문제 설명
복서 선수들의 몸무게 weights와, 복서 선수들의 전적을 나타내는 head2head가 매개변수로 주어집니다. 복서 선수들의 번호를 다음과 같은 순서로 정렬한 후 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성해주세요.
- 전체 승률이 높은 복서의 번호가 앞쪽으로 갑니다. 아직 다른 복서랑 붙어본 적이 없는 복서의 승률은 0%로 취급합니다.
- 승률이 동일한 복서의 번호들 중에서는 자신보다 몸무게가 무거운 복서를 이긴 횟수가 많은 복서의 번호가 앞쪽으로 갑니다.
- 자신보다 무거운 복서를 이긴 횟수까지 동일한 복서의 번호들 중에서는 자기 몸무게가 무거운 복서의 번호가 앞쪽으로 갑니다.
- 자기 몸무게까지 동일한 복서의 번호들 중에서는 작은 번호가 앞쪽으로 갑니다.
제한 사항
- weights의 길이는 2 이상 1,000 이하입니다.
- weights의 모든 값은 45 이상 150 이하의 정수입니다.
weights[i]는 i+1번 복서의 몸무게(kg)를 의미합니다.
- head2head의 길이는 weights의 길이와 같습니다.
- head2head의 모든 문자열은 길이가 weights의 길이와 동일하며, 'N', 'W', 'L'로 이루어진 문자열입니다.
head2head[i]는 i+1번 복서의 전적을 의미하며,head2head[i][j]는 i+1번 복서와 j+1번 복서의 매치 결과를 의미합니다.- 'N' (None)은 두 복서가 아직 붙어본 적이 없음을 의미합니다.
- 'W' (Win)는 i+1번 복서가 j+1번 복서를 이겼음을 의미합니다.
- 'L' (Lose)는 i+1번 복사가 j+1번 복서에게 졌음을 의미합니다.
- 임의의 i에 대해서
head2head[i][i]는 항상 'N'입니다. 자기 자신과 싸울 수는 없기 때문입니다. - 임의의 i, j에 대해서
head2head[i][j]= 'W' 이면,head2head[j][i]= 'L'입니다. - 임의의 i, j에 대해서
head2head[i][j]= 'L' 이면,head2head[j][i]= 'W'입니다. - 임의의 i, j에 대해서
head2head[i][j]= 'N' 이면,head2head[j][i]= 'N'입니다.
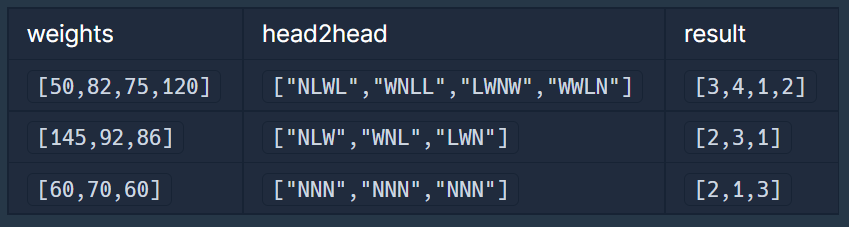
입출력 예 (설명은 생략)
소스코드
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] weights, String[] head2head) {
int[] answer = new int[weights.length];
List<Integer> boxerWeights = new ArrayList<>();
List<Info> infos = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < weights.length; i++) {
boxerWeights.add(weights[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < head2head.length; i++) { // i = 나(i)의 복싱 경기수
int winCount = 0;
int totalCount = 0;
int overWinCount = 0;
int weightMe = boxerWeights.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < head2head[i].length(); j++) { // j = 상대 선수와 경기
char round = head2head[i].charAt(j);
int weightYou = boxerWeights.get(j);
if (round == 'N' || i == j) continue;
if (round == 'W') {
winCount++;
if (weightMe < weightYou) {
overWinCount++;
}
}
totalCount++;
}
double winRate = (totalCount > 0) ? (double) winCount / totalCount : 0.0;
infos.add(new Info(new Boxer(i + 1, weightMe), winRate, overWinCount));
}
Collections.sort(infos);
for (int i = 0; i < answer.length; i++) {
answer[i] = infos.get(i).boxer.index;
}
return answer;
}
private static class Info implements Comparable<Info> {
Boxer boxer;
Double winRate;
int overWinCnt;
public Info(Boxer boxer, double winRate, int overWinCnt) {
this.boxer = boxer;
this.winRate = winRate;
this.overWinCnt = overWinCnt;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Info o) {
if (this.winRate.equals(o.winRate)) {
if (this.overWinCnt == o.overWinCnt) {
if (this.boxer.weight == o.boxer.weight) {
return this.boxer.index - o.boxer.index;
}
return o.boxer.weight - this.boxer.weight;
}
return o.overWinCnt - this.overWinCnt;
}
return o.winRate.compareTo(this.winRate);
}
}
private static class Boxer {
int index;
int weight;
public Boxer(int index, int weight) {
this.index = index;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
}
Comment
-
class를 여러개로 나누어 정보를 저장하고Comparable을 사용하여 정렬했다. -
double winRate = (totalCount > 0) ? (double) winCount / totalCount : 0.0;해당 라인과 같이 처리해주지 않으면totalCount가 없을 때, 오류가 난다. -
조금더 리팩토링할 수 있을 것 같다.
