이벤트(event)
-
브라우저에서의 이벤트란
사용자가 클릭을 했을 '때', 스크롤을 했을 '때', 필드의 내용을 바꾸었을 '때'와 같은 것을 의미하며 브라우저는 이를 감지하고 알려주어 사용자와 브라우저 간에 interaction을 할 수 있게 한다.- 브라우저에서 이벤트를 감지하기 위해서는
이벤트 리스너를 사용한다.
- 브라우저에서 이벤트를 감지하기 위해서는
document.querySelector('.myButton').addEventListener('click', function () {
alert('Clicked!');
});-
위에는
click이라는 이벤트가 발생시이벤트 핸들러 function () { ... }가 처리를 하는이벤트 리스너를 정의한 코드이다. -
위의 addEventListener와 DOM 이벤트들은 setTimeout 와 같은 방식으로 동작한다.
-
그 밖에 더 많은 이벤트는 이벤트 종류에서 확인 할 수 있다.
이벤트 핸들러 등록 방식과 this
1) inline
HTML 요소의 이벤트 핸들러 속성(attribute)에 이벤트 핸들러를 등록하는 방식
<input type='button' onclick='fn()' value='button' />
<script>
function fn () {
alert('Hello world');
console.log(this);
}
</script>
/* Angular/React/Vue.js와 같은 프레임워크/라이브러리에서는
동일한 관심사로 생각하여 분리하지 않고
인라인 이벤트 핸들러 방식으로 이벤트를 처리한다고 한다. */❓ 참조
inline방식은 일반 함수로서 호출되므로 이벤트 핸들러 내부의this는 전역 객체 window를 가리킨다.
2) Property Listener
이벤트 대상에 해당하는 객체의 프로퍼티로 이벤트를 등록하는 방식
<input type='button' id='target' value='button' />
<script>
const element = document.getElementById('target');
element.onclick = function(){
alert('Hello world 1');
}
element.onclick = function(){
alert('Hello world 2');
console.log(this);
}
/* Hello world 1는 실행되지 않는다.*/
</script>❓ 참조
Property Listener방식은 메소드이므로this는 이벤트에 바인딩된 요소를 가리킨다.
❓ 참조
Attribute와 Property
HTML의 속성은 Attribute CSS의 속성은 Property라고 배웠는데
문서를 보면 HTML에서도 Property를 쓸 때가 있다 .
이는attribute는 html 문서 안에서의 정적인(바뀌지 않는) 속성 그 자체를 의미하고,property는 html DOM 안에서 동적인(바뀌는) 속성을 의미한다.
3) addEventListener( )
-
이벤트 핸들러를 등록하는 가장 권장하는 방식
-
2)와 다르게 여러개의 이벤트 핸들러를 등록할 수 있다.
<input type='button' id='target' value='button' />
<script>
const element = document.getElementById('target');
element.addEventListener('click', function () {
alert('Hello world 1');
console.log(this);
});
element.addEventListener('click', function () {
alert('Hello world 2');
});
/* Hello world 1와 Hello world 2가 정상적으로 실행된다.*/
</script>❓ 참조
addEventListener 메소드에 지정한 이벤트 핸들러 내부의this는 이벤트리스너에 바인딩된 요소를 가리킨다.
Event 예제
회원가입 할 때의 예제를 들어보자.
- 아래 코드는 addEventListener( )를 이용하여
input tag에 글자를 입력할 때마다 이벤트를 발생시키는 코드로 입력한 글자가 2글자 미만일 때 메시지를 출력해준다.
📝코드
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<label for='your-name'>이름:
<input type='text' id='your-name'>
<p class='message'></p>
</label>
<script>
const input = document.querySelector('input[type=text]');
const message = document.querySelector('.message');
input.addEventListener('input', function () {
if(input.value.length < 2){
message.innerHTML='2글자 이상 입력해주세요.';
message.style.color='red';
} else {
message.innerHTML='';
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>💻결과


이벤트 객체
이벤트가 발생하면 이벤트 객체는 동적으로 생성되며 이벤트를 처리할 수 있는 이벤트 핸들러의 parameter로 전달된다.
addEventListener('click', function (e) { // 해당 e가 event obejct
console.log(e);
});parameter로 전달된 이벤트 객체(Event Object)는 객체이므로 다양한 Property와 method를 가지고 있다. 해당 내용은 Event Object에서 확인 할 수 있다.
그 중에서 대표적으로 사용되는 target과 currentTarget을 알아보자.
1) currentTarget
MDN 문서에 따르면 It always refers to the element to which the event handler has been attached 즉, event handler가 붙여진 요소를 참조한다고 한다.
2) target
반면에 target은 실제로 이벤트를 발생시킨 요소를 참조한다.
다음의 예제를 통해서 살펴보자.
📝코드
<button id='target'>
<span style='background-color: red;'>Hello</span>
</button>
<script>
const element = document.getElementById('target');
element.addEventListener('click', function(event){
console.log(event.currentTarget);
console.log(event.target);
});
</script>💻결과
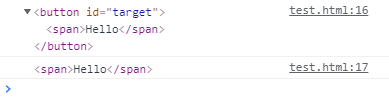
event handler가 붙여진 요소는 button 이였기 때문에 event.currentTarget은 부모 요소인 button을 반환하며,
여기서 우리는 span을 눌러 이벤트를 발생 시켰기 때문에 event.target은 자식 요소인 span을 반환하는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.