1. NoSQL이란 ?
기존 RDBMS 방식을 탈피한 데이터베이스를 의미
기존의 관계형 DB가 가지고 있는 특성뿐만 아니라 다른 특성들을 부가적으로 지원
RDBMS가 가지고 있는 한계를 극복하기 위한 데이터 저장소의 새로운 형태로, 수평적 확장성을 가지고 있음 문서, 그래프, 키 값, 인 메모리, 검색을 포함해 다양한 데이터 모델을 사용
1.1 NoSQL 특징
- DBMS와 달리 데이터간의 관계를 정의하지 않음
- RDBMS에 비해 훨씬 더 대용량의 데이터를 저장할 수 있음
- 반정형화, 비정형화된 데이터에 적합
- 분산형 구조이고 확장성이 뛰어남
- 고정되지 않은 테이블 스키마를 가짐
2. Redis란?
Remote Dictionary Server의 약자로, 원격 Dictinary 자료구조 서버.
레디스는 세계에서 가장 인기있는 Key-Value Store 중 하나
Key로 올 수 있는 자료형은 기본적으로 String이지만, Value는 다양한 타입을 지원
2.1 자바 해쉬맵과의 비교
둘 다 key-value 기반이고, 메모리 베이스며, 원하는 value를 원하는 표현 방식으로 넣을 수 있음
서버가 1대 있다는 가정에선 Redis의 장점이 크게 보이지 않지만, 분산 환경을 대입하면 장점이 보임
- 분산 환경에서의 장점 유저 요청이 크게 늘어나 서버를 몇 대 증설하였지만, 동일한 해쉬맵 데이터를 참조해야할 상황이 있다고 가정 이 때 원격 프로세스간에 동일한 해쉬맵 데이터를 참조해야 할 때, 분산환경에선 원격 프로세스간 데이터를 동기화 하기 어렵. 이 때 별도의 레디스 서버를 구성하고, 해당 레디스에서 값을 꺼내 쓴다면 메모리 기반 데이터 구조의 빠른 응답성을 확보함과 동시에 데이터 불일치 문제를 해결할 수 있음
- DBMS로서의 장점 또한 어플리케이션을 종료하면 휘발되어 사라져버리는 HashMap과 달리, Redis는 다양한 영속성(디스크에 백업) 옵션을 제공
Redis란? Spring boot 를 활용한 redis 사용
2.2 Redis 맥북에서 설치
$ brew install redis # Redis 설치$ brew services start redis # Redis 실행
$ brew services stop redis # Redis 중지
$ brew services restart redis # Redis 재시작$ redis-cli # CLI 사용3. 스프링에서 Redis 연동에 대한 이슈 생성
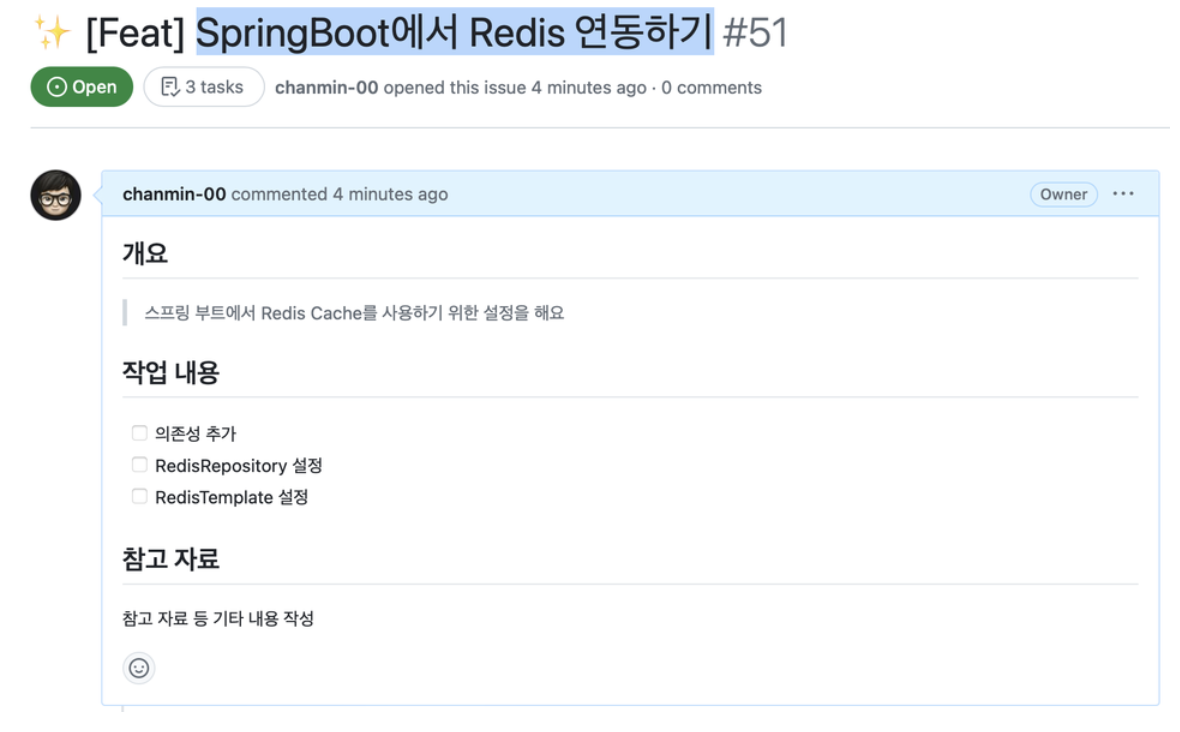
4. SpringBoot에서 Redis 설정
Spring Boot 에서 Redis 를 사용하는 방법은 RedisRepository 와 RedisTemplate 두 가지
이를 사용하기 위해서는 공통 의존성 주입이 필요
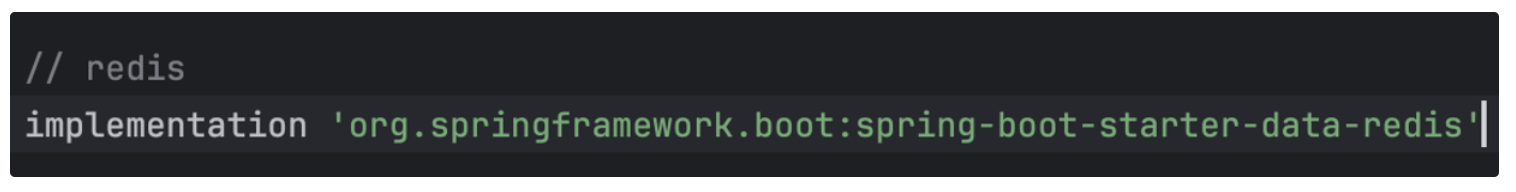
build.gradle에spring-boot-starter-data-redis추가하고 빌드
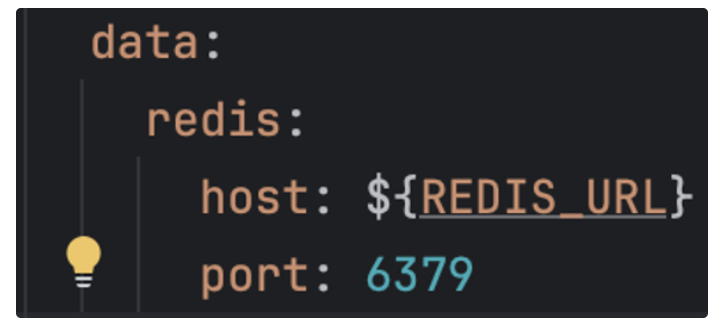
spring:
data:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379application.yaml에 host 와 port 를 설정localhost:6379는 기본값이기 때문에 만약 Redis 를localhost:6379로 띄웠다면 따로 설정하지 않아도 연결이 됨- 운영서버에서는 localhost가 아닌 별도의 엔드포인트를 사용하기 때문에 환경변수로 설정을 하고 Configuration 에서 Bean 에 등록
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.data.redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.data.redis.port}")
private int port;
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(host, port);
}
}- Redis 사용을 위한 기본 Configuration
4.1 RedisRepository
Spring Data Redis 의 Redis Repository 를 이용하면 간단하게 Domain Entity 를 Redis Hash 로 만들 수 있음
하지만 트랜잭션을 지원하지 않기 때문에 만약 트랜잭션을 적용하고 싶다면 RedisTemplate 을 사용
4.2 RedisTemplate
RedisTemplate 을 사용하면 특정 Entity 뿐만 아니라 여러가지 원하는 타입을 넣을 수 있음
template 을 선언한 후 원하는 타입에 맞는 Operations 을 꺼내서 사용
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.data.redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.data.redis.port}")
private int port;
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(host, port);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<?, ?> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<?, ?> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory());
return redisTemplate;
}
}- Config 파일에 설정 추가
RedisTemplate에LettuceConnectionFactory을 적용해주기 위해 설정
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTemplateTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
@Test
void testStrings() {
// given: 테스트 준비 단계, Redis에서 값을 설정하고 가져오기 위한 ValueOperations 객체를 생성합니다.
ValueOperations<String, String> valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
// 사용할 Redis 키를 정의합니다.
String key = "stringKey";
// when: 테스트 실행 단계, 정의한 키에 값을 설정합니다.
valueOperations.set(key, "hello");
// then: 테스트 검증 단계, Redis에서 값을 가져와서 예상한 값과 일치하는지 확인합니다.
String value = valueOperations.get(key);
// 가져온 값이 "hello"와 같은지 검증합니다.
assertThat(value).isEqualTo("hello");
}
@Test
void testSet() {
// given
SetOperations<String, String> setOperations = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
String key = "setKey";
// when
setOperations.add(key, "h", "e", "l", "l", "o");
// then
Set<String> members = setOperations.members(key);
Long size = setOperations.size(key);
assertThat(members).containsOnly("h", "e", "l", "o");
assertThat(size).isEqualTo(4);
}
@Test
void testHash() {
// given
HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
String key = "hashKey";
// when
hashOperations.put(key, "hello", "world");
// then
Object value = hashOperations.get(key, "hello");
assertThat(value).isEqualTo("world");
Map<Object, Object> entries = hashOperations.entries(key);
assertThat(entries.keySet()).containsExactly("hello");
assertThat(entries.values()).containsExactly("world");
Long size = hashOperations.size(key);
assertThat(size).isEqualTo(entries.size());
}
}
- Test 파일 추가
- 위에서부터 차례대로 Strings, Set, Hash 자료구조에 대한 Operations
- redisTemplate 을 주입받은 후에 원하는 Key, Value 타입에 맞게 Operations 을 선언해서 사용할 수 있음.
- 가장 흔하게 사용되는 RedisTemplate<String, String> 을 지원하는 StringRedisTemplate 타입도 따로 있음