GDG on Campus Backend-Spring 스터디 WIL
Week 05 - 스프링 MVC 및 RESTful 웹 서비스
1. 스프링 MVC
Spring Web MVC is the original web framework built on the Servlet API and has been included in the Spring Framework from the very beginning.
Servlet API를 기반으로 클라이언트의 요청을 처리하는 웹 프레임워크
MVC 패턴을 따른다.
Servlet
Java Servlets are the Java programs that run on the Java-enabled web server or application server. They are used to handle the request obtained from the web server, process the request, produce the response, and then send a response back to the web server.
geeksforgeeks.org
- 자바를 사용하여 웹을 만들기 위해 필요한 기술
- 클라이언트의 요청에 대한 결과를 반환해주기 위한 자바 프로그램
- Spring MVC 내부에서는 서블릿을 기반으로 웹 애플리케이션을 동작하며, 스프링 부트는 기본적으로 Apache Tomcat이 내장되어 있다. ittrue.tistory.com
DispatcherServlet
Front controller that manages the entire HTTP request and response handling process
geeksforgeeks.org
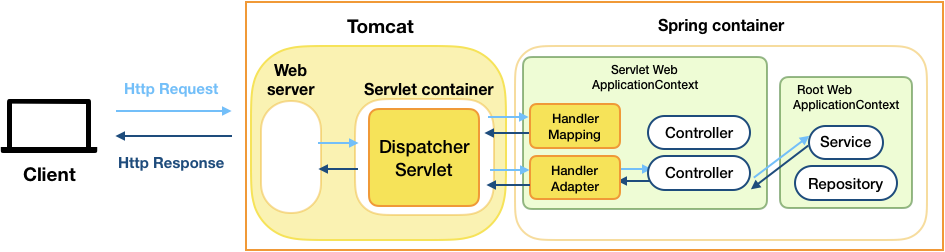
Spring에 내장되어있는 Tomcat의 DispatcherServlet이 모든 Request를 인터셉트한다. Handler Mapping을 조회하여 적합한 Controller를 결정하여 전달한다.
taes-k.github.io
View Resolver
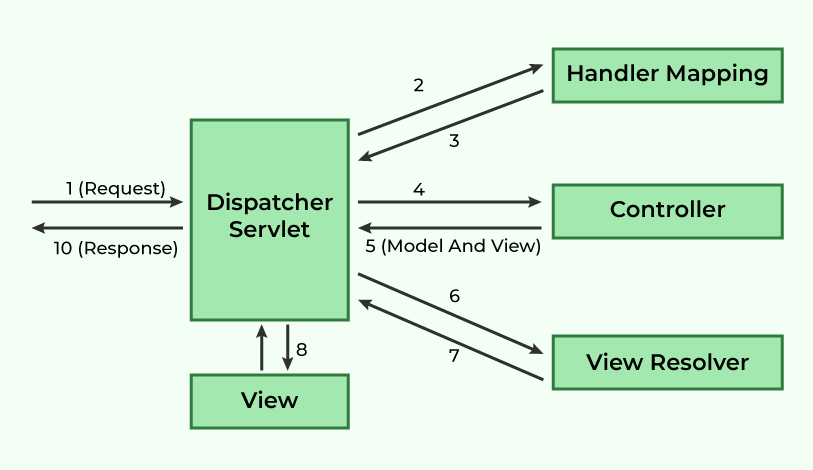
Spring MVC에서 Controller는 요청을 처리하고 필요한 데이터를 준비한 뒤, 결과를 나타내기 위해 뷰 이름을 반환한다. DispatcherServlet은 뷰 이름을 기반으로 적합한 view(뷰 객체)를 찾기 위해 ViewResolver를 사용한다.
ViewResolver는 뷰 이름과 실제 뷰를 매핑하여 적합한 뷰를 생성하고 반환한다. 다양한 뷰를 지원하기 위해 여러 ViewResolver를 지원하며 JSP, Thymeleaf 등 다양한 템플릿 엔진이 있다.
Thymeleaf ViewResolver 설정
-
의존성 추가
dependencies { implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf' implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web' } -
템플릿 파일 경로 설정
Spring Boot는 기본적으로src/main/resources/templates폴더에서 Thymeleaf 템플릿 파일을 찾는다. 설정이 따로 필요한 경우,application.yaml파일에 다음과 같은 설정을 추가한다.spring: thymeleaf: prefix: classpath:/custom-templates/ suffix: .html -
매핑
@Controller public class HelloController { @GetMapping("hello") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("data", "hello!!"); return "hello"; // 설정한 path 안의 hello.html로 변환 } }
RESTful 웹 서비스 설계
REST(Representational State Transfer)
-
웹을 위해 만들어진 software architectural style
-
네트워크 상에서 Client와 Server 사이의 통신 방식 중 하나
-
자원의 표현에 의한 상태 전달
자원을 자원의 표현(자원을 표현하기 위한 이름)으로 구분하여, 상태를 전달(JSON/XML)하는 모든 것을 의미한다. -
자원 기반의 구조(ROA, Resource Oriented Architecture)
설계의 중심에 Resource가 있고 HTTP Method를 통해 Resource를 처리하도록 설계된 아키텍쳐
구체적 의미
HTTP URI(Uniform Resource Identifier)를 통해 자원(Resource)을 명시하고, HTTP Method(POST, GET, PUT, DELETE)를 통해 해당 자원에 대한 CRUD Operation을 적용하는 것을 의미한다.
- 웹 사이트의 이미지, 텍스트, DB 내용 등의 모든 자원에 고유한 ID인 HTTP URI를 부여한다.
- CRUD Operation
Create생성(POST)
Read : 조회(GET)
Update : 수정(PUT)
Delete : 삭제(DELETE)
HEAD: header 정보 조회(HEAD)
hahahoho5915.tistory.com
REST 구성 요소
자원(Resource) : HTTP URI
행위(Verb) : HTTP Method
표현(Representations of Resource) : HTTP Message Payload(JSON, XML)
REST 설계 원칙
1. Client-Server Architecture(클라이언트-서버 구조)
2. Stateless(무상태성)
3. Cacheability(캐시 가능성)
GET 응답은 캐싱 가능하지만 POST는 기본적으로 캐싱되지 않음.
4. Layered System(계층화 시스템)
5. Uniform Interface(균일한 인터페이스)
6. Code on Demand(선택적 원칙)
RESTful
REST 아키텍처 스타일을 완전히 준수하는 웹 서비스
HATEOAS(Hypermedia As The Engine Of Application State)를 포함한 REST의 여섯 가지 설계 원칙을 모두 만족
RESTful API 예시
- 피드 조회 API: GET /feeds/{feedId}
- 피드 생성 API: POST /feeds
- 피드 수정 API: PUT /feeds/{feedId}
- 피드 삭제 API: DELETE /feeds/{feedId}
기능에 따라 HTTP 메서드를 적절히 사용했다. 네 가지 기능을 모두 POST로 구현할 수 있지만, RESTful 설계 원칙을 지키지 않은 API가 된다.
Spring에서의 RESTful 웹 서비스 구현
@RestController
@Controller와@ResponseBody의 기능을 모두 하는 어노테이션@RestController가 붙은 클래스의 모든 메서드는 기본적으로@ResponseBody가 적용되어, 반환되는 객체가 JSON 또는 XML 형식으로 자동 변환된다.
@RequestMapping
- 요청 URL을 매핑하는 데 사용된다.
- 클래스나 메서드 레벨에 선언할 수 있으며, HTTP 메서드를 지정하지 않으면 기본적으로 모든 HTTP 메서드를 허용한다.
@GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping, @PatchMapping
- 메서드 레벨에서의 경우 위와 같은 어노테이션들이 주로 쓰인다.
@RequestMapping같은 역할을 하지만 HTTP 메서드가 명확하게 지정되어 있어 코드의 가독성을 높여준다.
@RequestMapping("/feeds")
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class FeedController {
@GetMapping("/{feedId}")
public ResponseEntity<FeedGetResponse> getFeed(Principal principal,
@PathVariable("feedId") Long feedId) {
// 피드 조회
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<Void> createFeed(Principal principal,
@Valid @RequestBody FeedCreateRequest request) {
// 피드 생성
}
@PutMapping("/{feedId}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> updateFeed(Principal principal,
@PathVariable("feedId") Long feedId,
@Valid @RequestBody FeedUpdateRequest request) {
// 피드 수정
}
@DeleteMapping("/{feedId}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteFeed(Principal principal,
@PathVariable("feedId") Long feedId) {
// 피드 삭제
}
}Richardson Maturity Model for REST APIs
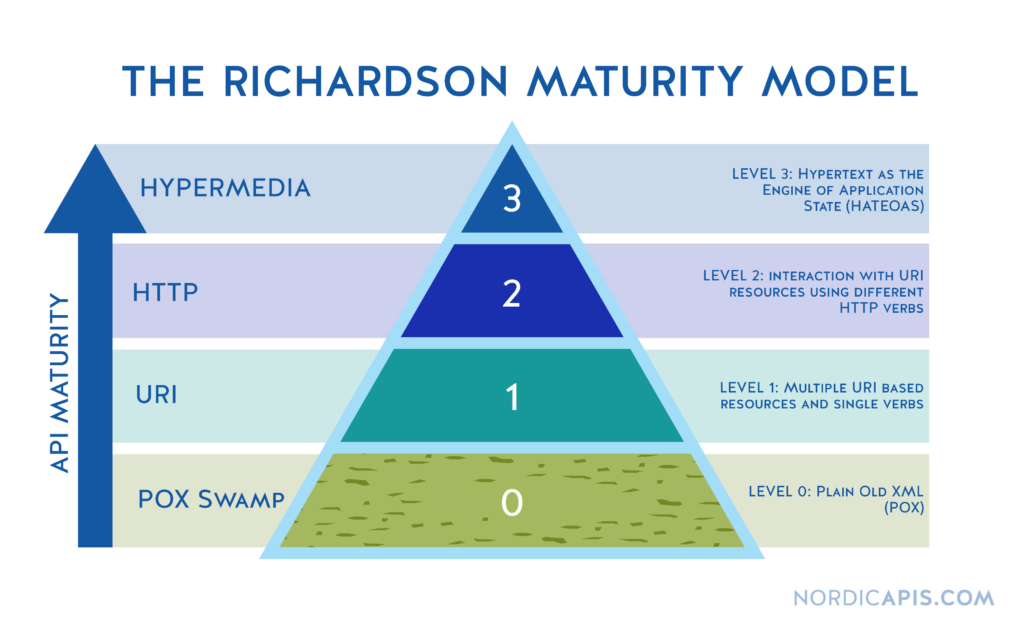
- Level 0
Single URI, Single Verb(HTTP method)
/feeds - Level 1
Multiple URIs, Single Verb(HTTP method)
단일 서비스 endpoint로 보내는 것이 아니라, 개별 리소스로 통신하는 것
/feeds/create - Leve 2
Multiple URIs, Multiple Verbs(HTTP method)
4가지 HTTP Method를 사용해서 CRUD를 표현하고 tatusCode도 활용하여 반환한다.
POST /feeds - Level 3
HATEOAS
HATEOAS까지 적용해야 완전한 RESTful API 설계라고 할 수 있다.
HATEOAS
Hypermedia As The Engine Of Application State
-
RESTful API가 클라이언트에게 응답을 제공할 때, 해당 리소스와 관련된 다른 동작(link)을 하이퍼미디어(hypermedia) 형식으로 포함해야 한다는 원칙
-
클라이언트는 API 문서를 참조하지 않아도 응답 안에 포함된 링크를 통해 시스템의 가능한 상태 전환을 알 수 있어야 한다.
-
클라이언트와 서버 간의 의존성을 줄이고, 클라이언트가 리소스를 자유롭게 탐색하도록 하여 RESTful 아키텍처의 유연성과 확장성을 극대화한다.
-
구현의 복잡성과 오버헤드로 실제로는 필수적으로 사용되지는 않는다.
HATEOAS 예시
HATEOAS가 적용되지 않은 RESTful API 응답
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Sample Feed",
"description": "This is a sample feed."
}HATEOAS가 적용된 RESTful API 응답
{
"id": 123,
"name": "Sample Feed",
"description": "This is a sample feed.",
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "/feeds/123"
},
"update": {
"href": "/feeds/123",
"method": "PUT"
},
"delete": {
"href": "/feeds/123",
"method": "DELETE"
},
"allFeeds": {
"href": "/feeds",
"method": "GET"
}
}
}_links: 현재 리소스와 관련된 작업의 URI를 포함
HATEOAS를 적용한 API 설계 방법
1. 의존성 추가
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-hateoas'
}2. 리소스에 Hypermedia support 추가
RepresentationModel<>을 extend 한다.
class FeedResource extends RepresentationModel<FeedResource> {
private final Long id;
private final String name;
private final String description;
// getters and setters
}3. 링크 추가
@GetMapping("/feeds/{feedId}")
public FeedResource getFeed(@PathVariable Long feedId) {
// 데이터 샘플
Feed feed = new Feed(feedId, "Sample Feed", "This is a sample feed.");
// FeedResource 생성
FeedResource resource = new FeedResource(feed);
// HATEOAS 링크 추가
resource.add(linkTo(methodOn(FeedController.class).getFeed(feedId)).withSelfRel()); // self
resource.add(linkTo(methodOn(FeedController.class).getAllFeeds()).withRel("allFeeds")); // allFeeds
resource.add(linkTo(methodOn(FeedController.class).updateFeed(feedId)).withRel("update").withType("PUT")); // update
resource.add(linkTo(methodOn(FeedController.class).deleteFeed(feedId)).withRel("delete").withType("DELETE")); // delete
return resource;
}