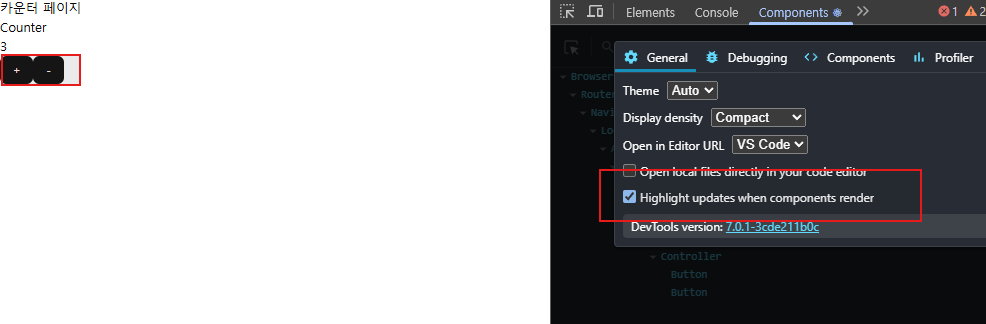
어떤 컴포넌트들이 리랜더링 되는지 확인 가능
문제점
- 현재 버튼값이 계속 리랜더링 -> 불필요한 랜더링
- 카운트만 바뀌면되는데 버튼이 리랜더링됨.
<버튼이 리랜더링 되는 이유>
- 컴포넌트에서 불러온 스토어 값들중, 하나라도 변경되면 컴포넌트가 리랜더링된다.
- 전체 스토어 객체가 계속 불러와짐 (지금 함수만 불러오는거 같지만 count 도 불러오게된다) -> 해당 컴포넌트를 리랜더링하게된다
=> 불필요한 버튼의 리랜더링!!!
const {increase, decrease} = useCountStore();
(⭐️⭐️⭐️count 값이 없더도 함수를 불러온 이상 불러온 것!⭐️⭐️⭐️)
===
const {increase, decrease, count} = useCountStore();import { useCountStore } from "@/store/count";
import { Button } from "../ui/button";
export default function Controller() {
문제점이 많음
const {increase, decrease} = useCountStore();
return (
<div>
<Button onClick={increase}>+</Button>
<Button onClick={decrease}>-</Button>
</div>
);
}해결방법
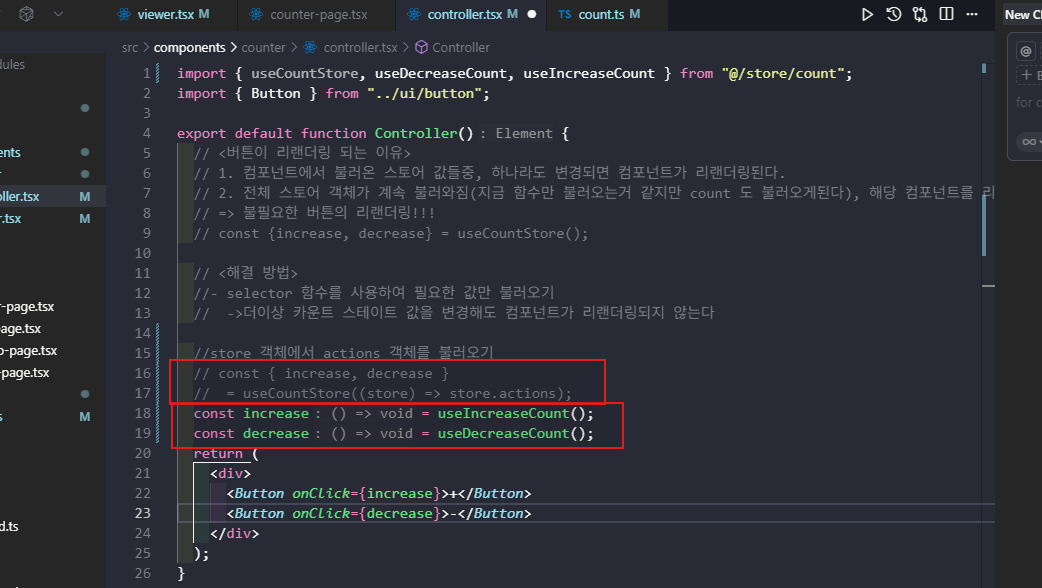
- selector 함수를 사용하여 필요한 값만 불러오기
->더이상 카운트 스테이트 값을 변경해도 컴포넌트가 리랜더링되지 않는다
const increase = useCountStore((store) => store.increase);
const decrease = useCountStore((store) => store.decrease);export default function Controller() {
const increase = useCountStore((store) => store.increase);
const decrease = useCountStore((store) => store.decrease);
return (
<div>
<Button onClick={increase}>+</Button>
<Button onClick={decrease}>-</Button>
</div>
);
}근데 각자 불러오기 귀찮은데요..?
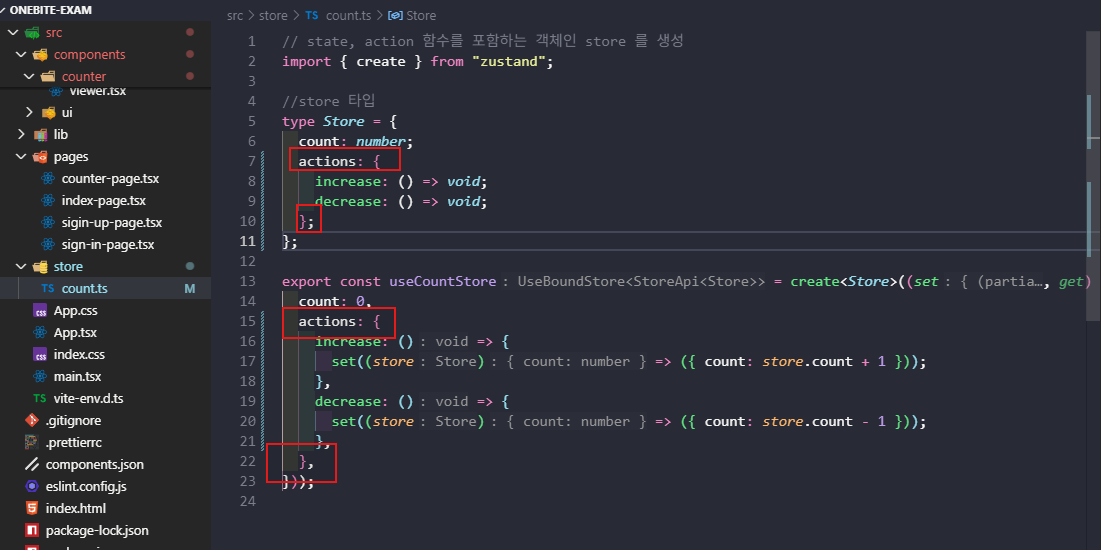
- store 객체에서 함수를 actions 객체 묶어서 불러오기
const { increase, decrease } = useCountStore((store) => store.actions);스토어 이름 바꾸기
- 이름 바꾸면 모든 컴포넌트에 이름바꿔야함
- 이에 수정사항에도 쉽게 반응할수 있는 구조 만들기
// 카운트 값을 가져오는 훅
export const useCount = () => {
const count = useCountStore((store) => store.count);
return count;
};
export const useIncreaseCount = () => {
const increase = useCountStore((store) => store.actions.increase);
return increase;
};
export const useDecreaseCount = () => {
const decrease = useCountStore((store) => store.actions.decrease);
return decrease;
};
한 훅으로 모든 컴포넌트의 이름을 안 변경해도 된다!
zustand 미들웨어
미들웨어란?
- 중간에 있는 도구
(로그 출력, 중복 확인)
1. conbine
// 결합하다.
import { combine } from "zustand/middleware";
create(
combine(
{
count: 0,
},
(set, get) => ({
actions: {
increaseOne: () => {
set((store) => ({ count: store.count + 1 }));
},
decreaseOne: () => {
set((store) => ({ count: store.count - 1 }));
},
},
}),
),
);combine 미들웨어를 사용하는이유
- 타입을 정의하지않아도 첫번째 인수를 토대로 타입을 추론.
⚠️ 주의 사항
- 타입이 카운트로만 정의
create(
combine(
{
count: 0,
},
(set, get) => ({
actions: {
increaseOne: () => {
get();
set((state) => ({ count: state.count + 1 }));
},
decreaseOne: () => {
set((state) => ({ count: state.count - 1 }));
},
},
}),
),
);
Zustand combine 미들웨어
📌 사용 이유
-
상태(state)와 액션(actions)의 명확한 분리
- 첫 번째 인자에 초기 상태 정의
- 두 번째 인자에 액션 함수 정의
-
자동 타입 추론
- TypeScript에서 별도의 타입 정의 없이 자동으로 타입 추론
- 개발 생산성 향상
-
코드 가독성 향상
- 구조화된 코드로 유지보수 용이
✅ 장점
- 타입 인터페이스를 수동으로 작성하지 않아도 됨
- 상태와 액션이 구조적으로 분리되어 유지보수 용이
- 보일러플레이트 코드 감소
- TypeScript 사용 시 개발 경험 향상
❌ 단점
- 상태와 액션을 자유롭게 섞을 수 없음 (구조 고정)
- 복잡한 커스텀 타입 사용 시 제한적
- 초보자에게는 추가 학습 곡선 존재
⚠️ 주의사항
-
첫 번째 인자는 초기 상태만
{ count: 0 } // ✅ 올바른 예 -
두 번째 인자는 액션 함수만
(set, get) => ({ actions: { increase: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count + 1 })) } }) -
초기값의 타입이 전체 타입을 결정
{ count: undefined } // ❌ 타입이 undefined로 고정됨 { count: 0 } // ✅ number 타입으로 추론 -
첫 번째 인자의 값만 상태로 인식됨
- 두 번째 인자에서 반환하는 값은 액션으로만 취급
📖 사용 예시
combine 사용 (추천)
import { create } from "zustand";
import { combine } from "zustand/middleware";
export const useCountStore = create(
combine(
// 1. 초기 상태
{
count: 0,
},
// 2. 액션 함수
(set, get) => ({
actions: {
increaseOne: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count + 1 })),
decreaseOne: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count - 1 })),
},
})
)
);
// 사용
export const useCount = () => useCountStore((store) => store.count);
export const useIncreaseCount = () => useCountStore((store) => store.actions.increaseOne);2. immer
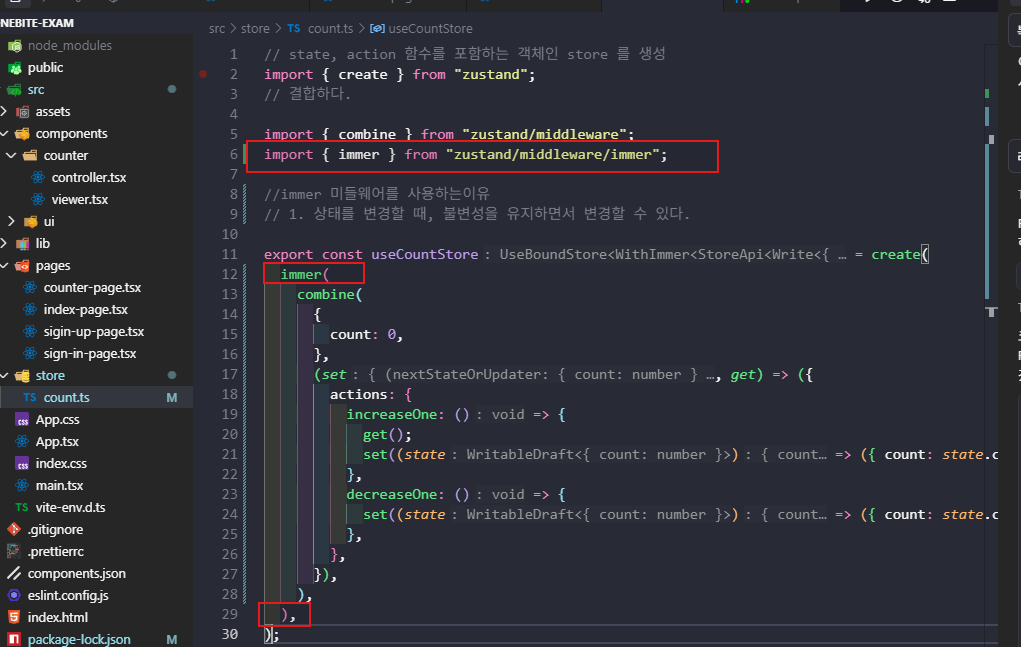
<immer 미들웨어를 사용하는이유>
- 상태를 변경할 때, 자동으로 불변성을 유지하면서 변경할 수 있다.
Zustand immer 미들웨어
📌 사용 이유
-
불변성 자동 관리
- 상태를 직접 수정하는 것처럼 코드를 작성해도 자동으로 불변성 유지
...spread연산자나 복잡한 복사 로직 불필요
-
코드 간결화
- 중첩된 객체나 배열 업데이트가 간단해짐
- 가독성이 크게 향상됨
-
실수 방지
- 불변성을 잊고 직접 수정하는 실수 방지
- 안전한 상태 업데이트 보장
✅ 장점
- 복잡한 중첩 구조의 상태 업데이트가 매우 간단해짐
- 직관적인 mutable 스타일 코드 작성 가능
- 불변성 관련 버그 감소
- 코드 가독성과 유지보수성 향상
- 배열 조작(push, splice 등)을 직접 사용 가능
❌ 단점
- 추가 라이브러리 의존성 발생 (immer 패키지 필요)
- 번들 크기 증가 (약 16KB)
- 간단한 상태 업데이트에서는 오버헤드가 될 수 있음
- immer의 동작 방식을 이해해야 함
- 성능이 중요한 대규모 업데이트에서는 약간의 오버헤드
⚠️ 주의사항
-
반드시 immer를 가장 바깥쪽에 배치
// ✅ 올바른 순서 create(immer(combine(...))) // ❌ 잘못된 순서 create(combine(immer(...))) -
set 함수에서 return 하지 않기
// ✅ 올바른 사용 (값을 반환하지 않음) set((state) => { state.count += 1; }); // ❌ 잘못된 사용 (객체를 반환하면 안됨) set((state) => { state.count += 1; return state; // 반환하면 안됨! }); -
원시 타입은 직접 반환해야 함
// ❌ 원시 타입은 직접 수정 불가 set((state) => { state = newValue; // 작동하지 않음 }); // ✅ 객체로 감싸서 사용 set((state) => { state.value = newValue; }); -
async 함수 안에서 draft 사용 주의
// ❌ 비동기 이후 draft 수정 set(async (state) => { await fetchData(); state.data = newData; // 위험! }); // ✅ 비동기 처리 후 새로운 set 호출 const data = await fetchData(); set((state) => { state.data = data; });
📖 사용 예시
immer 사용 (추천)
import { create } from "zustand";
import { combine } from "zustand/middleware";
import { immer } from "zustand/middleware/immer";
export const useCountStore = create(
immer(
combine(
{
count: 0,
nested: {
value: 10,
items: [1, 2, 3],
},
},
(set, get) => ({
actions: {
// 간단한 업데이트
increaseOne: () => {
set((state) => {
state.count += 1; // 직접 수정
});
},
// 중첩된 객체 업데이트
updateNested: () => {
set((state) => {
state.nested.value = 20; // 간단!
});
},
// 배열 조작
addItem: (item: number) => {
set((state) => {
state.nested.items.push(item); // 직접 push!
});
},
removeItem: (index: number) => {
set((state) => {
state.nested.items.splice(index, 1); // 직접 splice!
});
},
},
})
)
)
);immer 미사용 (기존 방식)
import { create } from "zustand";
import { combine } from "zustand/middleware";
export const useCountStore = create(
combine(
{
count: 0,
nested: {
value: 10,
items: [1, 2, 3],
},
},
(set, get) => ({
actions: {
// 간단한 업데이트
increaseOne: () => {
set((state) => ({ count: state.count + 1 }));
},
// 중첩된 객체 업데이트 - 복잡함!
updateNested: () => {
set((state) => ({
nested: {
...state.nested,
value: 20,
},
}));
},
// 배열 조작 - 더 복잡함!
addItem: (item: number) => {
set((state) => ({
nested: {
...state.nested,
items: [...state.nested.items, item],
},
}));
},
removeItem: (index: number) => {
set((state) => ({
nested: {
...state.nested,
items: state.nested.items.filter((_, i) => i !== index),
},
}));
},
},
})
)
);💡 언제 사용하면 좋을까?
immer 사용 권장:
- ✅ 중첩된 객체나 배열 구조가 많을 때
- ✅ 배열에 자주 push, splice, sort 등을 사용할 때
- ✅ 복잡한 상태 업데이트 로직이 많을 때
- ✅ 불변성 관리 실수를 줄이고 싶을 때
- ✅ 코드 가독성을 중요하게 생각할 때
immer 미사용 권장:
- ✅ 상태 구조가 매우 단순할 때
- ✅ 번들 크기를 최소화해야 할 때
- ✅ 성능이 매우 중요한 대규모 업데이트가 빈번할 때
- ✅ 외부 의존성을 최소화하고 싶을 때
🔄 combine과 immer를 함께 사용하기
두 미들웨어를 조합하면 최고의 개발 경험을 얻을 수 있습니다:
import { create } from "zustand";
import { combine } from "zustand/middleware";
import { immer } from "zustand/middleware/immer";
export const useStore = create(
immer( // ← 가장 바깥쪽에 immer
combine( // ← 안쪽에 combine
{ /* 초기 상태 */ },
(set, get) => ({ /* 액션 */ })
)
)
);장점:
- ✅ 타입 자동 추론 (combine)
- ✅ 상태와 액션 분리 (combine)
- ✅ 불변성 자동 관리 (immer)
- ✅ 간결하고 읽기 쉬운 코드
