GDG on Campus Backend-Spring 스터디 WIL
Week 04 - 관점 지향 프로그래밍(AoP) 및 커스텀 어노테이션
1. AOP(Aspect Oriented Programmig)
개념
횡단 관심사를 핵심 비즈니스 로직에서 분리하여 모듈성을 향상시키는 프로그래밍 패러다임
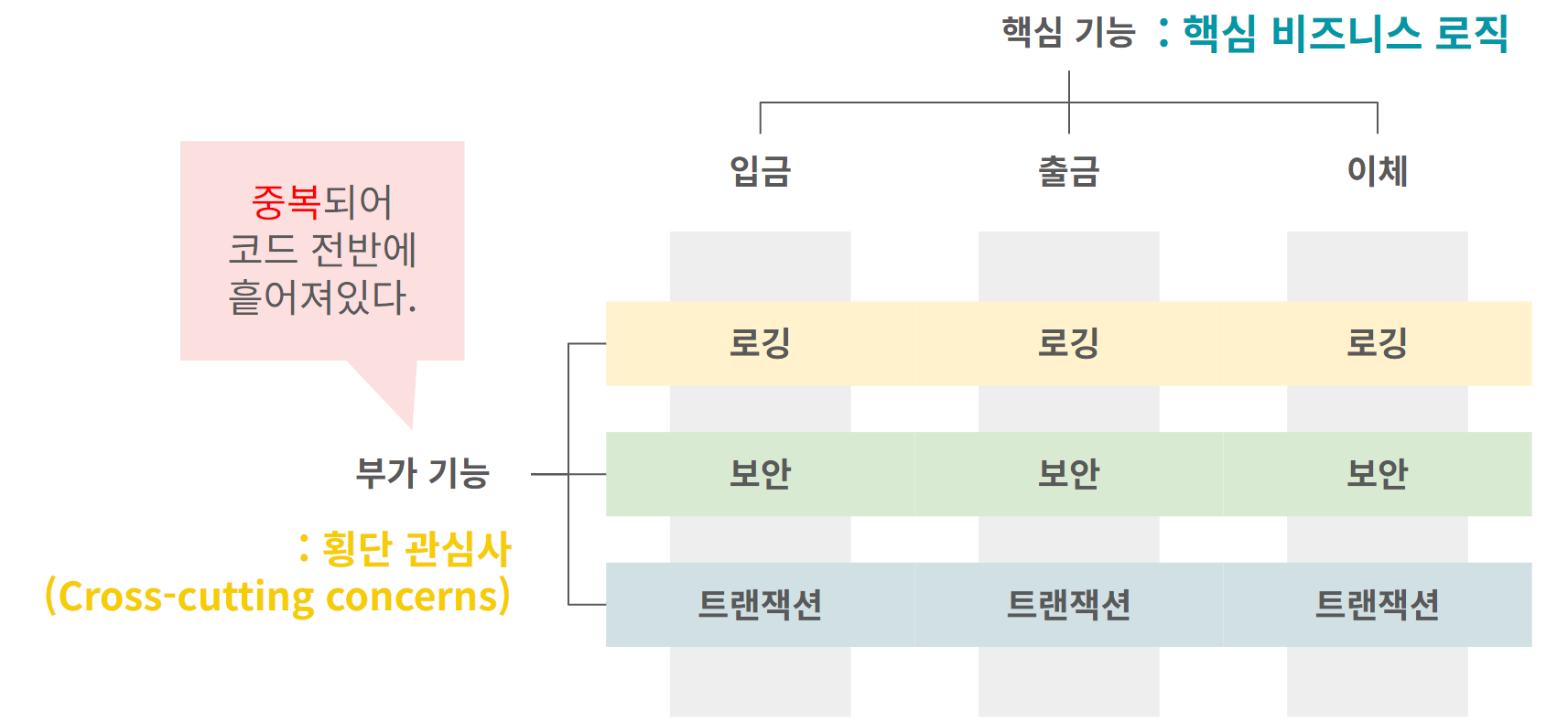
*횡단 관심사(cross-cutting concern): 여러 핵짐 비즈니스 로직에 중복되어 동작하는 부가 기능
애플리케이션은 핵심기능과 부가기능으로 이루어져 있다. 이때, 부가기능은 여러 핵심기능에서 중복적으로 동작한다. 부가기능이 전체 코드에 중복되어 흩어져있기 때문에, 코드를 유지보수 하기 힘들고, 저장공간이 낭비된다.
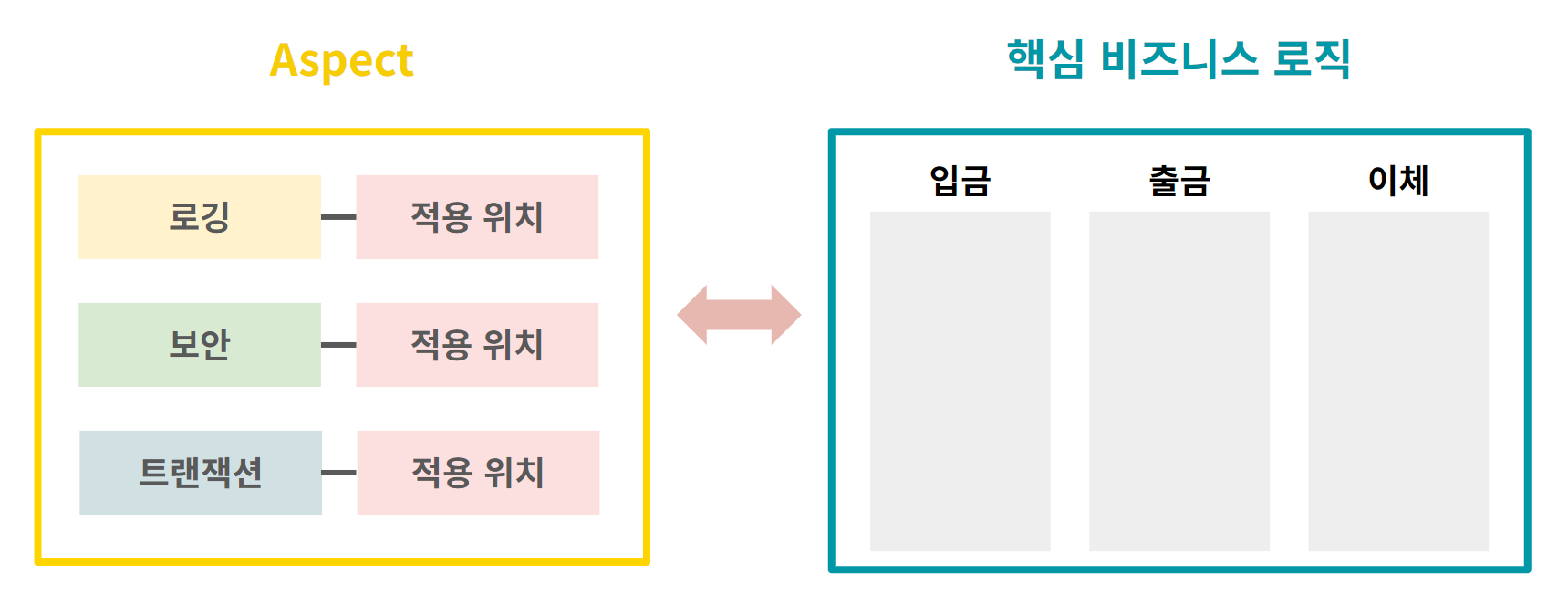
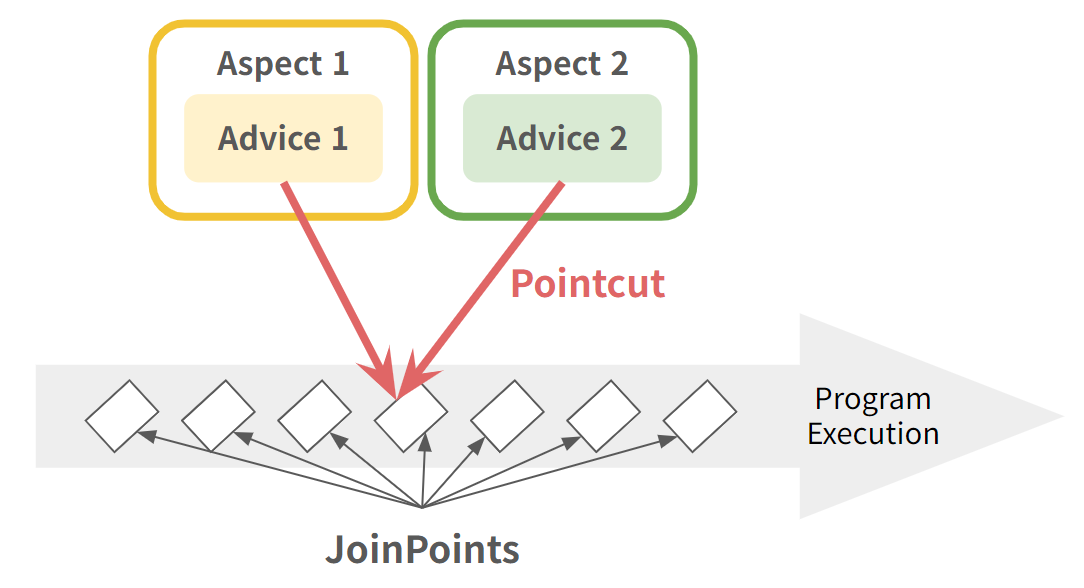
따라서 AOP는 부가기능을 Aspect라는 특별한 객체로 모듈화하여 핵심 기능에서 분리하는 것을 목표로 한다. Aspect 객체에는 부가기능(Advice)과, 그 부가기능이 적용될 위치(PointCut)이 정의되어 있다.
AOP는 OOP를 보완하는 프로그래밍 패러다임이다.
- OOP에서는 애플리케이션을 Class로 모듈화한다. 이때 Class들에 중복되는 부가 기능이 생기기 때문에, AOP에서 이런 중복되는 부가 기능들을 Aspect단위로 모듈화하는 것이다.
프로그래밍 패러다임이기 때문에, 프로그래밍 언어마다 구현체가 있다. Spring에서는 Spring AOP로 구현한다.
대표적인 Aspect는 인증/인가, 로깅, 트랜잭션 처리, 에러 처리 등이 있다.
용어
*이 용어들은 Spring-specific 용어가 아니라 AOP에서 통용되는 용어이다.
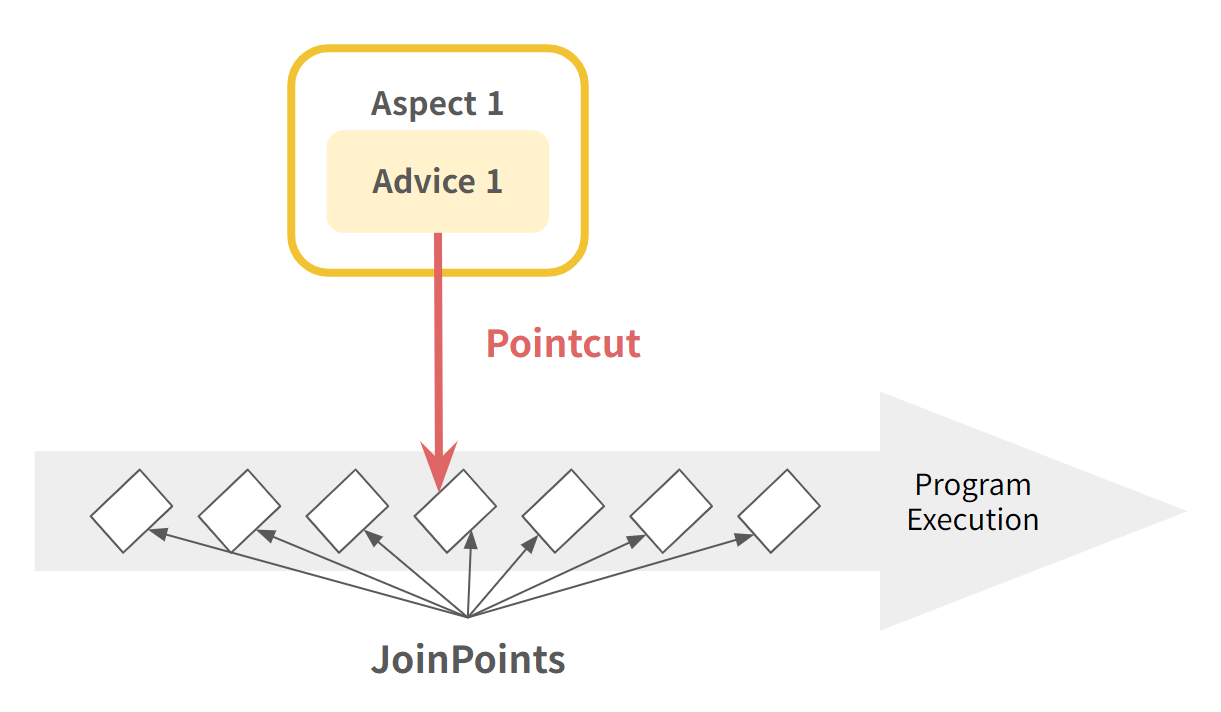
Aspect
- 여러 클래스에 공통적으로 있는 부가기능을 모듈화한 것
- Advice(What & When) + PointCut(Where)
JoinPoint
- 프로그램 실행 중의 한 지점. 메서드 실행, 생성자 호출 시점 또는 예외 처리 등이 될 수 있다.
- Advice가 적용될 수 있는 지점
- Spring에서는 항상 메서드 실행시점이다.
Advice
특정 JoinPoint에서 Aspect가 수행하는 부가기능
What&When
PointCut
- 어떤 JoinPoint에 Advice를 적용할지 결정하는 기준.
- 클래스 이름/메서드 이름/파라미터 등으로 정의할 수 있다.
Target Object
- Aspect가 적용될(advised) 객체. Advised Object라고도 한다.
- 클래스/메소드가 될 수 있다.
- Spring에서는 항상 프록시 객체이다.
Weaving
- PointCut에 의해 결정된 Target의 JoinPoint에 Advice(부가기능)을 삽입하는 과정
- types: 컴파일 타임, 로드 타임, 런타임 위빙
- Spring AOP에서는 런타임 위빙만 사용한다.
Spring AOP
Spring AOP vs AspectJ
Spring AOP와 AspectJ는 목적이 다르다. Spring AOP는 간단한 AOP 기능 제공을 목적으로 하고, AspectJ는 완전한 AOP를 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다.
| Spring AOP | AspectJ | |
|---|---|---|
| JoinPoint | 메서드 레벨만 지원 | 생성자, 필드 메서드 등 다양한 레벨 지원 |
| Weaving | runtime weaving만 제공 | compile-time, post-compile, load-time 제공 |
| 대상 | Spring Container가 관리하는 Bean에만 가능 | 모든 Java Object에 가능 |
| 속도 | AspectJ에 비해 훨씬 느리다. | Spring AOP에 비해 훨씬 빠르다. |
-
Spring AOP은 XML 스타일 또는
@AspectJannotation 스타일로 Aspect를 구현할 수 있다. -
Spring AOP를 사용하려면
build.gradle에 의존성을 추가해야 한다.dependencies { implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop' }
@AspectJ in Spring AOP
@AspectJ 란?
Annotation을 사용하여 일반 Java Class로 Aspect를 선언하는 방식.
Spring은 AspectJ 5와 같은 어노테이션을 지원한다. 하지만 실제 애플리케이션의 AOP 실행은 여전히 Spring AOP가 처리한다. 즉, Spring Container가 AOP 기능을 수행한다.
docs.spring.io
-
@AspectJ지원 활성화@Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class AppConfig { }@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
Spring이 AOP 프록시를 사용하여 Aspect를 적용할 수 있도록 한다. -
Aspect 선언
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; @Component @Aspect public class NotVeryUsefulAspect { }@Component
Spring AOP는 Bean(@Component, @Bean)으로 등록된 객체만 Aspect로 만들 수 있기 때문에@Component어노테이션을 붙여준다. -
PointCut 선언
@Pointcut("execution(* transfer(..))") // the pointcut expression private void anyOldTransfer() {} // the pointcut signature -
Advice 선언
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; @Aspect public class BeforeExample { @Before("execution(* com.xyz.dao.*.*(..))") public void doAccessCheck() { // ... } }// 정의된 PointCut 사용할 경우 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; @Aspect public class BeforeExample { // dataAccessOperation() PointCut 사용 @Before("com.xyz.CommonPointcuts.dataAccessOperation()") public void doAccessCheck() { // ... } }
프록시
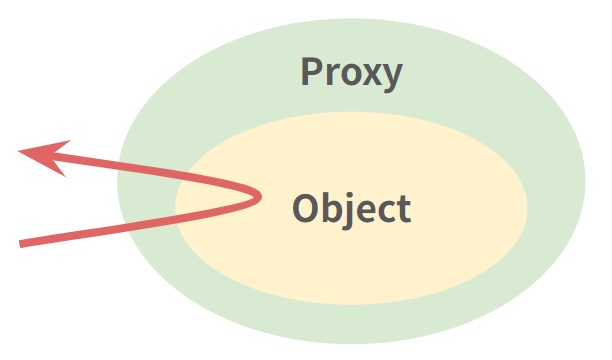
Spring AOP는 Proxy를 기반으로 한다.
Spring AOP는 기존 코드를 수정하지 않고 부가 기능을 추가하기 위해 프록시를 이용한다.
프록시 객체는 원본 객체를 감싸고 있는 객체이다. 스프링 Container는 AOP가 적용된 객체를 프록시 객체로 생성한다. 따라서 클라이언트가 프록시 객체를 호출할 때, 프록시 객체가 원본 객체를 감싸고 부가적인 로직을 수행한다.
Spring은 두가지 방식을 통해 AOP를 제공한다.
- JDK dynamic Proxy : Java 내부에 구현되어있는 Proxy
- CGLIB Proxy : Open source로 구현되어있는 Proxy
Aspect Ordering
만약 동일한 JoinPoint에 여러 개의 Advice가 적용된다면?
우리가 원하는 순서대로 Aspect들이 수행되지 않을 수 있다. 예를 들어, 로깅과 보안이 같은 JoinPoint에 적용될 때, 로깅이 먼저 적용되어야 하는데, 이 순서가 지켜지지 않을 수 있다.
따라서 Aspect들의 순서(우선순위)를 지정해주어야 한다.
Aspect Ordering에는 두가지 방법이 있다.
-
@Order어노테이션@Aspect @Order(1) @Component public class MyAspect1 { // Executes first } @Aspect @Order(2) @Component public class MyAspect2 { // Executes later } -
Ordered인터페이스import org.springframework.core.Ordered; @Aspect @Component public class MyAspect1 implements Ordered { @Override public int getOrder() { return 1; } // Executes first } @Aspect @Component public class MyAspect2 implements Ordered { @Override public int getOrder() { return 2; } // Executes later }
AOP의 장점
-
코드의 재사용성, 모듈성, 가독성, 유지보수성 향상
-
개발자는 핵심 비즈니스 로직에 더 집중할 수 있음
2. Custom Annotation
Annotation
코드 사이에 주석처럼 쓰이면서 특별한 의미, 기능을 수행하도록 하는 기술로, 프로그램에게 추가적인 정보를 제공해주는 메타데이터
용도
- 컴파일러에게 코드 작성 문법 에러를 체크하도록 정보를 제공한다.
- 소프트웨어 개발툴이 빌드나 배치 시 코드를 자동으로 생성할 수 있도록 정보를 제공한다.
- 런타임 시 특정 기능을 실행하도록 정보를 제공한다.
Spring에서 제공되는 대부분의 어노테이션은 3번, 런타임 시 특정 기능을 실행하도록 정보를 제공하는 용도로 사용되고 있다.
Custom Annotation
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Indexed
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}-
@interface타입으로 커스텀 어노테이션 정의 -
메타 어노테이션 추가
메타 어노테이션: 다른 어노테이션에 적용되기 위한 어노테이션
@Target@Retention@Documented@Inherited@Indexed
Custom Annotation 기반 AOP
-
build.gradledependency 추가dependencies { implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop' } -
Custom Annotation 작성
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface LogExecutionTime{ } -
Aspect 생성
@Aspect @Component public class ExampleAspect { @Around("@annotation(LogExecutionTime)") public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed(); long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; logger.info("{} executed in {}ms", joinPoint.getSignature(), executionTime); return proceed; } }PointCut, Advice 작성
💡 Custom Annotation기반 AOP를 사용하는 이유
@Around("@annotation(LogExecutionTime)")
이렇게 간단하게 어노테이션만 지정해주고, 적용하기를 원하는 클래스에 해당 어노테이션을 붙여주면 된다. -
클래스에 적용
public class SampleClass { @LogExecutionTime public void serve() throws InterruptedException{ Thread.sleep(2000); } }
