오늘은 노마드코더 ReactJS 스터디 다섯 번째 날입니다! 오늘도 화이탱!
#4.0 (Props)
props is a way of sending data from a parent component to a child component
not a good way - as you are copying and pasting the same thing, better to have the same component and change only the text in the button
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17.0.2/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17.0.2/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
function SaveBtn(){
return <button style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
}}>Save Changes</button>
}
function ConfirmBtn(){
return <button style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
}}>Confirm</button>
}
function App(){
return(
<div>
<SaveBtn />
<ConfirmBtn />
</div>
);
};
const root = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, root);
</script>
</html>use the same function but configure only the text
rending would mean Btn({banana:"Save Changes"})
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17.0.2/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17.0.2/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
//props is the property given to the button
//whatever props you send to the Btn component will be put in the first argument of the Btn function
// == props will go into the object and will be given in the first argument to the component
function Btn(props){
return <button style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
}}>{props.banana}</button>
}
function App(){
return(
//value of the banana will be "save changes" and "continue"
<div>
<Btn banana="Save Changes" />
<Btn banana="Continue" />
</div>
);
};
const root = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, root);
</script>
</html>don't use props that much --> following is the same code from above without using props as an argument
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17.0.2/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17.0.2/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
//props is the property given to the button
//whatever props you send to the Btn component will be put in the first arguement of the Btn function
// == props will go into the object and will be given in the first arguement to the component
function Btn({banana}){
return <button style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
}}>{banana}</button>
}
function App(){
return(
//value of the banana will be "save changes" and "continue"
<div>
<Btn banana="Save Changes" />
<Btn banana="Continue" />
</div>
);
};
const root = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, root);
</script>
</html>we can add more argument in the object
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17.0.2/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17.0.2/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
//props is the property given to the button
//whatever props you send to the Btn component will be put in the first arguement of the Btn function
// == props will go into the object and will be given in the first arguement to the component
function Btn({banana, big}){
return <button style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
fontSize: big ? 18 : 15,
}}>{banana}</button>
}
function App(){
return(
//value of the banana will be "save changes" and "continue"
<div>
<Btn banana="Save Changes" big={true} />
<Btn banana="Continue" />
</div>
);
};
const root = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, root);
</script>
</html>#4.1 (Memo)
using React.useState to change the content of the button
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17.0.2/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17.0.2/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
//props is the property given to the button
//whatever props you send to the Btn component will be put in the first arguement of the Btn function
// == props will go into the object and will be given in the first arguement to the component
function Btn({banana, onClick1}){
return <button
onClick={onClick1}
style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
}}>{banana}</button>
}
function App(){
const [value, setValue] = React.useState("Save Changes");
const changeValue = () => setValue("Revert Changes");
return(
//if I put onClick in the function Btn, then it is an eventlistern, the onClick in the custom component Btn/ is not an eventlistener, this is just a prop even though the name might be the same
<div>
<Btn banana={value} onClick1={changeValue}/>
<Btn banana="Continue" />
</div>
);
};
const root = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, root);
</script>
</html>we don't want to re-render if the prop doesn't change
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17.0.2/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17.0.2/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
//props is the property given to the button
//whatever props you send to the Btn component will be put in the first arguement of the Btn function
// == props will go into the object and will be given in the first arguement to the component
function Btn({banana, onClick1}){
console.log(banana,"was rendering")
return <button
onClick={onClick1}
style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
}}>{banana}</button>
}
const MemorizedBtn = React.memo(Btn)
function App(){
const [value, setValue] = React.useState("Save Changes");
const changeValue = () => setValue("Revert Changes");
return(
//if I put onClick in the function Btn, then it is an eventlistern, the onClick in the custom component Btn/ is not an eventlistener, this is just a prop even though the name might be the same
<div>
<MemorizedBtn banana={value} onClick1={changeValue}/>
<MemorizedBtn banana="Continue" />
</div>
);
};
const root = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, root);
</script>
</html>output change from
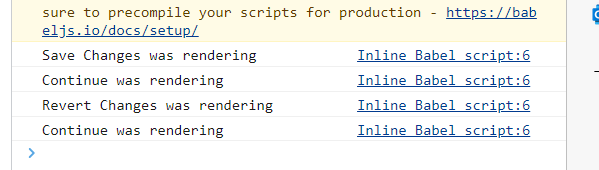
to
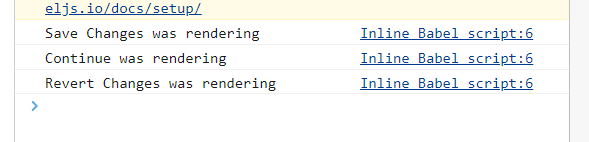
#4.2 (Prop Types)
using 'propTypes' to define the proptypes
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17.0.2/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17.0.2/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/prop-types@15.7.2/prop-types.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
function Btn({banana, fontSize}){
return <button
style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
fontSize,
}}>{banana}</button>
}
Btn.propTypes = {
banana: PropTypes.string,
fontSize: PropTypes.number,
}
function App(){
return(
<div>
<Btn banana="Save changes" fontSize={18} />
<Btn banana={14} fontSize={"Continue"} />
</div>
);
};
const root = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, root);
</script>
</html>output : we see an error in the console as fontSize for the second Btn is not a number and banana is not a string (UI works find)
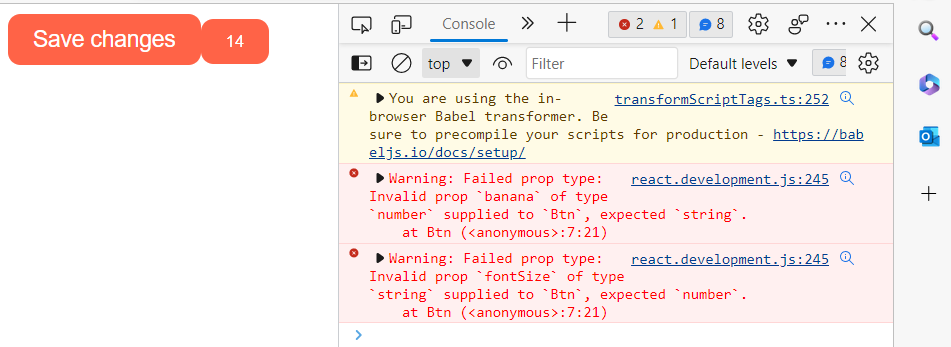
giving values to the ones that are not defined
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@17.0.2/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@17.0.2/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/prop-types@15.7.2/prop-types.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone/babel.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel">
//you can give default values if it is not defined (ex. fontSize)
function Btn({banana, fontSize=5}){
return <button
style={{
backgroundColor: "tomato",
color:"white",
padding: "10px 20px",
border: 0,
borderRadius: 10,
fontSize,
}}>{banana}</button>
}
Btn.propTypes = {
banana: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
fontSize: PropTypes.number.isRequired,
}
function App(){
return(
<div>
<Btn banana="Save changes" fontSize={18} />
<Btn banana="Font size is 5" />
</div>
);
};
const root = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, root);
</script>
</html>#5.0 (Create React App Introduction)
- node js 사용자 버전 설치
- 윈도우키 + R 누르면 실행창 뜸
3 .열기 칸에 cmd 라고 입력하고 확인 (혹은 command prompt 열기) - 나오는 창에 node -v 입력해서 잘 설치됐는지 확인
- vscode 상단 메뉴에서 Terminal - New Terminal 클릭
- npm start하면 window에 새로운 창이 자동으로 뜸
- 자동으로 설치되었던 src 폴더에 모든 파일을 저장할 것 --> 가장 중요한 것은 index.js
#5.1 (Tour of CRA)
first option of applying button color is making a css file and importing that css file in index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import App from './App';
import "./styles.css";
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>
);style.css file
button {
color: white;
background-color: tomato;
}if we import the css that will be applied to all the buttons in every file
option 2 - we cound manually include the style in javascript code
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
function Button({text}) {
return <button style={{
backgroundColor:"tomato",
color:"white",
}}>{text}</button>;
}
Button.propTypes= {
text: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
};
export default Button;option 3 - the best option is to make a module.css and import styles in the javacript, create a class, and apply the style
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
import styles from "./Button.module.css";
function Button({text}) {
return <button className={styles.btn}>{text}</button>;
}
Button.propTypes= {
text: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
};
export default Button;css file would have a class and the css file name will be Button.module.css
.btn {
color: white;
background-color: tomato;
}making another css file named App.module.css (the name doesn't matter however needs to end with .module.css)
.title{
font-family: Impact, Haettenschweiler, 'Arial Narrow Bold', sans-serif;
font-size: 18px;
}App.js would contain the classname as styles.whateverclassname
import Button from "./Button";
import styles from "./App.module.css";
function App() {
return (
<div><h1 className={styles.title}>Welcome back!!!</h1>
<Button text={"Continue"} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;the output

