
meow
Proviously...
-
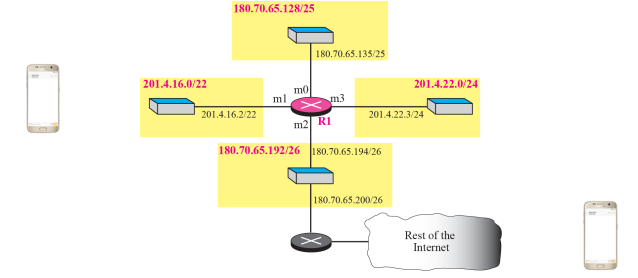
IP addresses are designed to work with stationary hosts because part of the address defines the network to which the host is attached.
-
However...
이제.. 단말이 가만히 있지 않음..ㅠ

-
In end-to-end connection, if one end moves, the network session breaks. So does all the networking services layered on top of IP
-
Solution?
- Option 1: Completely redesign each layer of the protocol suite. 🙄→🤮
- Option 2: Provide additional services at the network layer in a backward compatible manner - Mobile internetworking!
Mobile IP
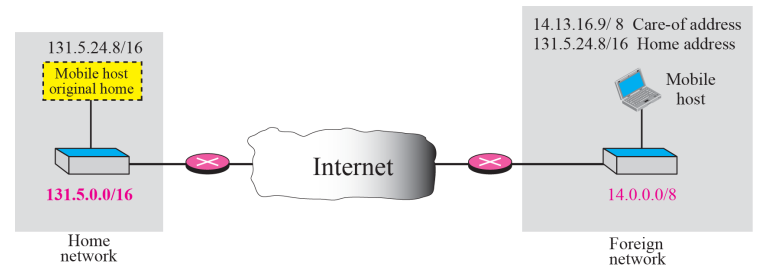
- Mobile IP has two addresses for a mobile host: home address and care-of-address
- The home address is permanent.
- The care-of address changes as the mobile host moves from one network to another.
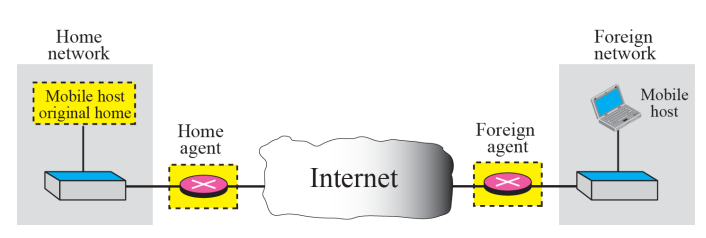
Mobile ip introduces Agents: Home agent & foreign agent
- To make the change of address transparent to the rest of the Internet.
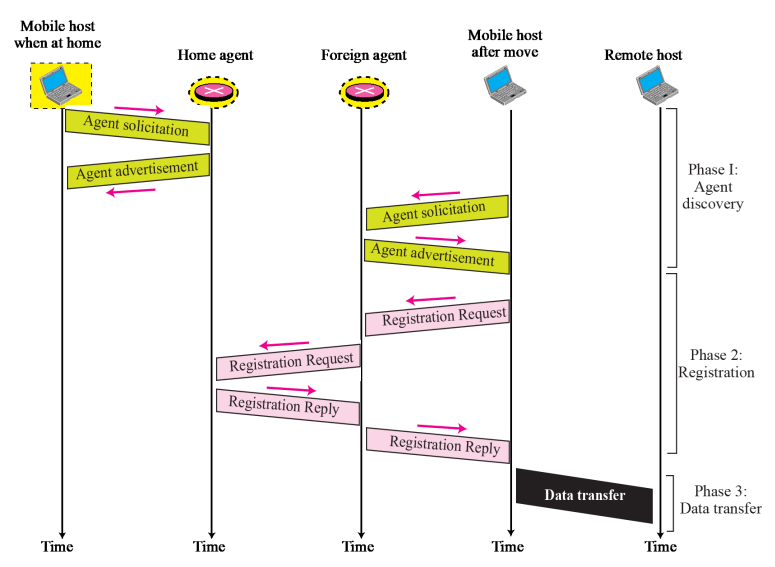
Three phases
-
Agent discovery
-
ICMP
-
Router advertisement
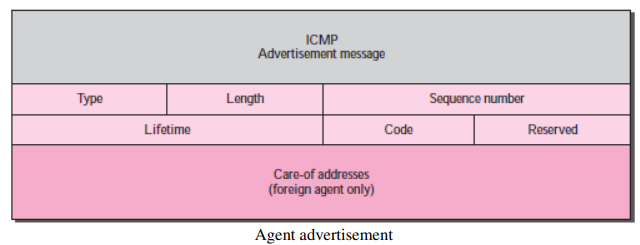
-
Router solicitation
-
-
-
Registration
- After a mobile host has moved to a foreign network and discovered the foreign agent -> it must register!
- Request and Reply
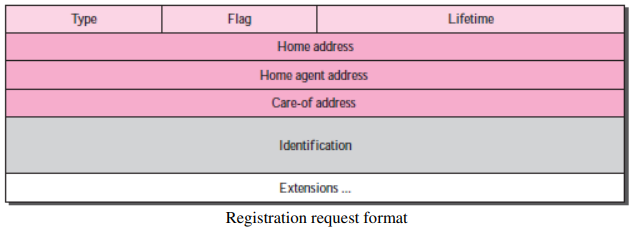
-
Data transfer
- The movement of the mobile host is transparent to the rest of the Internet..
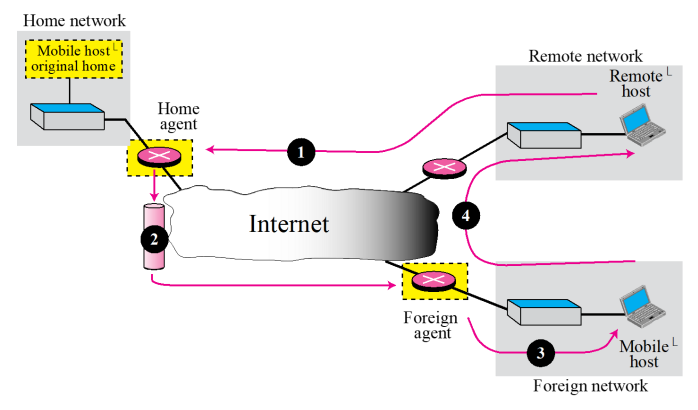
- From Remote Host to Home Agent
The remote host sends a packet as though the mobile host is at its home network.
This is done using the proxy ARP. - From Home Agent to Foreign Agent
After receiving the packet, the home agent sends the packet to the foreign agent using the tunneling concept. - From Fereign Agent to Mobile Host
- From Mobile Host to Remote Host
When a mobile host wants to send a packet to a remote host, it sends as it does normally.
- Mobile host
- Source - home address
- Destination - address of remote host
The packet comes from th foreign network, it has the home address of the mobile host.
-> Remote host is unaware of any movement by the mobile host.
- The movement of the mobile host is transparent to the rest of the Internet..
There are inefficiencies.. 😥
Inefficiency in Mobile IP
- Double crossing
- Double Crossing occurs when a remote host communicates with a mobile host that has moved th the same network(or site) as the remote host.
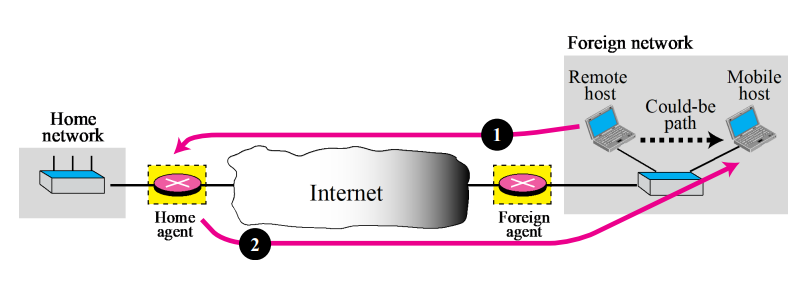
- When the mobile host sends to the remote host → No inefficiency!
- When the remote host sends a packet to the mobile host → the packet crosses the Internet twice
- Double Crossing occurs when a remote host communicates with a mobile host that has moved th the same network(or site) as the remote host.
- Triangle routing
- Triangle routing occurs when the remote host communicates with a mobile host that is not attached to the same network(or site) as the mobile host
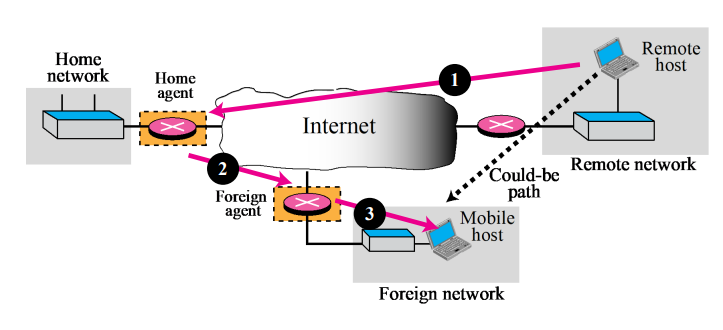
- When the mobile host sends to the remote host → No inefficiency!
- When the remote host sends to the mobile host, the packet goes from the remote host to the home agent and then to the mobile host
- Triangle routing occurs when the remote host communicates with a mobile host that is not attached to the same network(or site) as the mobile host
- The reson of this inefficiency?
- Home Agent manages the location/address information.
***
Mobile IPv4 RFC 문서입니다아.
글로벌소프트웨어캠퍼스와 교보DTS가 함께 진행하는 챌린지입니다.



야옹 야옹 야야옹