[논문 리뷰] HALO: Hierarchical Autonomous Logic-Oriented Orchestration for Multi-Agent LLM Systems
Overview
-
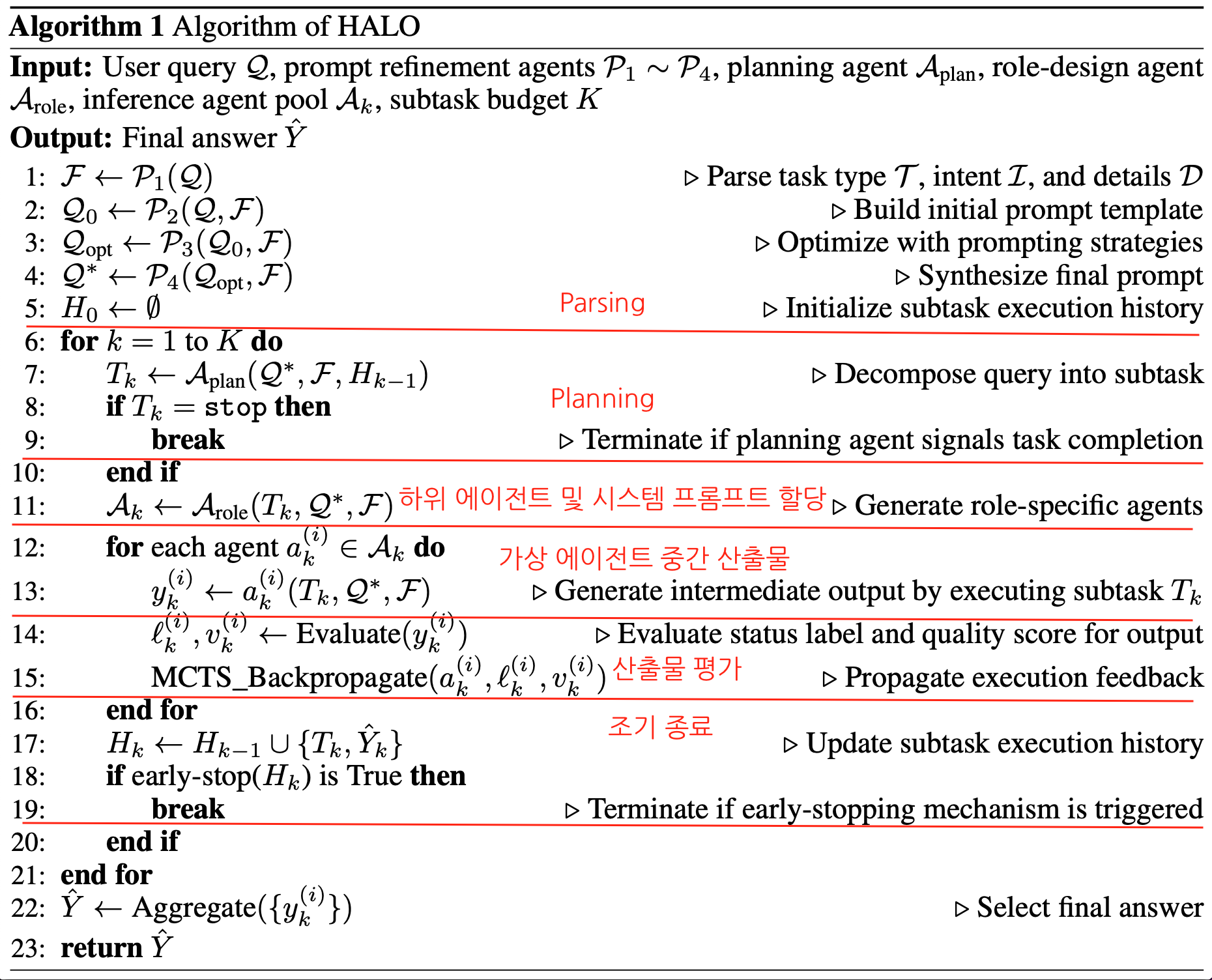
HALO Framework
High-level : Planning agent
Mid-level : role-design agents
Low-level : inference agent → Workflow search engine (subtask execution with Monto Carlo Tree Search(MCTS)) -
Adaptive Prompt Refinement module
: raw query → task-specific prompt
Challenges
How to maintain robust performance in complex interaction environments and expert-level task?
- limitation :
(1) heavily depend on expert insight and manually-designed policies (rigid and predefined role space)
(2) users’ lack expertise in prompt engineering- main problems :
(1) how can agentic systems self-organize and coordinate in unfamiliar environments with minimal manual intervention ?
(2) how can user queries be refined to improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of multi-agent collaboration?- HALO solution:
(1) an extensible agent-role instantiation mechanism and a dynamic communication architecture
(2)prompt engineering module
HALO Framework
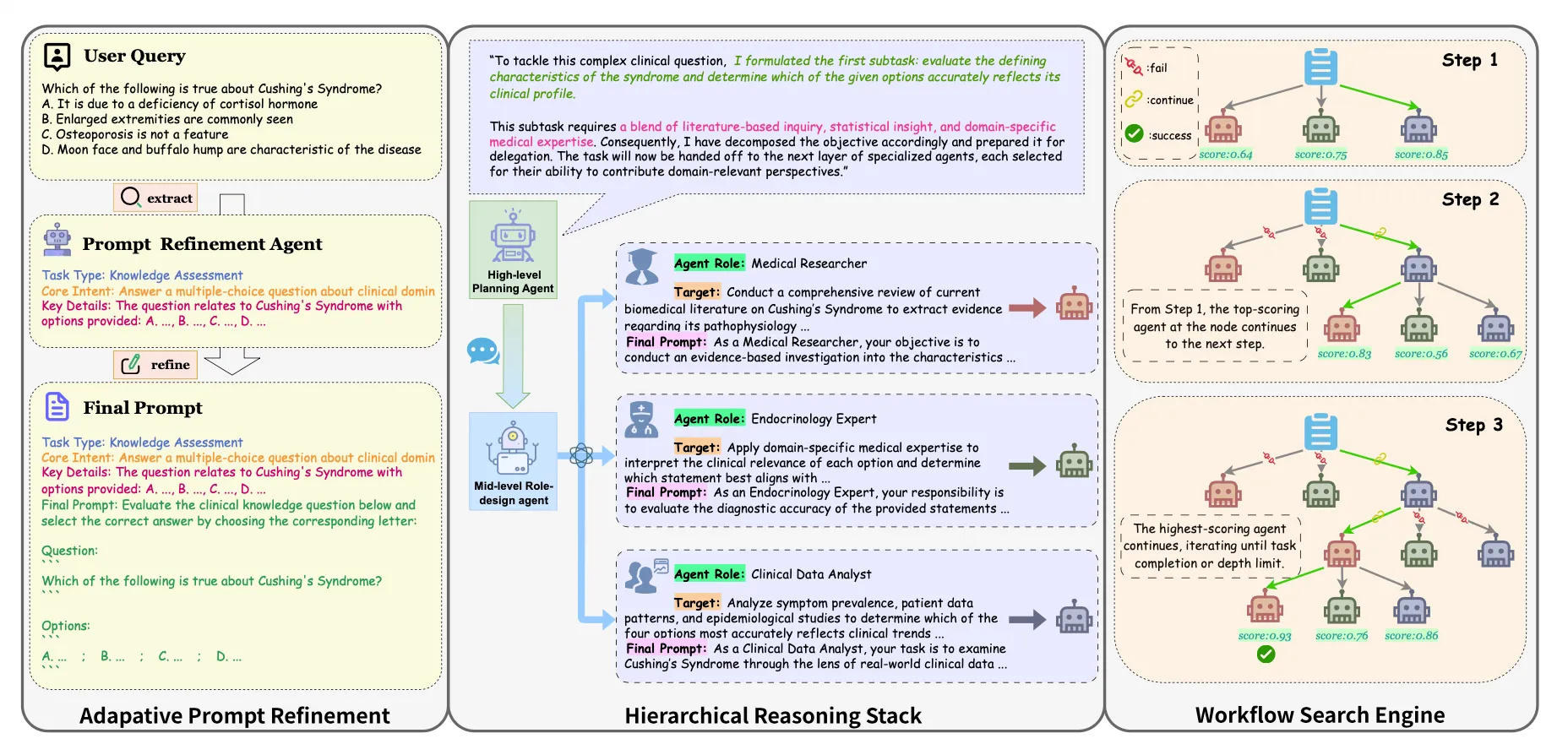
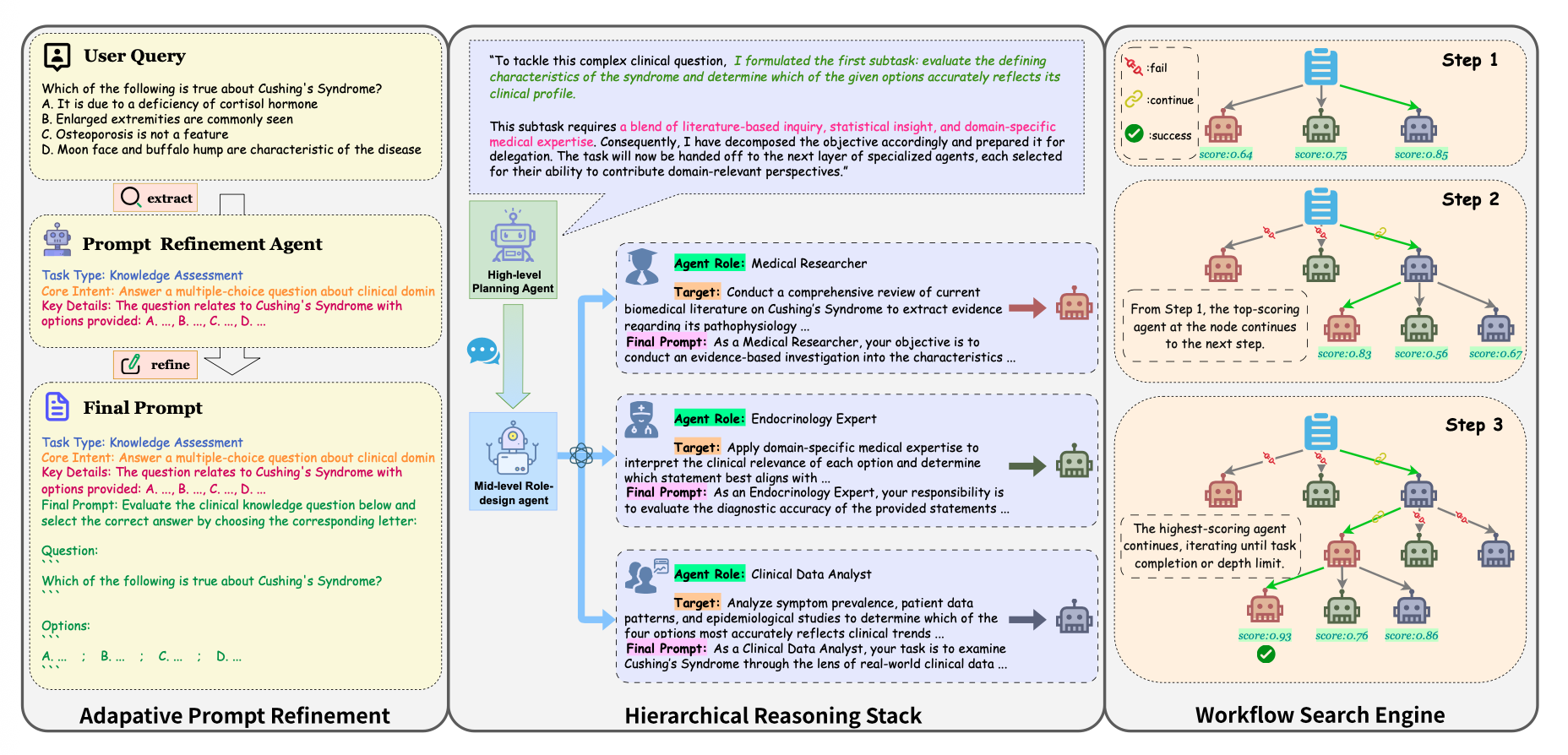
(1) Adaptive prompt Refinement
-
four collaborative agents
→ different phase of prompt refinement (query parsing ~ final synthesis) -
detailed in Section 3.2
-
Agent P1
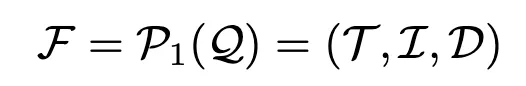
- Task Parser Agent
- analyze the original query Q
→ three components :
1) task type T
2) core intent
3) key details D - F → a Global semantic context throughout the entire reasoning flow
-
Agent P2
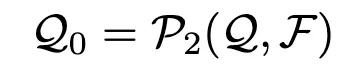
- Prompt Template Agent
- Qo : task description 재구성, clear reasoning objectives, bounded input conditions. explicit output format
-
Agent P3
- Prompt Optimization Agent
- slow thinking prompting strategies, tool calling instructions, optimized prompt
-
Agent P4
- Prompt Generator Agent
- Sythesizes the optimized structure
- the entry point for downsream multi-agent reasoning
-
(2) Hierarchical Reasoning Stack (Section 3.3)
- three-tier multi-agent collaboration architecture
-
High-level : Planning agent [과업을 한번에 세분화하지 않고 점진적으로 하나의 세부 과업을 만들면, 그걸 기반으로 다음 과업을 갱신하는 형태로 계획을 세움]
refined prompt Q*, Global structure task representation F, subtask execution history H k-1 (Tk 이전에 수행된 하위 과업들의 실행 이력을 나타냄)
-
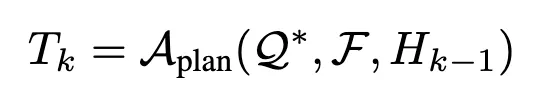
Aplan은 정제된 프롬프트 Q∗와 전역 구조화된 과업 표현 F을 입력받는다.
이 정보를 바탕으로 전체 작업을 하위 과업들의 순서적 집합{T1,T2,...,TK}으로 분해한다.
전체 과업을 한 번에 모두 세분화하는 대신,
Aplan은 단계적(step-wise) 전략을 사용하여 한 번에 하나의 하위 과업만 생성하고, 이전 하위 과업들의 수행 이력 Hk−1을 바탕으로 자신의 분해 정책(decomposition policy)을 점진적으로 갱신한다.
-
Mid-level : role-design agents [LLM 기반 하위 에이전트를 생성하는 역할+ 시스템 프롬프트 할당]
2-1. 하위 에이전트 생성
Tk가 Arole에게 과업을 이행하면 아래와 같이 LLM 기반 하위 에이전트 ak를 생성한다.
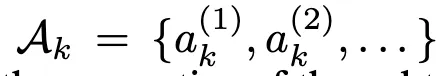
하위 에이전트를 생성하는 과정은 다음과 같다
- 하위 과업 TkT_kTk의 의미적 정보(semantics),
- 정제된 프롬프트 Q∗,
- 전역 구조화된 과업 표현 F 에 의해 공동으로 가이드 → 이를 통해 각 생성된 에이전트 ak(i)가 해당 하위 과업 Tk의 요구 사항에 잘 정렬(aligned)되도록 보장
2-2. 역할별 시스템 프롬프트 생성
각 역할에 맞는 시스템 프롬프트를 할당 받으며 하위 과업 Tk에 의해서 행동을 제어한다. 즉, 역할 설계 에이전트는 (Tk,Q∗,F)을 입력받아 특화된 역할 프롬프트ρk(i)를 생성
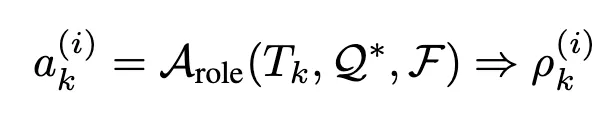
- Low-level : inference agent
3-1. 협력적 추론 수행
Tk,Q*, F를 받은 Inference agent는 협력적 추론을 수행하고 이에 맞는 집합 Yk라는 중간 산출물을 생성
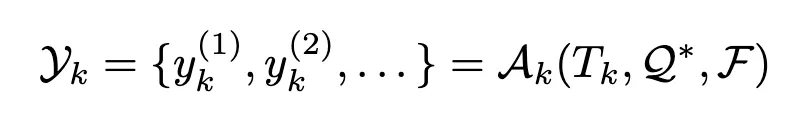
-
조기종료( early-stopping)
- HALO는 고수준 계획 에이전트 Aplan 내부에 조기 종료 메커니즘(early-stopping mechanism)을 통합 (비잔틴 합의 이론에서 영감→ 이 이론에 따르면 하나의 통신 라운드에서 p개의 오류(faulty) 에이전트를 견디기 위해서는 최소 3p + 1개의 에이전트가 필요하다.)
- HALO는 수행 이력 Hk에 포함된 하위 과업 중 66% 이상이 동일한 일관된 답변 Y^에 도달했을 경우, 추론 과정을 조기에 종료
(3) Workflow Search Engine (Section 3.4)
- At the low-level with inference agents
- reformulate subtask execution as a workflow search process (Monte Carlo Tree Search, MCTS)
- Node : corresponds to an agent-generated response / intermediate reasoning step
- Edge: denote possible transitions between reasoning states
- search trees with Node & Edge : represent a candidate reasoning trajectory for each substask
- Section 3.4
- HALO는 여러 에이전트가 서로 다른 역할로 협력하는 추론 과정을 트리 형태의 탐색 공간으로 모델링
- Node: 트리의 한 점(node)은 하나의 “역할을 수행 중인 에이전트”
- Edge: 엣지(edge)는 에이전트 간의 의사소통 혹은 정보 전달(communication transition)
- Node + Edge: 하나의 하위 과업에 대한 후보 추론 경로(candidate reasoning trajectory)를 형성
- 추론하기 위한 MCTS paradigm (Selection, Expansion, Simulation, Backpropagation)
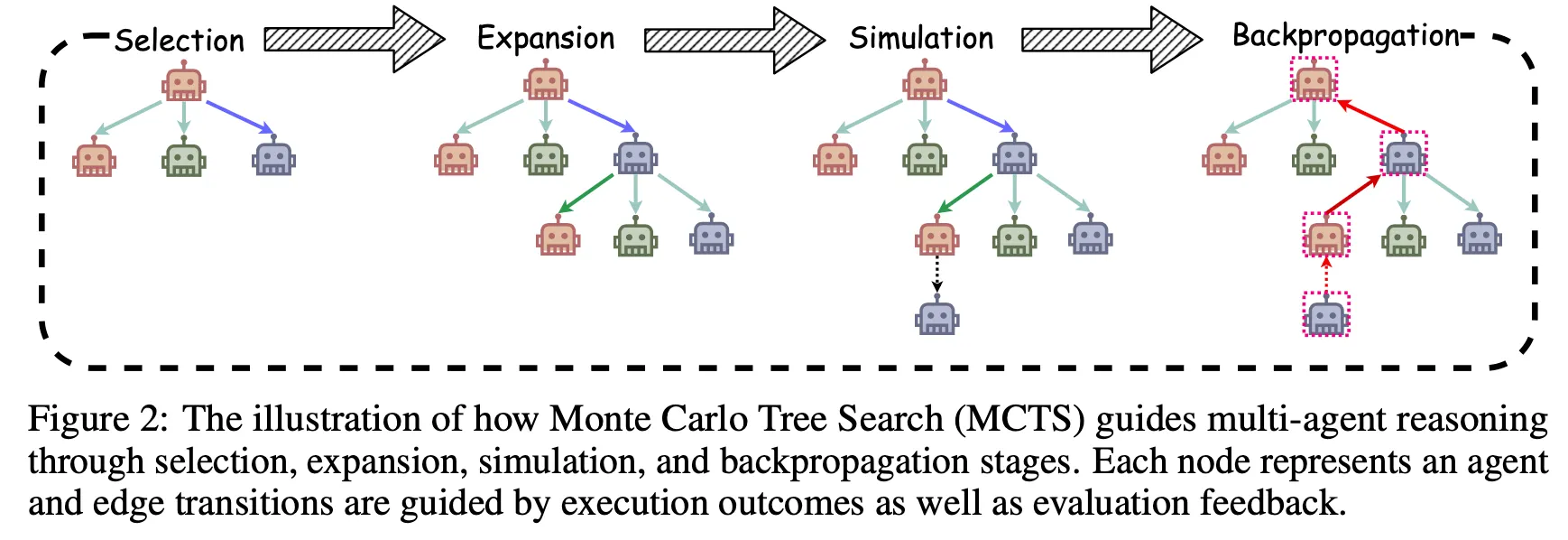
- Selection → best agent를 선택 with UCT algorithm
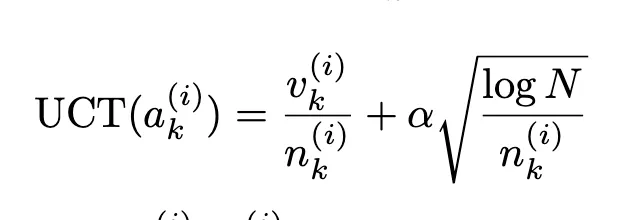
UCT는 “성과가 좋거나, 아직 많이 시도하지 않은 노드”를 우선적으로 선택하는 알고리즘 !
- 첫번째 항 : 평균 보상값(Vk : the score value of agent) ; 지금까지의 보상이 크면 그 노드를 더 자주 선택 → 활용(exploitation)
- 두번째 항 : 현재 노드의 방문 횟수가 적을수록 값이 커짐 → 탐험(exploration)
| 기호 | 의미 |
|---|---|
| N | 전체 탐색 횟수 (부모 노드가 몇 번 방문되었는지) |
| nk | 현재 노드 k의 방문 횟수 |
| α | 탐험 정도를 조절하는 상수(Exploration constant), 보통 √2 사용 |
- Expansion → role-specific agent들을 만드는 역할
- Simulation → 시뮬레이션을 위해 expansion한 agent 각각의 실제가 아닌 가상 agent를 만들어서 중간 산출물(intermediate output) yk를 만든 다음, 두개의 보조 에이전트에 의해 평가됨 (judging agent & scoring agent)
-
에이전트 ak(i+1)은 하위 과업 Tk에 대해 시뮬레이션된 추론 경로(simulated reasoning trajectory)를 시작한다.
💡 즉, 실제 실행 전에 “가상의 추론 경로”를 만들어 앞으로의 reasoning 단계를 예측·시험하는 것
-
“˜(틸드)”가 붙은 에이전트들은 실제가 아닌 가상(simulated) 에이전트이며, HALO가 “만약 이 방향으로 진행한다면 어떤 결과가 나올까?”를 탐색하기 위해 사용하는 것
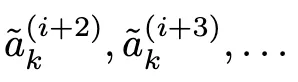
-
각 시뮬레이션 에이전트 a~k(j)는 하위 과업 Tk, 정제된 프롬프트 Q∗, 전역 구조화된 과업 표현 F을 입력으로 받아 중간 산출물(intermediate output) y~k(j)를 생성한다.
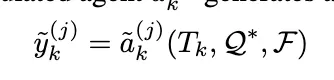
📘 즉, HALO는 실제 수행 없이 가상의 reasoning output을 여러 단계로 예측 생성하는 과정
-
결과 평가: 두 보조 에이전트(auxiliary agents) -appendix B 참고
가상 산출물y~k(j)은 두 개의 보조 에이전트(auxiliary agents)에 의해 평가
1) judge agent
판단 에이전트(judging agent)는 현재 하위 과업이 완료되었는지를 나타내기 위해 상태 레이블(status label)ℓ~k(j)을 부여한다.
이 값은 성공(success), 실패(fail), 계속 진행(continue) 중 하나
2) scoring agent
*평가 에이전트(scoring agent)는 생성된 산출물의 효과성(effectiveness)**을 수치적으로 평가하기 위해 품질 점수(quality score) v~k(j)∈[0,1]을 계산
- Backpropagation → reward signal adjustment mechanism based on the judgement outcome
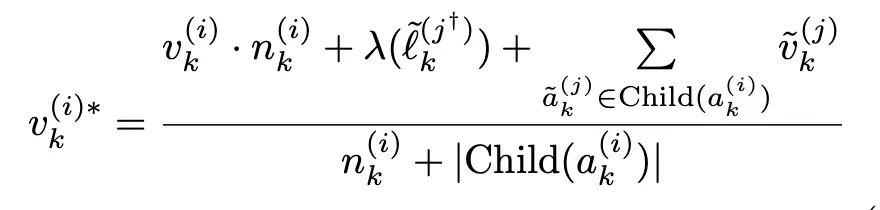
보상 계수 λ 정의:
λ(ℓ~k(j))는 상태 레이블 ℓ~k(j)에 대응하는 영향 계수(impact factor)로, 시뮬레이션 결과에 대한 보상(reward) 또는 페널티(penalty)를 반영한다.
부모 노드의 새로운 값은 “현재 노드의 기존 점수 × 노드 방문횟수 + 시뮬레이션 보상값 + (시뮬레이션)리프 노드의 품질 점수의 합”을 자식 수 + 기존 방문 수로 나눈 가중 평균(weighted average) 형태로 업데이트를 함께 반영하여 계산된다. 이를 통해 HALO는 과업 완료 상태에 대한 민감도를 높이고, reasoning trajectory 전반의 평가 정확도를 향상
HALO framework 알고리즘 정리
Related work
(1) Prompt optimization 프롬프트 최적화 ; manual intervention 없이도 modularity ⬆️
- CAMEL : integrates a task-planner agent
→ CAMEL은 여러 에이전트(agent)가 역할(role)을 배정받아 역할 놀이(role-playing) 방식으로 상호작용하면서 과제를 해결하도록 설계됨, → 각 에이전트가 특정 역할을 맡고, 역할에 맞게 대화를 나누면서 협력 또는 상호작용
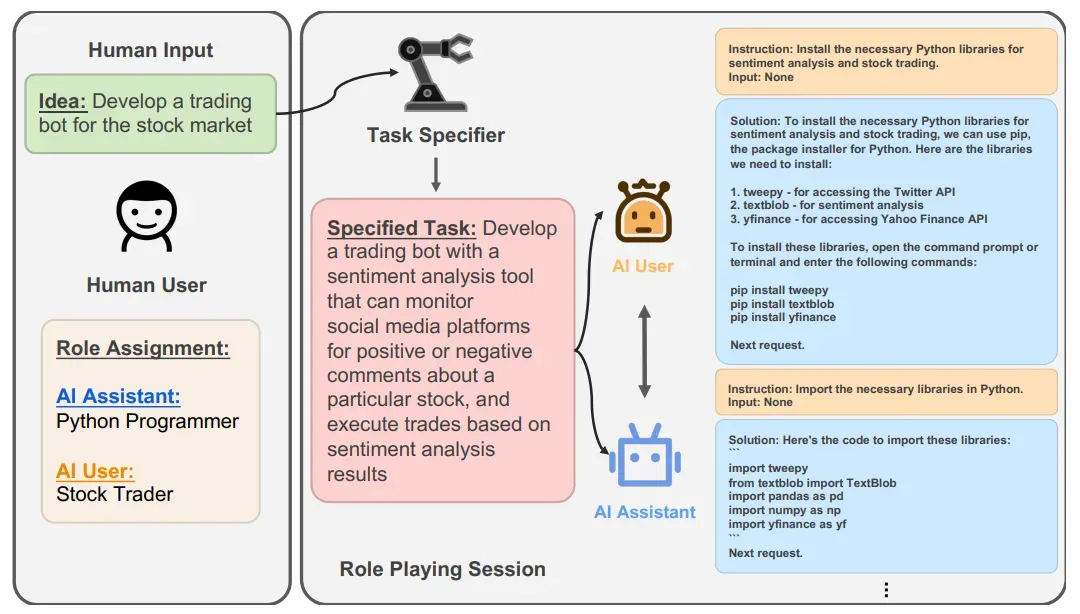
-
ComfyAgent: incorporate prompt generation as part of evolving workflows
→ ComfyAgent 내부에 여러 역할의 에이전트를 두고 협업하면서 워크플로우를 구축. 주로 Planner, Memory, Action 모듈 등이 있음. -
challenge : prompts that runtime context changes largely open in scenarios where agent roles or task objectives are not predefined
(2) Role design in LLM-based architecture
- common strategy(ex. MetaGPT) : static role configuration ; governs their behavior through standard operating procedures → 문제: fixed roles ; open-ended or dynamic settings agent responsibilities must evolve in response to task changes
- MetaGPT: 인간이 사용하는 표준 운영 절차 (SOP: Standard Operating Procedure)를 에이전트 워크플로우에 “프롬프트 시퀀스” 형태로 내재화
- newer framework(ex. TPTU, DyLAN) : role generation mechanisms (agents to create, adapt, or inherit roles dynamically.)
- TPTU :Task Planning + Tool Usage — 를 LLM 기반 에이전트에게 요구되는 핵심 역량으로 보고, 이를 구조화하여 평가하고 개선하기 위한 프레임워크 즉, 단순히 “텍스트를 생성하는 것”에서 벗어나, “임무를 분해하고, 어떤 도구를 쓸지 결정하고, 도구를 호출하고, 중간 결과를 관리하면서 완성해 나가는 에이전트”
- DyLAN(현 논문과 가장 비슷한듯) : LLM 기반 에이전트를 동적으로 선택하고, 그들 사이 통신 구조를 동적으로 조정하면서 협업하도록 설계된 프레임워크
→ 자세히 설명- 2단계 방식 (Two-stage paradigm)
- 팀 최적화 (Team Optimization) 단계: 후보 에이전트 집합 중에서 주어진 작업에 가장 기여할 가능성이 높은 에이전트를 선정
- 작업 해결 (Task Solving) 단계: 선정된 에이전트들이 실제로 협업하면서 최종 답을 도출
- Agent Importance Score
- 팀 최적화 단계에서, 각 후보 에이전트가 초기 협업 시도(trial)에서 얼마나 기여했는지를 판단하는 비지도 지표
- 이 점수를 기반으로 에이전트를 선택하거나 제외하는 방식→ 필요없는 에이전트 비활성화 (중간에 LLM 기반의 랭커(ranker) 역할을 두어, 어느 에이전트가 계속 참여할지 판단하게 함)
- 2단계 방식 (Two-stage paradigm)
(3) Cooperation optimization strategies
-
Centralized framework(ex. AgentLaboratory, ScoreFlow, WORKFLOW-LLM) : controller agent
-
Decentralized approaches: control and decision-making across agents / peer-to-peer communication, identity-based protocols
-
Game-theoretic negotiation : greater autonomy and robustness in unstructured environments
-
Game-theoretic Workflow : LLM에게 단순한 “무엇을 해라” 지시를 넘어서, “이런 사고 과정을 거쳐야 한다”라는 구조적 지침을 제공 (규칙 설명 → 전략 탐색 → 균형 분석 →….)
-
ex. AFlow : workflows through dynamic graph traversal
- Workflow Optimization을 코드 수준의 탐색(search) 문제로 재정의하고, 자동화된 방식으로 워크플로우를 생성하고 개선하는 시스템
- 워크플로우를 코드(code)로 표현. 노드(node)는 LLM 호출을 대표하고, 엣지(edge)는 노드 간의 의존성 및 흐름을 나타냄 → 워크플로우 구조를 탐색하는 데 Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) 기법을 활용. 노드를 추가하거나 수정하고, 이 변경을 평가하면서 탐색 트리를 확장 (본 논문과 동일) + 트리 상위에 피드백을 되돌려 주어 탐색에 반영. 즉, 좋은 워크플로우 구조는 더 자주 탐색되게 유도 -
building more context-sensitive agent teams
Experiments
1. Experimental setup
1) Code generation : HumanEval dataset (164 Python programming problems and units test), 평가지표- pass@1 metric (code accuracy)
2) General reasoning : MMLU dataset (57 subjects with 15,908 questions in multiple-choice format with four options), 평가지표 - accuracy, 13% sampling
3) Arithmetic reasoning: : MATH dataset (12,500 math problems- 7 subareas with 5 diffculty levels) 500 math problems sampling, 평가 - accuracy
2. HALO setup
1) LLM: GPT -4o
2) random seed : 10
3) temperature : 0.8
4) max tokens : 2048
5) same number of few-shot examples
6) code interpreters as tools in the code generation task
3. Main results
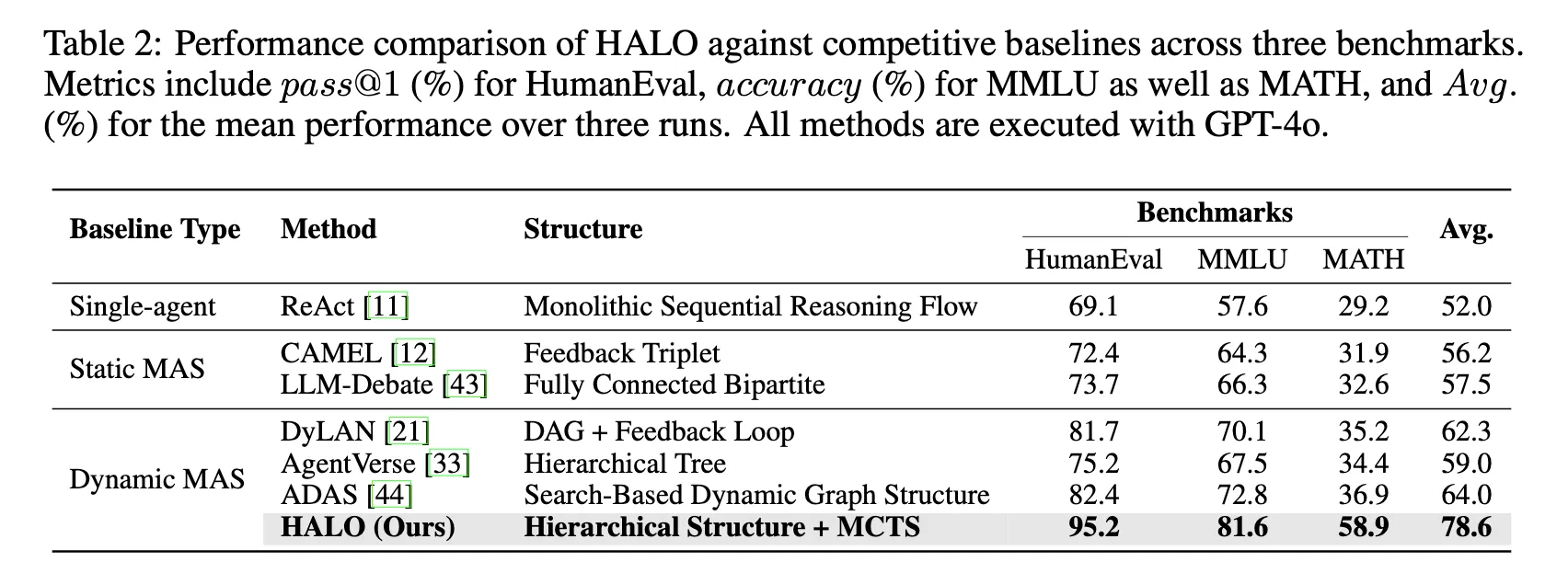
-
인지적 과부하(cognitive overload) 해결
HALO는 계층적 추론 아키텍처(hierarchical reasoning architecture)를 통해 기존 단일 에이전트 프레임워크(ReAct 등)의 한계인 인지적 과부하 문제를 극복하였다.
ReAct는 하나의 에이전트가 계획 수립, 추론, 반성(reflection)을 동시에 수행해야 하지만, HALO는 이 과정을 과업 분해(task decomposition), 역할 할당(role instantiation), 하위 과업 추론(subtask inference)으로 분리하여 에이전트 간 역할을 분담
HALO는 ReAct 대비 다음과 같은 개선을 보였다 (Table 2 기준):
- HumanEval pass@1: 69.1% → 95.2% (+26.1%)
- MMLU 정확도: 57.6% → 81.6% (+24.0%)
- MATH 정확도: 29.2% → 58.9% (+29.7%)
평균적으로 26.6% 성능 향상(78.6% vs. 52.0%)을 달성하였다. → 이는 HALO의 분산형 계층 추론 구조가 단일형(monolithic) 구조보다 우월함
- 적응형 에이전트 생성과 탐색 기반 워크플로우
기존의 정적 MAS(예: CAMEL, LLM-Debate)는 고정된 역할과 수동 워크플로에 의존하고, 동적 MAS(예: DyLAN, AgentVerse, ADAS)는 세밀한 역할–과업 정렬(fine-grained alignment)이 부족하다.
반면 HALO는 MCTS 기반 탐색(Monte Carlo Tree Search)을 통해 실시간 피드백에 따라 적절한 역할을 동적으로 생성하고, 실행 경로를 반복적으로 개선한다.
그 결과(Table 2):
- 평균 성능: HALO 78.6% vs. ADAS 64.0% ( +14.6% )
- HumanEval: 82.4% → 95.2% (+12.8%)
- MMLU: 72.8% → 81.6% (+8.8%)
- MATH: 36.9% → 58.9% (+22.0%)
→ HALO는 대규모 다중 에이전트 추론(multi-agent reasoning at scale)을 정교하게 조율하는 데 탁월함을 입증
- 전문적·고난도 추론 능력
HALO는 복잡하고 전문적인(reasoning-intensive) 과업에서도 높은 성능을 보였다.
MMLU의 추상적 과목(abstract subjects)과 MATH의 고난도 세부 영역(subareas)을 비교한 결과:
- MMLU(추상 과목): HALO 70.8% vs. ADAS 56.4% → +14.4% 향상
- MATH(고난도 영역): HALO 43.9% vs. ADAS 24.4% → +19.5% 향상
4. Ablation study
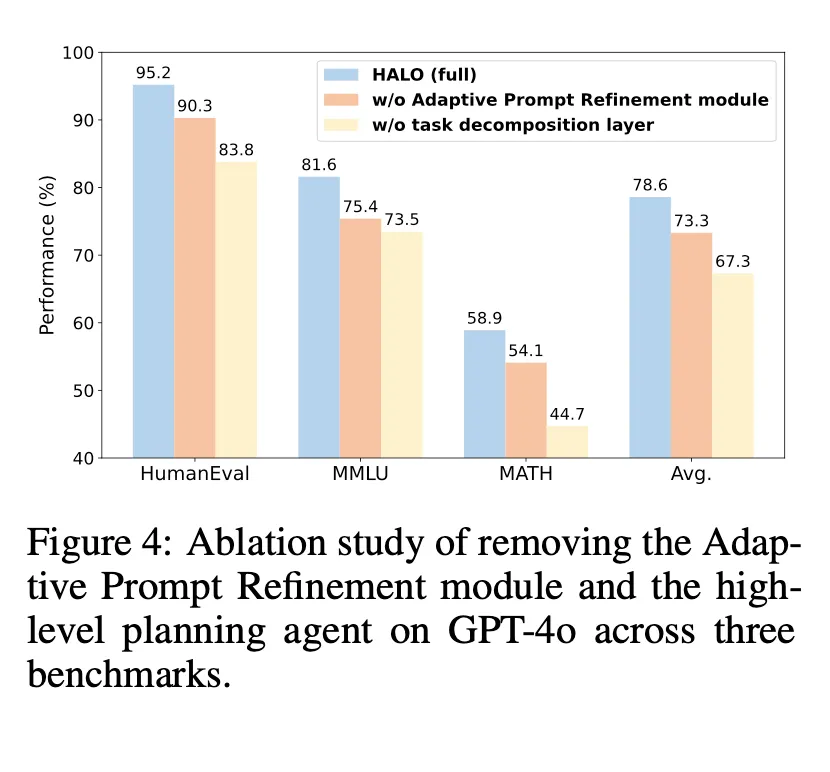
1) Adaptive Prompt Refinement
performance drops by 5.3% on average, with MMLU suffering the most (81.6% →75.4%). This result highlights the importance of structured prompt construction in enhancing task understanding and aligning reasoning trajectories with user intent.
2) High-level planning agent
this leads to an average performance drop of 11.3% across all benchmarks. Notable drops on HumanEval (95.2% →83.8%) and MATH (58.9% →44.7%) demonstrate that removing task decomposition impairs reasoning coherence, highlighting its critical role in HALO.