가로 n, 세로n 크기의 2차원 타일맵을 2차원 정수 배열 변수로 저장해놓은 maps가 있다.
int[,] maps = {
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 } };숫자 1은 사람이 다닐 수 있는 길, 숫자 0은 사람이 다닐 수 없는 벽이고, 이동은 상하좌우로만 가능하다고 가정해보자.
출발점인 좌상단의 위치를 [0, 0], 목적지인 우하단의 위치를 [n -1, n -1]이라고 할 때, 장애물을 피해 목적지까지 도착할 수 있는 최단거리를 찾으려면 어떻게 해야할까?
내 현재 위치에서 도달할 수 있는 4방향을 모두 둘러본 뒤, 이동이 가능한 장소(1)이라면 이동하고 내가 왔다는것을 기록하고, 이동이 불가능한 장소(0)이라면 건너뛰면 될 것이다.
int width = maps.GetLength(0);
int height = maps.GetLength(1);우선 주어진 맵의 가로와 세로의 크기를 담아둔다.
Queue<Tuple<int, int, int>> queue = new Queue<Tuple<int, int, int>>();정수 3개를 사용하는 Queue를 선언해준다. Queue는 선입선출의 자료구조이다. 먼저 삽입Enqueue된 자료가 먼저 출력Dequeue된다. 최단거리를 찾기 위해 정수 3개가 필요한 이유는, 각 x좌표, y좌표, 현재 이동거리가 필요하기 때문이다. 이를 위해 Tuple<int, int, int>로 묶어주었다.
bool[,] visited = new bool[width, height];방문한 장소가 이미 방문했던 장소인지를 확인할 수 있는 방법도 필요하다. 여기선 2차원 불리언 배열을 사용해 내가 방문한 좌표의 불리언 값을 false에서 true로 바꿔주기로 했다.
int[] dx = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int[] dy = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };내가 있는 위치를 기준으로 이동 가능한 방향을 검사해야하니 상하좌우 4개의 공간을 검사해야한다.
내 위치를 n, n이라고 할 때, 4방향은 각각 n+1, n, n-1, n, n, n+1, n, n-1이 될 것이다.
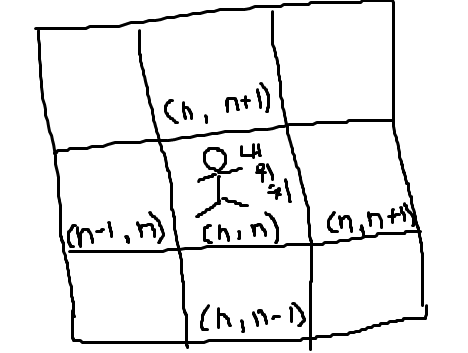
그럼 내가 임의의 점 n, n에 도달했을 때, 반복문을 통해 x좌표의 값에 dx를, y좌표의 값에 dy를 더해준다면 4개의 방향을 모두 확인할 수 있는 것이다.
queue.Enqueue(Tuple.Create(0, 0, 1));
visited[0, 0] = true;시작지점인 0, 0을 큐에 삽입해준다. 이미 방문한 지점이니 잊지말고 visited[0, 0]의 값도 true로 바꿔주어야 한다.
이제 큐에 계속 방문한 지점 삽입과 출력을 반복하면서, 도착지에 도달할 때까지 반복해주면 된다.
while(queue.Count > 0)
{
//큐에서 지금 위치를 꺼내본다.
Tuple<int, int, int> currentPosition = queue.Dequeue();
int x = current.Item1; //현재의 x좌표
int y= current.Item2; //현재의 y좌표
int distance = current.Item3; //현재까지 온 거리
if(x == width - 1 && y == height - 1)
{
//이때의 distance값이 최단거리이다.
}
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
//반복문을 4회 반복하며 현재 위치에서 도달할 수 있는 위치를 확인한다.
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
//가고자하는 위치가 0보다 작거나 맵의 크기보다 크다면 도달할 수 없다.
//이미 방문한곳은 방문하지 않는다.
//벽(1)일경우에도 방문하지 않는다.
if( nx >= 0 && nx < xLength && ny >= 0 && ny < yLength && !visited[nx, ny] && maps[nx, ny] == 1)
{
visited[nx, ny] = true;
queue.Enqueue(Tuple.Create(nx, ny, distance + 1));
}
}
//모두 다 순회했는데 도달하지 못했으면 길이 없는것.
}그렇다면 왜 최단경로를 찾기 위해선 선입선출 자료구조인 Queue를 사용해서 순회해야할까?
using System;
using Syste.Collections.Generic;
public class Solution
{
public static void Main()
{
int[,] maps = {
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 } };
Console.WriteLine(DFS(maps));
Console.WriteLine(BFS(maps));
}
public static int DFS(int[,] maps)
{
int xLength = maps.GetLength(0);
int yLength = maps.GetLength(1);
Stack<Tuple<int, int, int>> stack = new Stack<Tuple<int, int, int>>();
bool[,] visited = new bool[xLength, yLength];
stack.Push(Tuple.Create(0, 0, 1));
visited[0, 0] = true;
int[] dx = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int[] dy = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
while (stack.Count > 0)
{
Tuple<int, int, int> current = stack.Pop();
int x = current.Item1;
int y = current.Item2;
int distance = current.Item3;
if (x == xLength - 1 && y == yLength - 1)
{
return distance;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dx.Length; i++)
{
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx >= 0 && nx < xLength && ny >= 0 && ny < yLength && !visited[nx, ny] && maps[nx, ny] == 1)
{
visited[nx, ny] = true;
stack.Push(Tuple.Create(nx, ny, distance + 1));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static int BFS(int[,] maps)
{
int xLength = maps.GetLength(0);
int yLength = maps.GetLength(1);
Queue<Tuple<int, int, int>> queue = new Queue<Tuple<int, int, int>>();
bool[,] visited = new bool[xLength, yLength];
queue.Enqueue(Tuple.Create(0, 0, 1));
visited[0, 0] = true;
int[] dx = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int[] dy = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
while(queue.Count > 0)
{
Tuple<int, int, int> current = queue.Dequeue();
int x = current.Item1;
int y = current.Item2;
int distance = current.Item3;
if(x == xLength - 1 && y == yLength - 1)
{
return distance;
}
for( int i = 0; i < dx.Length; i++ )
{
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if( nx >= 0 && nx < xLength && ny >= 0 && ny < yLength && !visited[nx, ny] && maps[nx, ny] == 1)
{
visited[nx, ny] = true;
queue.Enqueue(Tuple.Create(nx, ny, distance + 1));
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}모든 길이 열린 5x5 배열의 맵에서 queue와 stack을 통해 순회를 해보았다.
17
9스택을 사용한 순회의 결과는 17, 큐를 사용한 순회의 결과는 9가 나왔다.
이는 큐의 선입선출 방식으로 각 레벨을 순차적으로 탐색하기 때문이다.
스택은 나중에 들어온 데이터를 먼저 출력하기 때문에 가능한 깊게 탐색하게 되고, 이는 최단거리 반환을 보장하지 않는다.
