Card
@Composable
public fun Card(
onClick: () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
enabled: Boolean = true,
shape: Shape = CardDefaults.shape,
colors: CardColors = CardDefaults.cardColors(),
elevation: CardElevation = CardDefaults.cardElevation(),
border: BorderStroke? = null,
interactionSource: MutableInteractionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() },
content: @Composable() (ColumnScope.() -> Unit)
): Unit카드 형태의 UI 요소를 생성할 때 사용
이 함수는 여러 매개변수를 통해 카드의 모양, 색상, 동작 등을 커스터마이징할 수 있다.enabled: 카드를 클릭할 수 있는지 여부를 결정.
shape: 카드의 모양을 정의하는 Shape 객체. 기본값은 CardDefaults.shape
border: 카드의 테두리를 정의하는 BorderStroke 객체. 기본값은 null
interactionSource
사용자와의 상호작용을 추적하는 MutableInteractionSource 객체
기본값은 remember { MutableInteractionSource() }
Column
다음 매개변수를 통해 정렬할 수 있다.
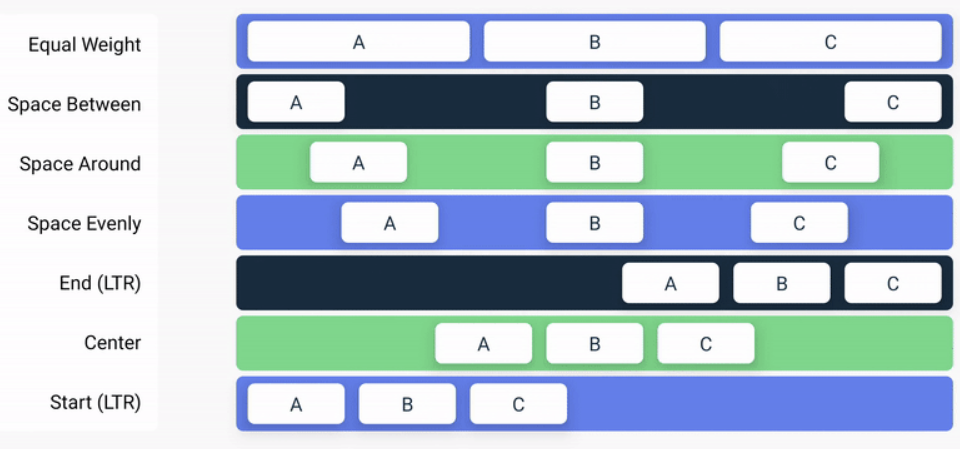
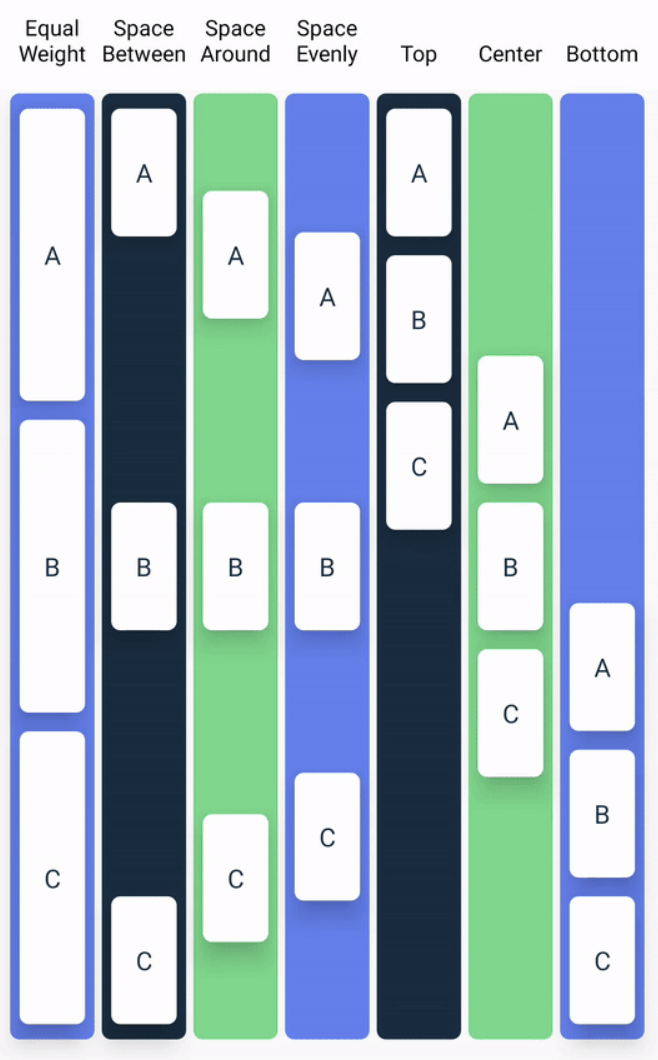
- verticalArrangement: Arrangement.Vertical // Arrangement.(Top-deafult, Center, Bottom, SpaceBetween, SpaceEvenly)를 통해 수직 정렬 할 수 있다.
- horizontalAlignment: Alignment.Horizontal // Alignment.(Start, CenterHorizontally, End) 를 통해 정렬
- content: @Composable() (ColumnScope.() -> Unit)
- modifier: Modifier,
FlowRow
@Composable
@ExperimentalLayoutApi
public inline fun FlowRow(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
horizontalArrangement: Arrangement.Horizontal = Arrangement.Start,
verticalArrangement: Arrangement.Vertical = Arrangement.Top,
maxItemsInEachRow: Int = Int.MAX_VALUE,
content: @Composable() (FlowRowScope.() -> Unit)
): Unit수평으로 아이템을 배치하고, 공간이 부족하면 자동으로 다음 줄로 넘어가서 배치하는 레이아웃
- 주로 리스트나 그리드 형태로 아이템을 배치할 때 사용
maxItemsInEachRow : 한 줄에
ListItem
@Composable
public fun ListItem(
headlineContent: @Composable () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
overlineContent: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
supportingContent: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
leadingContent: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
trailingContent: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
colors: ListItemColors = ListItemDefaults.colors(),
tonalElevation: Dp = ListItemDefaults.Elevation,
shadowElevation: Dp = ListItemDefaults.Elevation
): UnitListItem은 리스트 항목을 쉽게 구성할 수 있도록 제공.
이 함수는 여러 슬롯을 사용하여 리스트 항목의 다양한 부분을 정의할 수 있다.
이를 통해 각 리스트 항목의 헤드라인, 서포팅 텍스트, 선행 및 후행 콘텐츠 등을
쉽게 구성할 수 있다LazyVerticalStaggeredGrid
@Composable
public fun LazyVerticalStaggeredGrid(
columns: StaggeredGridCells,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
state: LazyStaggeredGridState = rememberLazyStaggeredGridState(),
contentPadding: PaddingValues = PaddingValues(0.dp),
reverseLayout: Boolean = false,
verticalItemSpacing: Dp = 0.dp,
horizontalArrangement: Arrangement.Horizontal = Arrangement.spacedBy(0.dp),
flingBehavior: FlingBehavior = ScrollableDefaults.flingBehavior(),
userScrollEnabled: Boolean = true,
content: LazyStaggeredGridScope.() -> Unit
): Unit스크롤 가능한 수직 스태거드 그리드(아이템들이 비대칭적으로 배치되는 그리드)를
만들기 위한 함수
스태거드 그리드는, 아이템의 크기가 일정하지 않거나 다양한 경우에 유용columns: StaggeredGridCells
그리드의 열 수를 정의합니다.
StaggeredGridCells.Fixed와 StaggeredGridCells.Adaptive로 설정
📌
StaggeredGridCells.Fixed
- 고정된 수의 열을 생성
- StaggeredGridCells.Fixed(3)은 3개의 고정된 열을 가진 스태거드 그리드를 생성
StaggeredGridCells.Adaptive
- 열의 크기를 기반으로 동적으로 열의 수를 조정
최소 열 크기를 지정하여 그리드가 화면 크기에 맞게 열의 수를 자동으로 조정 - StaggeredGridCells.Adaptive(150.dp)은 최소 열 크기가 150dp인 열을 생성하며, 화면 크기에 따라 열의 수가 동적으로 결정
state: LazyStaggeredGridState
그리드의 스크롤 상태를 관리하는 상태 객체입니다. 기본값은 rememberLazyStaggeredGridState()입니다.
verticalItemSpacing: Dp
각 아이템 사이의 수직 간격을 설정. 기본값은 0.dp
horizontalArrangement: Arrangement.Horizontal
각 열 사이의 수평 간격을 설정. 기본값은 Arrangement.spacedBy(0.dp)
flingBehavior: FlingBehavior
플링(fling) 동작을 정의하는 객체.
기본값은 ScrollableDefaults.flingBehavior()
📌 플링(fling) 동작
사용자 인터페이스(UI)에서 스크롤과 관련된 제스처 중 하나로, 사용자가 스크린을 빠르게 스와이프한 후, 그 스와이프 동작에 따른 관성으로 인해 콘텐츠가 자동으로 스크롤되는 동작을 의미. 플링은 일반적으로 스크롤을 멈추지 않고 자연스럽게 계속 움직이게 하여 사용자가 더 부드럽고 직관적인 경험을 할 수 있도록 한다
Row
- modifier: Modifier,
- horizontalArrangement: Arrangement.Horizontal,
- verticalAlignment: Alignment.Vertical,
- content: @Composable() (RowScope.() -> Unit)
| Row | Column |
|---|---|
 |  |
LazyColumn과 LazyRow
LazyColumn : 화면에 보이는 항목만 렌더링하므로 항목이 많은 목록을 렌더링할 때 성능이 향상 된다.
- 기본적인 사용법 : LazyColumn API는 범위 내에서 items 요소를 제공하며, 여기서 로직을 렌더링하는 개별 항목은 다음과 같이 작성된다.
- Android view의 RecyclerView와 동일
📌참고: LazyColumn은 RecyclerView와 달리 자식 요소를 재활용하지 않는다.
LazyColumn은 스크롤하는 동안 새로운 Composable을 생성하며, Android View를 인스턴스화하는 것에 비해 Composable을 생성하는 것이 더 효율적이기 때문이다.
import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.LazyColumn
import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.items
...
@Composable
private fun Greetings(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
names: List<String> = List(1000) { "$it" }
) {
LazyColumn(modifier = modifier.padding(vertical = 4.dp)) {
items(items = names) { name ->
Greeting(name = name)
}
}
}LazyRow
-
modifier: Modifier,
-
state: LazyListState,
-
contentPadding: PaddingValues(all:Dp or horizontal: Dp, vertical: Dp)
// modifier로 패딩을 줄 경우 콘텐츠를 자르게 되는 현상이 발생하기 때문에 contentPadding에 패딩을 줘서 이런 현상을 막아주도록 한다. -
reverseLayout: Boolean,
-
horizontalArrangement: Arrangement.Horizontal,
// Arrangement.spacedBy(dp)를 사용하여 각 하위 컴포저블 사이에 고정된 공간을 추가할 수 있다. -
verticalAlignment: Alignment.Vertical,
-
flingBehavior: FlingBehavior,
-
userScrollEnabled: Boolean,
-
content: LazyListScope.() -> Unit
LazyColumn
- modifier: Modifier,
- state: LazyListState,
- contentPadding: PaddingValues,
- reverseLayout: Boolean,
- verticalArrangement: Arrangement.Vertical,
- horizontalAlignment: Alignment.Horizontal,
- flingBehavior: FlingBehavior,
- userScrollEnabled: Boolean,
- content: LazyListScope.() -> Unit
LazyHorizontalGrid
rows: GridCells,
// GridCells.(Fixed, FixedSize, Adaptive)
1. Fixed(count:Int) : 고정된 열 수를 가진 그리드 생성
2. FixedSize(size:Dp) : ?
3. Adaptive(minSize:Dp) : 최소 크기를 가진 적응형 그리드 생성 각 행은 최소 크기를 기준으로 가능한 많은 아이템을 포함하며, 화면 크기에 따라 열의 수가 조정된다.
modifier: Modifier,
state: LazyGridState,
contentPadding: PaddingValues,
reverseLayout: Boolean,
horizontalArrangement: Arrangement.Horizontal, // 수평 간격
verticalArrangement: Arrangement.Vertical, // 수직 간격
flingBehavior: FlingBehavior,
userScrollEnabled: Boolean,
content: LazyGridScope.() -> Unit
Surface
Compose Material 라이브러리의 구성요소이다. Material Design 패턴을 따르며, 앱의 테마를 변경하여 조정할 수 있다.
- modifier: Modifier,
- shape: Shape, // MaterialTheme.shapes.medium을 통해 둥근 모서리 테두리로 설정 할 수 있다.
- color: Color,
- contentColor: Color,
- tonalElevation: Dp,
- shadowElevation: Dp,
- border: BorderStroke?,
- content: @Composable () -> Unit
Text
- text: String,
- modifier: Modifier,
- color: Color,
- fontSize: TextUnit,
- fontStyle: FontStyle?,
- fontWeight: FontWeight?,
- fontFamily: FontFamily?,
- letterSpacing: TextUnit,
- textDecoration: TextDecoration?,
- textAlign: TextAlign?,
- lineHeight: TextUnit,
- overflow: TextOverflow,
- softWrap: Boolean,
- maxLines: Int,
- minLines: Int,
- onTextLayout: (TextLayoutResult) -> Unit,
- style: TextStyle // MaterialTheme.typography.* 로 설정가능
TextField
@OptIn(markerClass = {androidx.compose.material3.ExperimentalMaterial3Api::class})
@Composable
public fun TextField(
value: String,
onValueChange: (String) -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
enabled: Boolean = true,
readOnly: Boolean = false,
textStyle: TextStyle = LocalTextStyle.current,
label: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
placeholder: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
leadingIcon: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
trailingIcon: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
prefix: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
suffix: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
supportingText: @Composable() (() -> Unit)? = null,
isError: Boolean = false,
visualTransformation: VisualTransformation = VisualTransformation.None,
keyboardOptions: KeyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions.Default,
keyboardActions: KeyboardActions = KeyboardActions.Default,
singleLine: Boolean = false,
maxLines: Int = if (singleLine) 1 else Int.MAX_VALUE,
minLines: Int = 1,
interactionSource: MutableInteractionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() },
shape: Shape = TextFieldDefaults.shape,
colors: TextFieldColors = TextFieldDefaults.colors()
): Unitprefix: 텍스트 필드의 앞에 표시
suffix: 텍스트 필드의 뒤에 표시
supportingText: 텍스트 필드의 아래쪽에 표시되는 지원 텍스트를 나타낸다
visualTransformation
- 텍스트 필드의 시각적 변환을 지정.
- 예를 들어, 비밀번호 입력 시 텍스트를 마스킹할 수 있다
keyboardOptions - 키보드의 동작을 지정. 예를 들어, 입력 유형(숫자, 텍스트 등)과 액션(완료, 다음 등)을 설정할 수 있다
keyboardActions - 키보드 액션 버튼이 눌렸을 때 수행할 작업을 지정.
- 예를 들어, 완료 버튼을 눌렀을 때 동작을 정의할 수 있다
interactionSource - 상호작용 상태를 처리하는 데 사용
- 예를 들어, 클릭, 포커스 등의 상태를 추적할 수 있다.
BasicTextField
@Composable
public fun BasicTextField(
value: String,
onValueChange: (String) -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
enabled: Boolean = true,
readOnly: Boolean = false,
textStyle: TextStyle = TextStyle.Default,
keyboardOptions: KeyboardOptions = KeyboardOptions.Default,
keyboardActions: KeyboardActions = KeyboardActions.Default,
singleLine: Boolean = false,
maxLines: Int = if (singleLine) 1 else Int.MAX_VALUE,
minLines: Int = 1,
visualTransformation: VisualTransformation = VisualTransformation.None,
onTextLayout: (TextLayoutResult) -> Unit = {},
interactionSource: MutableInteractionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() },
cursorBrush: Brush = SolidColor(Color.Black),
decorationBox: @Composable (innerTextField: @Composable () -> Unit) -> Unit = @Composable { innerTextField -> innerTextField() }
): Unit- 텍스트 입력을 처리하기 위한 기본적인 텍스트 필드를 구현
- 이는 커스터마이징 가능한 텍스트 필드를 만들기 위한 컴포저블 함수로, 다양한 매개변수를 통해 텍스트 필드의 동작과 스타일을 세밀하게 조정할 수 있다.
onTextLayout
- 텍스트가 레이아웃될 때 호출되는 콜백 함수
- 텍스트 레이아웃의 결과를 처리할 수 있다
decorationBox
- 텍스트 필드를 감싸는 데코레이션을 정의
- innerTextField는 텍스트 필드 컴포저블 함수로, 이를 감싸는 커스텀 UI를 정의할 수 있. 기본값은 텍스트 필드를 그대로 출력
Image
- painter : Painter // 이미지
- contentDescription : String? // 이미지 부가 설명(텍스트), 이미지 설명이 라벨로 존재한다면 null값을 넣자
- contentScale : ContentScale // ContentScale.* 이미지의 크기 조절(여러 옵션이 존재한다. ex) Fit, FillBounds, Crop)
- Crop : 지정된 영역보다 작을 때는 이미지가 늘어나지 않고 지정된 영역에 맞추어 크롭되어 표시되며, 이미지가 지정된 영역보다 클 경우에는 이미지 축소된다.
- modifier: Modifier,
- alignment: Alignment,
- alpha: Float,
- colorFilter: ColorFilter?
Checkbox
checked: Boolean,
onCheckedChange: ((Boolean) -> Unit)?,
modifier: Modifier,
enabled: Boolean,
colors: CheckboxColors,
interactionSource: MutableInteractionSource
NavigationBar
컴포저블 내에서 하나 이상의 NavigationBarItem 요소를 추가하면 Material 라이브러리에 의해 자동으로 스타일이 지정된다.
modifier: Modifier,
containerColor: Color, // 하단 탐색의 배경색 설정
contentColor: Color,
tonalElevation: Dp,
windowInsets: WindowInsets,
content: @Composable() (RowScope.() -> Unit)
NavigationItem
selected: Boolean, // 초기 클릭 상태 지정
onClick: () -> Unit,
icon: @Composable () -> Unit, // 아이콘 설정
modifier: Modifier,
enabled: Boolean,
label: @Composable() (() -> Unit)?,
alwaysShowLabel: Boolean,
colors: NavigationBarItemColors,
interactionSource: MutableInteractionSource
NavigationRail
modifier: Modifier,
containerColor: Color,
contentColor: Color,
header: @Composable() (ColumnScope.() -> Unit)?,
windowInsets: WindowInsets,
content: @Composable() (ColumnScope.() -> Unit)
NavigationRailItem
selected: Boolean,
onClick: () -> Unit,
icon: @Composable () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier,
enabled: Boolean,
label: @Composable() (() -> Unit)?,
alwaysShowLabel: Boolean,
colors: NavigationRailItemColors,
interactionSource: MutableInteractionSource
Scaffold
Material Design을 구현하는 앱을 위한 최상위 수준 컴포저블을 제공한다. 여기에는 다양한 Material 개념의 슬롯이 포함되어 있다.
modifier: Modifier,
topBar: @Composable () -> Unit,
bottomBar: @Composable () -> Unit,
snackbarHost: @Composable () -> Unit,
floatingActionButton: @Composable () -> Unit,
floatingActionButtonPosition: FabPosition,
containerColor: Color,
contentColor: Color,
contentWindowInsets: WindowInsets,
content: @Composable (PaddingValues) -> Unit
AndroidView
public fun <T : View> AndroidView(
factory: (Context) -> T,
modifier: Modifier,
update: (T) -> Unit
): UnitAndroidView를 사용하면 factory에서 View를 생성할 수 있게 해준다. 또한 뷰가 확장되었을 때와 이후 리컴포지션에서 호출되는 update를 제공한다.
📌 AndroidView를 사용하면 프로그래미틱 방식으로 뷰를 만들 수 있다. XML 파일에서 뷰를 확장하려는 경우 androidx.compose.ui:ui-viewbinding 라이브러리의 AndroidViewBinding API와 함께 ViewBinding을 사용하면 된다.
SwipeToDismiss
@Composable
@ExperimentalMaterial3Api
@ComposableInferredTarget
public fun SwipeToDismiss(
state: DismissState,
background: @Composable() (RowScope.() -> Unit),
dismissContent: @Composable() (RowScope.() -> Unit),
modifier: Modifier,
directions: Set<DismissDirection>
): UnitMaterial 3 라이브러리의 일부로 제공되는 Compose 함수
주로, 사용자가 화면에서 스와이프하여 아이템을 제거하는 기능을 구현하는 데 사용
아이템을 제거하는 대신 일종의 "액션"을 수행하는 데에 활용할 수 있다.
- 예를 들어, 사용자가 아이템을 스와이프하여 일정 거리까지 옮기면 특정 작업을 수행하거나 사용자 정의 애니메이션을 트리거하는 등의 상황에 활용할 수 있다.
props
state: DismissState 타입으로, 스와이프 동작의 상태를 제어
background: 스와이프된 아이템의 배경을 그리기 위한 Composable 블록
dismissContent: 스와이프된 아이템을 표시하는 Composable 블록
modifier: Modifier를 통해 SwipeToDismiss의 외형을 조정할 수 있다.
directions: 스와이프가 허용되는 방향을 설정합니다. DismissDirection.StartToEnd 또는 DismissDirection.EndToStart 중 하나를 선택할 수 있다.
예시
SwipeToDismiss(
state = dismissState,
modifier = modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(100.dp),
dismissContent = { // content
},
background = { // dismiss content
val direction = dismissState.dismissDirection ?: return@SwipeToDismiss
val color by animateColorAsState(
when (dismissState.targetValue) {
DismissValue.Default -> backgroundColor.copy(alpha = 0.5f) // dismissThresholds 만족 안한 상태
DismissValue.DismissedToEnd -> Color.Green.copy(alpha = 0.4f) // -> 방향 스와이프 (수정)
DismissValue.DismissedToStart -> Color.Red.copy(alpha = 0.5f) // <- 방향 스와이프 (삭제)
}, label = ""
)
val icon = when (dismissState.targetValue) {
DismissValue.Default -> Icons.Default.Circle
DismissValue.DismissedToEnd -> Icons.Default.Edit
DismissValue.DismissedToStart -> Icons.Default.Delete
}
val scale by animateFloatAsState(
when (dismissState.targetValue == DismissValue.Default) {
true -> 0.8f
else -> 1.5f
}, label = ""
)
val alignment = when (direction) {
DismissDirection.EndToStart -> Alignment.CenterEnd
DismissDirection.StartToEnd -> Alignment.CenterStart
}
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(color)
.padding(horizontal = 30.dp),
contentAlignment = alignment
) {
Icon(
modifier = Modifier.scale(scale),
imageVector = icon,
contentDescription = null
)
}
}
)TopAppBar
@ExperimentalMaterial3Api
@Composable
@ComposableInferredTarget
public fun TopAppBar(
title: @Composable () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier,
navigationIcon: @Composable () -> Unit,
actions: @Composable() (RowScope.() -> Unit),
windowInsets: WindowInsets,
colors: TopAppBarColors,
scrollBehavior: TopAppBarScrollBehavior?
): Unittitle: @Composable () -> Unit 타입, 제목을 정의
navigationIcon: @Composable () -> Unit 타입, 네비게이션 아이콘을 정의
- Top App Bar 왼쪽에 표시
- 기본값은 COMPILED_CODE로, 네비게이션 아이콘이 없는 상태
actions: @Composable() (RowScope.() -> Unit) 타입, 추가적인 작업을 위한 아이콘 등을 정의
- toolbar menu에 해당하는 아이콘, 오른쪽 배치, RowScope로 감싸져 있어서 여러개 있어도 IconButton만 넣어주면 된다
- RowScope를 통해 행 레이아웃을 구성할 수 있다
- 기본값은 COMPILED_CODE로, 추가 작업이 없는 상태
windowInsets: WindowInsets 타입, 시스템 창(window insets)을 어떻게 처리할지 정의
- 기본값은 COMPILED_CODE로, 시스템 창에 대한 처리가 없음을 나타낸다
colors: TopAppBarColors 타입, 색상을 정의
- 이를 사용하여 배경색, 아이콘 색상 등을 지정
- 기본값은 COMPILED_CODE로, 색상이 지정되지 않은 상태
scrollBehavior: TopAppBarScrollBehavior 타입, 스크롤 동작을 정의
- 예를 들어, 스크롤에 따라 Top App Bar를 숨기거나 보이게 할 수 있다
- 기본값은 COMPILED_CODE로, 스크롤 동작이 지정되지 않은 상태
💡TopAppBarDefaults.enterAlwaysScrollBehavior() 등등 함수들이 있다.
스크롤 동작을 설정하는 함수
EnterAlways (기본값): 사용자가 아래로 스크롤할 때 앱 바가 위로 숨겨진다
- 사용자가 위로 스크롤하면 앱 바가 다시 나타난다
EnterAlwaysCollapsed: 앱 바가 항상 보이지만 스크롤할 때 축소된다 - 사용자가 아래로 스크롤하면 앱 바가 표시되고, 위로 스크롤하면 앱 바가 축소된다
ExitUntilCollapsed: 사용자가 아래로 스크롤할 때 앱 바가 숨겨진다(축소되진 않음) - 사용자가 위로 스크롤하면 앱 바가 다시 나타난다
CenterAlignedTopAppBar
Material Design 라이브러리에서 제공되는 컴포저블
- props를 사용하여 화면 상단에 중앙 정렬된 Top App Bar를 만들어준다
- 여러 가지 설정을 할 수 있도록 다양한 매개변수를 가지고 있다
@ExperimentalMaterial3Api
@Composable
@ComposableInferredTarget
public fun CenterAlignedTopAppBar(
title: @Composable () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = COMPILED_CODE,
navigationIcon: @Composable () -> Unit = COMPILED_CODE,
actions: @Composable() (RowScope.() -> Unit) = COMPILED_CODE,
windowInsets: WindowInsets = COMPILED_CODE,
colors: TopAppBarColors = COMPILED_CODE,
scrollBehavior: TopAppBarScrollBehavior? = COMPILED_CODE
): UnitNavHost
NavHost는 네비게이션을 관리하기 위한 중요한 요소 중 하나
- 앱에서 다양한 화면 간의 전환 및 스택 관리를 쉽게 할 수 있도록 도와주는 구성 요소
@Composable
public fun NavHost(
navController: NavHostController,
startDestination: String,
modifier: Modifier = COMPILED_CODE,
route: String? = COMPILED_CODE,
builder: NavGraphBuilder.() -> Unit
): UnitnavController: NavController 타입, 현재 앱의 네비게이션 상태를 나타낸다
- 네비게이션을 제어하고 화면 간 전환을 담당하는 중요한 요소
startDestination: String 타입, 앱이 시작될 때 첫 번째 목적지를 나타냄
- ex) "home", "detail", "settings" 등의 목적지 이름을 지정
route: String 타입, NavHost 자체의 경로를 정의
- 이것은 일반적으로는 사용되지 않는다
- NavHost를 중첩하여 사용할 때 자식 NavHost의 경로를 정의할 때 사용될 수 있다
- 본값은 COMPILED_CODE로, 사용되지 않는 기본값
builder: NavGraphBuilder.() -> Unit 타입, NavHost 안에서 목적지를 정의
- NavGraphBuilder는 네비게이션 그래프를 만들기 위한 DSL(Domain Specific Language)
- DSL을 사용하여 목적지와 목적지 간의 연결 등을 정의할 수 있다
예시
@Composable
fun MyApp() {
val navController = rememberNavController()
NavHost(navController = navController, startDestination = "screen1") {
composable(route = "screen1") {
Screen1(navController = navController)
}
composable(route = "screen2") {
Screen2()
}
}
}NavController와 startDestination이 필요
NavController는 현재 앱의 상태를 나타내며, 각 화면 간의 전환을 처리rememberNavController()을 사용하여 NavController를 생성하고 기억
startDestination은 앱이 시작될 때 처음 표시되는 화면을 지정
composable 함수는 NavHost의 두 번째 매개변수로 전달되는 builder 블록 안에서 사용
- builder 블록에서는 각 목적지에 해당하는 composable 함수를 정의하여 네비게이션 그래프를 구성
route 정의 예시
interface NavigationDestination {
//Unique name to define the path for a composable
val route: String
//String resource id to that contains title to be displayed for the
val titleRes: Int
}
object HomeDestination : NavigationDestination {
override val route = "home"
override val titleRes = R.string.app_name
}📌NavHostController
NavHostController는 앱의 네비게이션을 관리하고 화면 간의 전환을 처리하는 데 사용
목적지로 이동: navigate() 메서드를 사용, 다른 화면으로 이동
- 이 메서드는 목적지의 경로를 받아서 해당 화면으로 이동
뒤로가기: popBackStack(), navigateUp() 메서드를 사용, 현재 화면을 빠져나와 이전 화면으로 돌아갈 수 있다
- 이는 일반적으로 뒤로가기 버튼이나 기기의 뒤로가기 동작과 관련
- navigateUp()은 이전 화면이 없으면 앱을 닫습니다.
📌 popBackStack(), navigateUp() 차이점
동작 방식
navigateUp(): 이전 화면이 없으면 앱을 닫는다
popBackStack(): 이전 화면이 스택에 없으면 앱을 닫지 않고 현재 화면만 닫는다
스택 조작
navigateUp(): 네비게이션 스택에서 현재 목적지를 제거하지 않고 이동
- 스택 상태를 유지
popBackStack(): 네비게이션 스택에서 현재 목적지를 제거하고 이동 - 스택의 상태가 변경
앱 내부에서의 네비게이션 스택 관리: NavHostController는 네비게이션 스택을 관리
- 이 스택은 앱 내에서 현재 위치한 화면의 이력을 추적
- 새로운 화면으로 이동하면 스택에 추가되고, 뒤로가기를 하면 스택에서 제거
Safe Args와 함께 사용: Navigation Compose에서는 Safe Args를 사용하여 목적지로 데이터를 전달할 수 있다
SideEffect
SideEffect는 상태의 변경이나 다른 효과를 일으킬 수 있는 코드 블록을 실행하는 데 사용
📌 사용하는 이유
Composable 함수는 렌더링 시 매번 호출되기 때문에 Composable 함수 내에 상태 변경 로직을 넣으면 렌더링마다 상태가 변경되어 원하지 않는 결과를 초래할 수 있다
SideEffect를 사용하면 Composable 함수의 주된 기능과는 별개로 상태 변경 로직을 분리하여 사이드 이펙트를 발생시킬 수 있다
SideEffect 안에서 상태 변경이 일어나면, Composable 함수가 다시 호출되지 않고 이펙트만 발생
- 불필요한 재렌더링을 피하고 성능을 최적화
- 코드의 가독성을 높이고 상태 변경을 명확히 분리하여 관리할 수 있다
@Composable
public fun SideEffect(
effect: () -> Unit
): Uniteffect: () -> Unit 타입, 상태의 변경이나 다른 효과를 일으킬 수 있는 코드 블록을 받는다
- 이 코드 블록은 상태를 변경하는 것과 같은 사이드 이펙트를 발생시키는데 사용
BackdropScaffold
@OptIn(markerClass = {androidx. compose. material. ExperimentalMaterialApi::class})
@Composable
public fun BackdropScaffold(
appBar: @Composable () -> Unit,
backLayerContent: @Composable () -> Unit,
frontLayerContent: @Composable () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
// frontLayerContent가 닫혀있는지, 열려있는지 결정 BackdopValue.Revealed / BackdopValue.Concealed
scaffoldState: BackdropScaffoldState = rememberBackdropScaffoldState(Concealed),
snackbarHost: @Composable (SnackbarHostState) -> Unit = { SnackbarHost(it) },
// 백드롭을 열고 닫는 기능을 사용할지 여부
gesturesEnabled: Boolean = true,
// frontLayer를 올렸을 때, 보이는 backLayer의 최소 높이를 지정. 기본값은 PeekHeight(56.dp)
peekHeight: Dp = BackdropScaffoldDefaults.PeekHeight,
// frontLayer의 헤더 높이 설정. 기본값 HeaderHeight(48.dp)
headerHeight: Dp = BackdropScaffoldDefaults.HeaderHeight,
// 기본값: appBar가 항상보임. false: frontLayer가 끝까지 올라가야 appBar 보임
persistentAppBar: Boolean = true,
// 기본값(true): frontLayer가 backLayer밑으로 고정된 위치를 가짐.
// false: frontLayer가 고정된 위치가 아닌 끝까지 올라가거나 헤더만 보이게 됨
stickyFrontLayer: Boolean = true,
backLayerBackgroundColor: Color = MaterialTheme.colors. primary,
backLayerContentColor: Color = contentColorFor(backLayerBackgroundColor),
frontLayerShape: Shape = BackdropScaffoldDefaults.frontLayerShape,
frontLayerElevation: Dp = BackdropScaffoldDefaults.FrontLayerElevation,
frontLayerBackgroundColor: Color = MaterialTheme.colors. surface,
frontLayerContentColor: Color = contentColorFor(frontLayerBackgroundColor),
// frontLayer가 완전히 열리지 않았을 때 색상 기본값(0.6f)
frontLayerScrimColor: Color = BackdropScaffoldDefaults.frontLayerScrimColor
): UnitBackdrop 레이아웃을 구현하는 데 사용
- 백드롭 레이아웃: 두 개의 레이어를 포함하고 있으며, 일반적으로 뒤쪽 레이어는 대시보드나 필터 옵션 등을 제공하고, 앞쪽 레이어는 주요 콘텐츠를 나타낸다
- 사용자는 앞 레이어를 위로 드래그하여 뒤쪽 레이어를 표시하거나 숨길 수 있다
