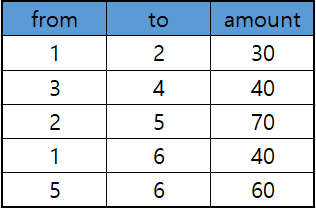
문제
아이디어
- 박스를 받는 마을번호를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬한다. 왜냐하면 최대한 빨리 트럭에 실었던 박스를 배송해야 최대 박스 수를 구하기 유리하기 때문이다.
- 위와 같이 정렬하면 이동 경로가 뒤죽박죽이 될 수 있기 때문에 각 마을에서 박스를 얼마나 내리는지, 트럭에 남은 용량은 얼마가 될지 추적하기가 어렵다. 따라서 크기
N의 용량 배열을 두어 각 마을에서 트럭이 담을 수 있는 용량을 관리한다.
예제 입력 2 기준 과정은 다음과 같다.
0. 박스 정보 정렬, 용량 관리 배열 초기화
- 초기는 트럭의 용량
C만큼이다.
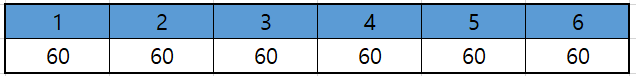
1. 1번에서 2번으로 30만큼 배송
- 총 배송 박스 : 30
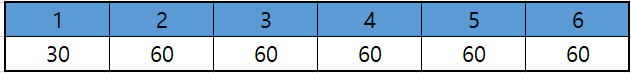
2. 3번에서 4번으로 40만큼 배송
- 총 배송 박스 : 30 + 40
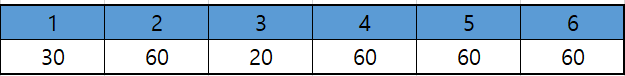
3. 2번에서 5번으로 70만큼 배송
- 2번 ~ 5번 사이에서는 20 용량을 넘을 수 없기 때문에 20만큼만 배송한다.
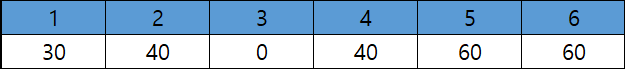
- 총 배송 박스 : 30 + 40 + 20
4. 1번에서 6번으로 40만큼 배송
- 1번 ~ 6번 사이에서는 0 용량을 넘을 수 없기 때문에 배송할 수 없다.
5. 5번에서 6번으로 60만큼 배송
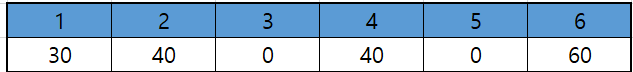
- 총 배송 박스 : 30 + 40 + 20 + 60 = 150
예상 시간 복잡도
- 예상 시간 복잡도 :
O(M log M)
코드 구현
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class BJ_8980 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //마을 수
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); //트럭의 용량
int m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); //보내는 박스 개수
Box[] boxes = new Box[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int amount = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
boxes[i] = new Box(from, to, amount);
}
Arrays.sort(boxes);
int[] capacity = new int[n + 1]; //각 마을에서 트럭이 담을 수 있는 용량
Arrays.fill(capacity, c);
int total = 0;
for (Box box : boxes) {
int from = box.from;
int to = box.to;
int amount = box.amount;
//from ~ to 구간에서 트럭이 실을 수 있는 최대 박스 수
int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = from; i < to; i++) {
max = Math.min(max, capacity[i]);
}
//트럭의 최대 용량을 넘지 않도록 조정
//최대 용량을 넘지 않더라도 필요한 만큼만 배송해 용량을 최대한 아낀다.
max = Math.min(max, amount);
//from ~ to 구간 트럭에 실은 박스만큼 감소
for (int i = from; i < to; i++) {
capacity[i] -= max;
}
total += max;
}
System.out.println(total);
}
static class Box implements Comparable<Box> {
int from, to, amount;
public Box(int from, int to, int amount) {
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.amount = amount;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Box o) {
if (this.to == o.to) {
return this.from - o.from;
}
return this.to - o.to;
}
}
}