
입력
첫째 줄에 두 정수 A, B가 주어진다. 다음 줄에는 두 정수 N, M이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 각 로봇의 초기 위치(x, y좌표 순) 및 방향이 주어진다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 각 명령이 명령을 내리는 순서대로 주어진다. 각각의 명령은 명령을 내리는 로봇, 명령의 종류(위에 나와 있는), 명령의 반복 회수로 나타낸다. 각 명령의 반복 회수는 1이상 100이하이다.
출력
첫째 줄에 시뮬레이션 결과를 출력한다. 문제가 없는 경우에는 OK를, 그 외의 경우에는 위의 형식대로 출력을 한다. 만약 충돌이 여러 번 발생하는 경우에는 가장 먼저 발생하는 충돌을 출력하면 된다.
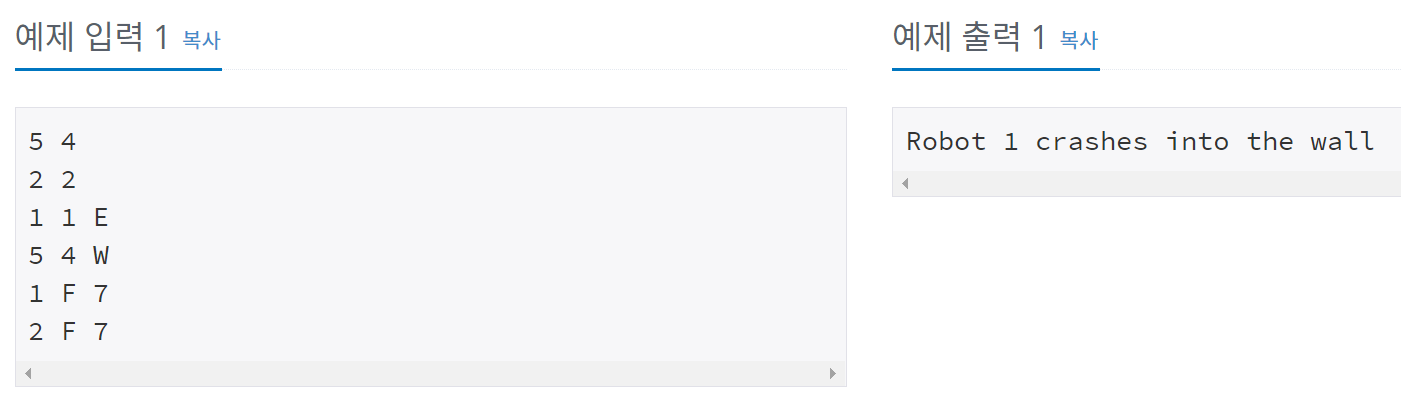
예제 입&출력
소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
private static int A, B, N, M;
private static boolean isCrush;
private static Pos[] pos;
private static int[][] check;
private static final int[] dx = {0, 1, 0, -1};
private static final int[] dy = {1, 0, -1, 0};
private static HashMap<String, Integer> dirMap = new HashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
String answer = "";
A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
B = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
pos = new Pos[N + 1];
check = new int[B + 1][A + 1];
dirMap.put("N", 0);
dirMap.put("E", 1);
dirMap.put("S", 2);
dirMap.put("W", 3);
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
String dir = st.nextToken();
pos[i] = new Pos(x, y, dirMap.get(dir));
check[y][x] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int robot = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
String command = st.nextToken();
int commandCount = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
answer = getCrush(robot, command, commandCount);
if (isCrush) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
private static String getCrush(int robot, String command, int commandCount) {
for (int i = 0; i < commandCount; i++) {
Pos curRobotPos = pos[robot];
if (command.equals("L") || command.equals("R")) {
int nextRobotDir = getNextDir(curRobotPos.dir, command);
pos[robot] = new Pos(curRobotPos.x, curRobotPos.y, nextRobotDir);
} else if (command.equals("F")) {
int nextX = curRobotPos.x + dx[curRobotPos.dir];
int nextY = curRobotPos.y + dy[curRobotPos.dir];
if (nextX < 1 || nextY < 1 || nextX > A || nextY > B) {
isCrush = true;
return "Robot " + robot + " crashes into the wall";
} else {
if (check[nextY][nextX] != 0) {
isCrush = true;
return "Robot " + robot + " crashes into robot " + check[nextY][nextX];
} else {
check[curRobotPos.y][curRobotPos.x] = 0;
check[nextY][nextX] = robot;
pos[robot] = new Pos(nextX, nextY, curRobotPos.dir);
}
}
}
}
return "OK";
}
private static int getNextDir(int dir, String command) {
if (command.equals("L")) {
if (dir == 0) {
dir = 3;
} else {
dir--;
}
} else if (command.equals("R")) {
if (dir == 3) {
dir = 0;
} else {
dir++;
}
}
return dir;
}
private static class Pos {
int x;
int y;
int dir;
public Pos(int x, int y, int dir) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.dir = dir;
}
}
}
Comment
- 필자에겐 굉장히.. 어려운 난이도였다. 중요 부분들을 확인해보자!
Pos[]의index를 통해 정보를 가져오도록class를 생성했고, 네 방향에 대해서HashMap을 통해 저장했다.check[][]를 통해 해당하는 위치에0이 아닌 값(=존재하는 로봇의index)이 있음을 체크해줘야 한다.isCrush를 통해 벽이나, 다른 로봇에 부딪히는지 확인!- 좌표를 이용한 문제를 해결할 때는 항상
dx와dy를 가지고 놀 줄 알아야한다.
