ADsP
모의고사 풀기!

내일 배움캠프
오늘도 제공해주는 알고리즘 문제를 풀것이다.
Algorithm
문제 1.문자열 뒤집기
문제 설명
문자열 my_string이 매개변수로 주어집니다. my_string을 거꾸로 뒤집은 문자열을 return하도록 solution 함수를 완성해주세요.
제한사항
1 ≤ my_string의 길이 ≤ 1,000
class Solution {
public String solution(String my_string) {
return new StringBuilder(my_string).reverse().toString();
}
}자나 깨나 오타 조심.....StringBuilder 를 StringBulider 로 써서 에러를 내어 버렸다...
문제 2.가위 바위 보
문제 설명
가위는 2 바위는 0 보는 5로 표현합니다. 가위 바위 보를 내는 순서대로 나타낸 문자열 rsp가 매개변수로 주어질 때, rsp에 저장된 가위 바위 보를 모두 이기는 경우를 순서대로 나타낸 문자열을 return하도록 solution 함수를 완성해보세요.
제한사항
0 < rsp의 길이 ≤ 100
rsp와 길이가 같은 문자열을 return 합니다.
rsp는 숫자 0, 2, 5로 이루어져 있습니다.
class Solution {
public String solution(String rsp) {
StringBuilder answer = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : rsp.toCharArray()) {
switch (c) {
case '2':
answer.append('0');
break;
case '0':
answer.append('5');
break;
case '5':
answer.append('2');
break;
}
}
return answer.toString();
}
}
1.결과를 저장하기 위한 StringBuilder 객체 생성
2.현재 문자가 '2'(가위)일 경우 '0'(바위)를 결과에 추가
3.위와 같은 방법으로 '0', '5' 도 해줌
4.switch문을 종료
5.StringBuilder 객체를 문자열로 변환 후 반환
순서로 해주면 된다
이를 실행하기 위한 메인메소드로는
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 테스트 케이스
String rsp = "2052"; //입력 예
// Solution 객체 생성
Solution sol = new Solution();
// solution 메서드 호출
String result = sol.solution(rsp);
// 결과 출력
System.out.println("Input: " + rsp);
System.out.println("Output: " + result);
}
}
이렇게 두문제를 모두 풀어 보았다.

CSS
기본적인 CSS 를 위해 background-clip의 개념까지 알아볼것이다.
animation CSS
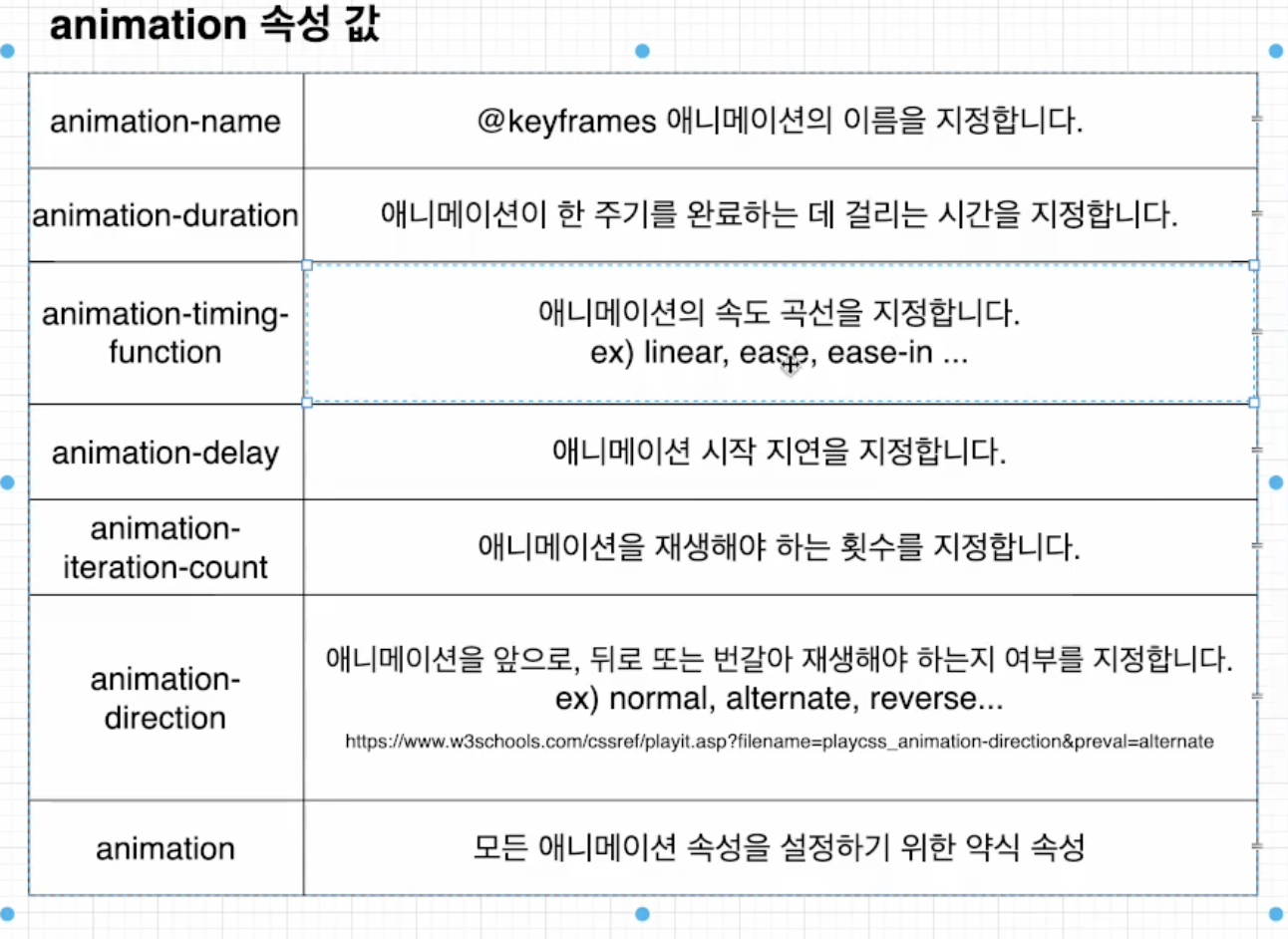
<style>
div {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
animation: animationName 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
}
@keyframes animationName {
0% {
background-color: lightblue;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
}
25% {
background-color: lightcoral;
left: 150px;
top: 0px;
}
50% {
background-color: lightcyan; left: 150px; top: 150px;
}
75% {
background-color: lightgray; left: 0px; top: 150px;
}
100% {
background-color: lightgreen; left: 0px; top: 0px;
}
}
</style>background-clip
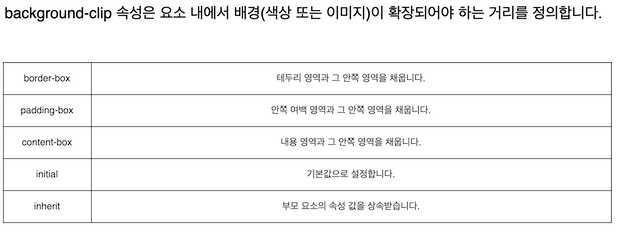
<head>
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#example1 {
border: 10px dotted black;
padding: 15px;
background-color: lightcoral;
background-clip: border-box;
}
#example2 {
border: 10px dotted black;
padding: 15px;
background-color: lightcoral;
background-clip: padding-box;
}
#example3 {
border: 10px dotted black;
padding: 15px;
background-color: lightcoral;
background-clip: content-box;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>background-clip: border-box (this is default):</p>
<div id="example1">
<p>The background extends behind the border.</p>
</div>
<p>background-clip: padding-box:</p>
<div id="example2">
<p>The background extends to the inside edge of the border.</p>
</div>
<p>background-clip: content-box:</p>
<div id="example3">
<p>The background extends to the edge of the content box.</p>
</div>
</body>
회고
CSS 의 기본과정까지는 마쳤는데 아 감이 안온다 큰일이다
자바꼴 나는건 아닌가 모르겠다.
실습만이 살길임을 느끼며 이해가 아닌 쀨륑이 필요하다
내 느낌을 찾아야지 가능할거같다!!!!

Java
복습을 최에에에대한 많이!
문자열 포메팅과 null
| %b | 불리언 |
|---|---|
| %d | 10진수 정수 |
| %f | 실수 |
| %c | 문자 |
| %s | 문자열 |
| %n | (포맷 문자열 내 바꿈) |
- 더 자세한 내용은 문서를 확인할 것
// ⭐️ 시스템의 printf 메소드 : String.format과 같은 형식으로 출력
// 줄바꿈을 하지 않으므로 직접 넣어줘야 함
System.out.printf("%s의 둘레는 반지름 X %d X %f입니다.%n", circle, two, PI);printf를 사용하니 유의할것
- ⭐️
%n은 OS별로 일정하게 줄바꿈이 되도록 적절한 개행문자를 넣어줌- 맥&리눅스 :
\n
- 맥&리눅스 :
// 💡 정수 다양하게 포매팅하기
String[] intFormats = {
"%d", // 1. 기본
"%13d", // 2. n 자리수 확보, 오른쪽 정렬
"%013d", // 3. 빈 자리수 0으로 채움
"%+13d", // 4. 양수는 앞에 + 붙임
"%,13d", // 5. 쉼표 사용
"%-13d", // 6. 자리수 확보, 왼쪽 정렬
"%+,013d" // 7.
};
// 💡 실수 다양하게 포매팅하기
String[] fltFormats = {
"%f", // 1. 기본 (소수점 6자리, 0으로 메움)
"%.2f", // 2. 소수점 n자리까지
"%13.2f", // 3. 정수자리 확보, 소수자리 제한
"%,f", // 4.정수부분이 길면
"%+013.2f", // 5.
"%-13.2f", // 6
};
null 문자열
String emptyStr = "";
String nullStr = null;
// ⭐️ 빈 문자열과 null은 다름
boolean bool1 = emptyStr == nullStr;
// ⚠️ null은 문자열 인스턴스 메소드 사용 불가
// 아래의 코드들은 모두 런타임 에러를 발생시킴
// int int1 = nullStr.length();
//boolean bool2 = nullStr.equals(emptyStr);
//String str1 = nullStr.concat("ABC");-
빈 문자열 (길이가 0) : 힙 공간에 자리를 차지
-
null문자열 : 힙에 할당되지 않음, 가리키는 곳이 없음배열!!!!!!!!!!!!!(중요:물론 리스트전에...)
-
특정 타입의 데이터를 묶음으로 다루기 위해 사용
-
지정된 자료형과 개수만큼 메모리 공간을 나란히 확보
- ⚠️ 개수의 변경이 불가능함
-
각각이 담는 자료형의 크기만큼 요소당 메모리 차지
-
💡 문자열의 경우: 각 문자열이 저장된 주소값을 담음
- JVM마다 4바이트 또는 8바이트 등 달라짐
// 이중 배열
boolean[][] dblBoolAry = new boolean[3][3];
int[][] dblIntAry = new int[][] {
// ⭐️ 요소 배열의 크기가 다를 수 있음
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5},
{6, 7, 8, 9},
};
// 삼중 배열
char[][][] trpChrAry = {
{{'자', '축'}, {'인', '묘'}},
{{'진', '사'}, {'오', '미'}},
{{'신', '유'}, {'술', '해'}},
};타입추론 (java10 이후)
- Java 10 에서 도입됨
var연산자로 변수 선언 - 타입을 명시하지 않음- 대입된 값을 통해 컴파일러가 추론
- 지역 변수에서만 사용 가능
드디어 챕터3 복습 끝 이제 메인 이벤트...제어문 메소드 복습....
제어문과 메소드
If/else
주어진 boolean 값에 따라 명령문 실행 여부를 결정
boolean open = true;
int saleFrom = 10, saleTo = 20;
int today = 15;
// 💡 if : 괄호 안의 boolean 값이 true면 다음 명령 실행
if (open) System.out.println("영업중");
if (!open) System.out.println("영업종료");
// 💡 실행할 명령이 한 줄 이상일 경우 블록 사용
if (today >= saleFrom && today <= saleTo) {
System.out.println("세일중입니다.");
System.out.println("전품목 20% 할인");
} // 💡 else : if문 안의 boolean 값이 false일 경우 실행
if (open) {
System.out.println("영업중");
} else {
System.out.println("영업종료");
}else if 를 이용해주는 것도 좋지만
전반적으로 가독성을 늘리기위해서 하나의 if문과 return을 이용해서 가독성을 높혀주는것도
좋은 방법!!!!!!!!!!
swich
💡 switch : 괄호 안에 기준이 될 변수를 받음
가능한 자료형: byte, short, int, char, String, enum(이후 배움)
if 문으로 사용하면 몹시 복잡하고 까다롭고 보기도 힘든것들을 표기하기에 좋음
for/foreach(이놈때문에 복습...젤 헷갈림)

- 실행 과정
- 루프 안에서 사용할 변수 초기화
- 루프를 실행하기 위한 조건 확인
- 조건을 충족시 실행할 내용
- 각 루프가 끝날때마다 이행할 내용
- 1번 이후 2를 충족할 동안 2~4 반복
- 변수명은 원하는대로 사용 가능
- 일반적으로 기본형에는
i를 많이 사용 - 문맥에 따라 index를 뜻함
- 일반적으로 기본형에는
// 종료조건이 없는 for 루프
for (;;) {
System.out.println("영원히");
}
System.out.println("닿지 않아"); // ⚠️ 실행되지 않음 // 종료조건을 만족시키지 못하는 무한루프
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("그래도");
i--;
}
System.out.println("닿지 않아"); // ⚠️ 실행되지 않음- 무한루프는 프로그램을 정지시킴
System.out.println("\n- - - - -\n");
int sumOfArray = 0;
for (int num : multiOf4) {
sumOfArray += num;
}- 배열의 특정 개수만 사용할 때는
for문, 전부 사용할 때는foreach문
후....for 문이 이해되지 않았다....
정확히 말하면 예시에서 나오는것이 이해되지않았다.
// 4의 배수 차례로 10개 배열에 담기
int count = 10;
int[] multiOf4 = new int[count];
for (int i = 1, c = 0; c < count; i++) {
if (i % 4 == 0) {
multiOf4[c++] = i;
}
}이것이였는데 왜 i 와 c 를 둘다 써야할지를 몰랐다 그래서 하나만 쓰는방식으로 바꿔보기로했다
int count = 10;
int[] multiOf4 = new int[count];
//카운트 갯수 즉 배열의 갯수는 같을 것이니까!
int num = 4 //그저 첫 수만 지정해주면 되는것을.....
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++){
multiOf4[i] = num;//4가 처음에 들어가고 0번쨰니까 [4]의 시작이된다
num += 4 //거기에 그저 4를 더해주고 1번째 인덱스값이니 [8]!!!!
//4의 배수 배열 완성....break, continue
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// 💡 continue : 한 루프만 건너뜀
if (i % 3 == 0) continue;
// 💡 break : 블록 전체를 종료
if (i == 10) break;
System.out.println(i);
}회고
for문을 했는데도 아직 난 이해가 가질않는다
닥치고 외워야하는걸까? 그냥 for문이란 이런것이다 라고 해야하는걸까
툭 치면 나오는 그런상태여야만 이해가갈까 모르겠다.
그래도 복습을 하니 도움이 되기는 한다.

