JS as a language
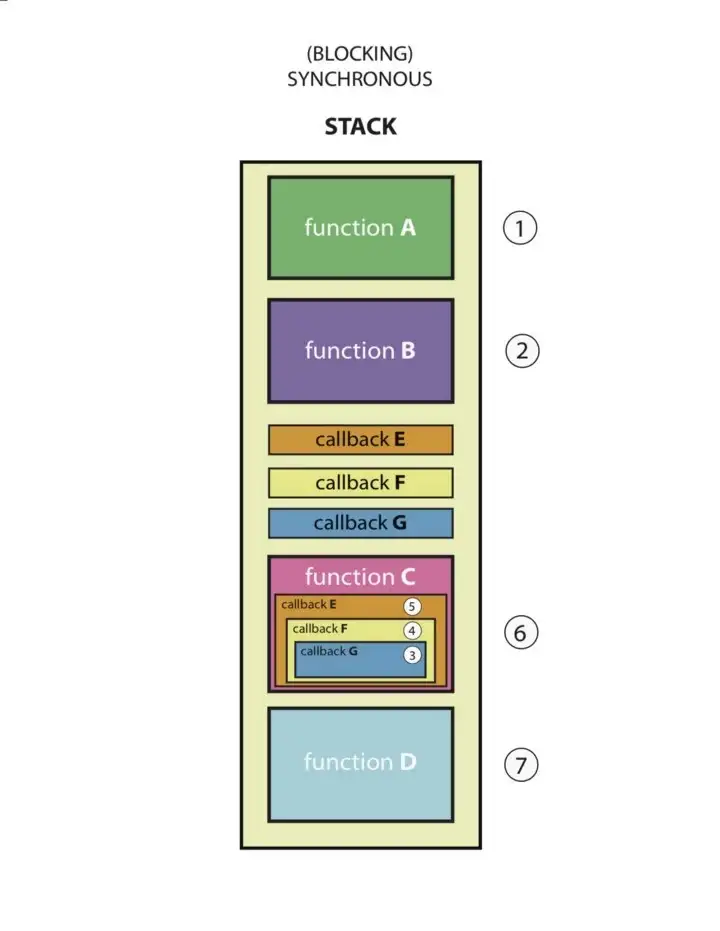
Javascript is a synchronous, blocking, single-threaded language. Basically means that there can only be one process at a single time. Therefore, it's slow when it comes to handling multiple requests. The solution to this is manipulating JS to behave in an asynchronous way.
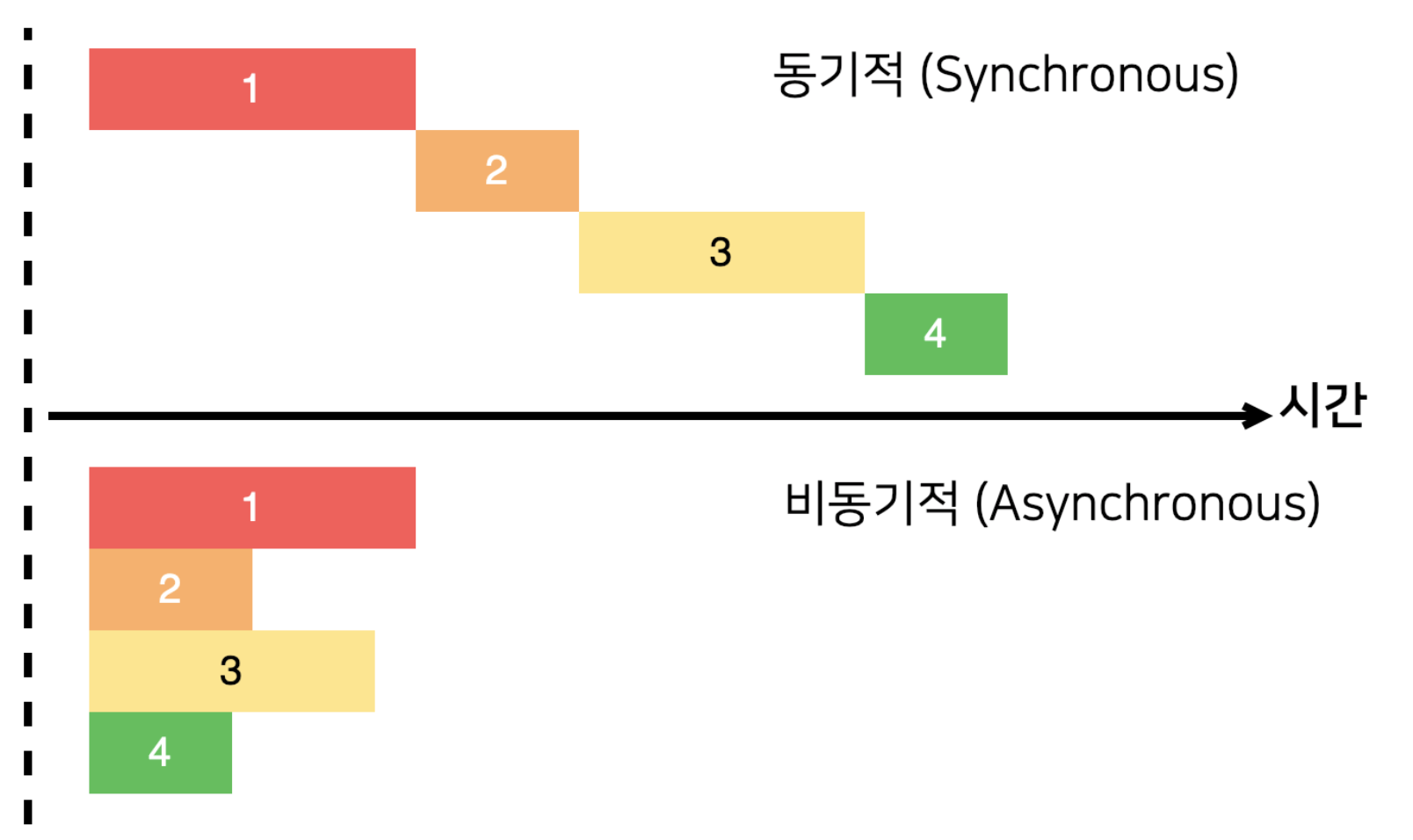
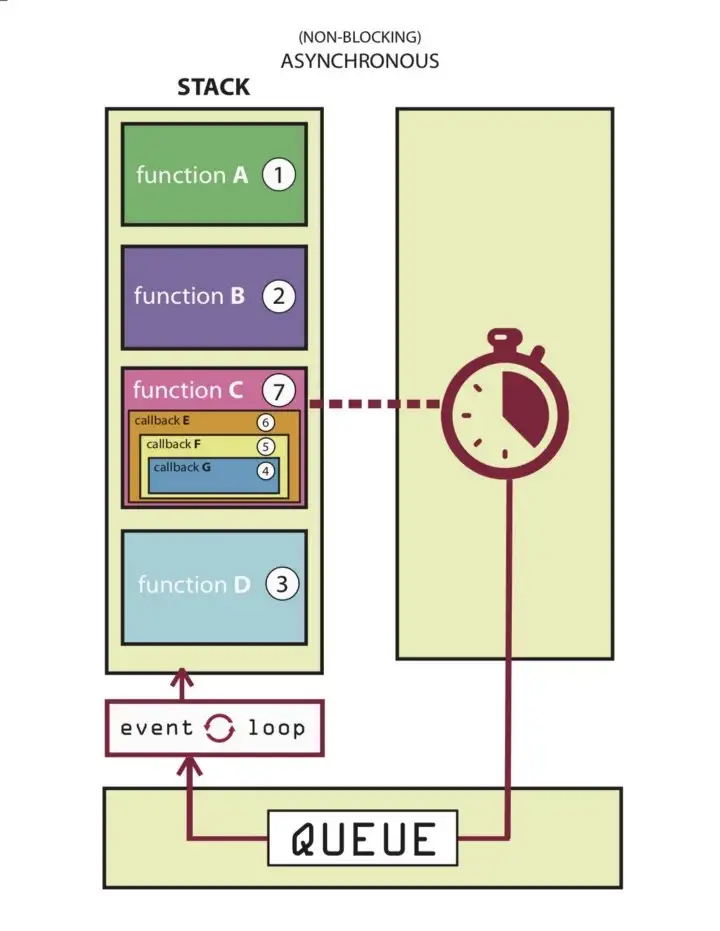
Running asynchronously allows for simultaneous processing of various tasks without stopping the workflow. It also allows other functions to be called in the process of waiting.
Methods
Asynchronous Callbacks
The earliest and most straightforward solution to being stuck in the synchronous world is using asynchronous callbacks (think setTimeout()).
Let’s use a database request as an example: asynchronous callbacks allow you to invoke a callback function which sends a database request (and any other nested callbacks) off to your app, where it waits for a response from the database, freeing up the rest of your code to continue running.
Asynchronous callbacks are valid solutions but since we do not know when func c will return all dependent fucntions/code must be nested inside func c.
This act of nesting often results in a phenomenon called "callback hell"

However, this is a pain to read and others to interpret what is going on.
Promise
The solution to callback hells is a promise. Unlike async callbacks, promises instead bundles all dependencies into one code block and is able to be separated.
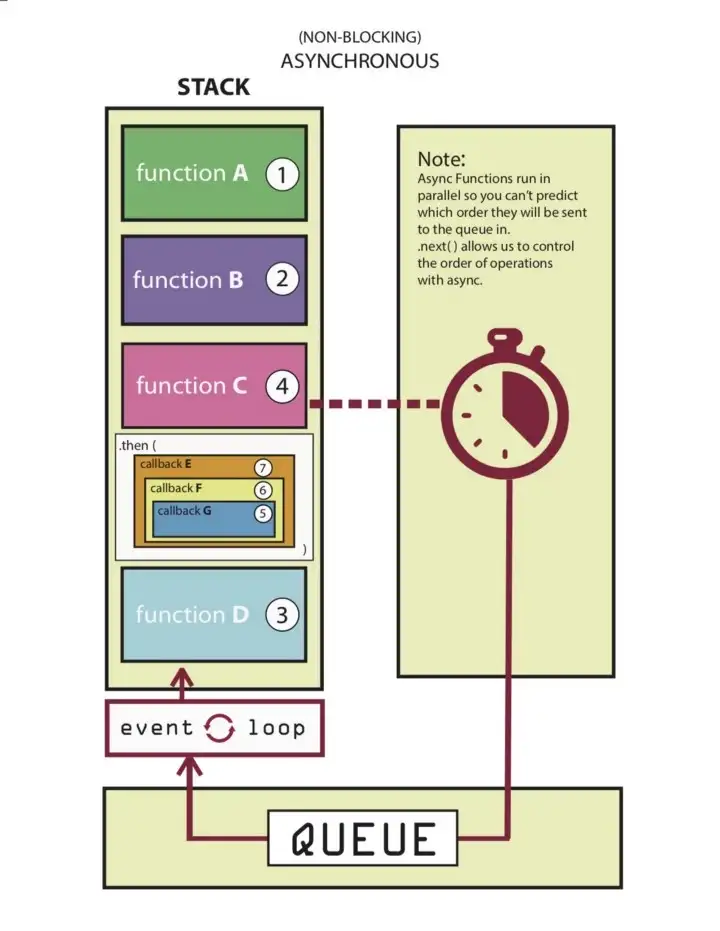
Now we can send the async callback func c and use .then() to hold all other dependencies and run them only when func c returns.
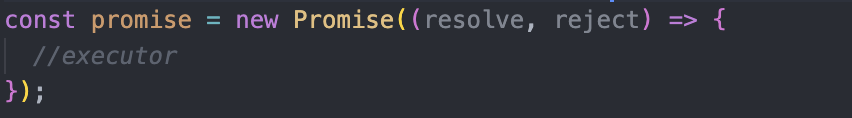
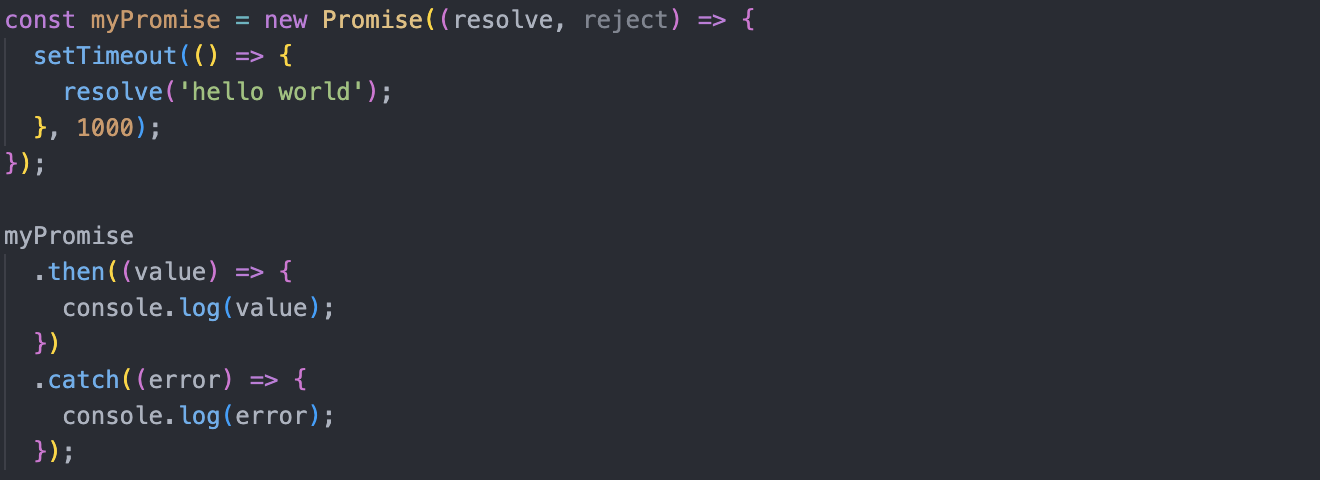
resolve is automatically executed when a new Promise is created. The executor argument resolve, reject, is a callback provided by JavaScript itself.
If you want to do more use .then() to run your desired method. .then() will run when the code succeeds and .catch() runs when there is an error.
async/await
Every async function returns a promise, and await functions act/functions as a promise.

async
async has the function return a promise
await
When the function meets an await it waits for the promise to be processed.
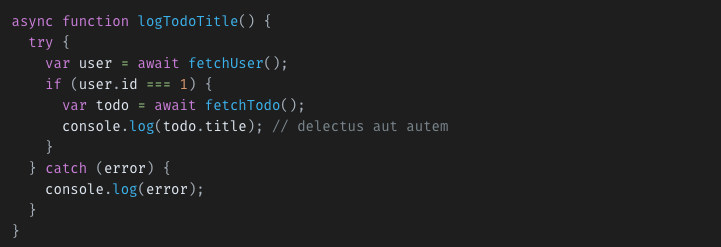
Example
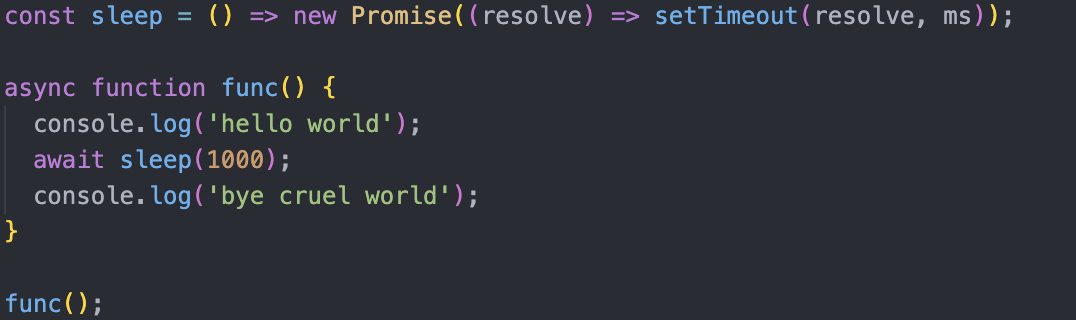
To handle errors async & await uses try-catch