
- Objection
- Process Control Block ( PCB )
- Process Context
- user context
- system context
1) Process Control Block ( PCB )
- process control block 이란?
-> OS 가 process들을 control 하기 위해 사용되는 data structures
-> 각각의 process 와 자원들의 현재 상태에 대한 정보 저장
-> table 형태로 저장
-> process 마다 PCB 하나씩 동시 생성 ( 없어질 때도 마찬가지 )
- process 들이 저장되는 방법
- Process list 로 저장.
- 이 process list 에는 PCB 가 서로 연결되어있음.
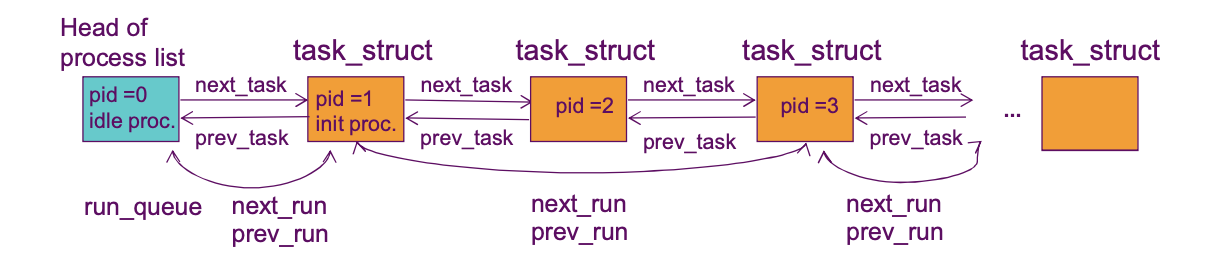
- 사진에서의 run_queue == ready_queue 임.
- PCB 에 저장되는 정보
- Identifier : process 식별자 ( 고유한 숫자, 변하지 않음 )
- State, Priority
- Program Counter ( PC )
- Memory pointers
- Address of memory context
-> program code, variables
- I/O status information
- Accounting information
- Process identification
- process 들의 고유 식별자
- process 가 생성될 때 생김.
- Processor state information
- process state 저장
- CPU register 저장.
- code, data, stack 등 각각의 시작주소
- instruction pointer ( = program counter )
- processor 상태
- stack pointer
- 현재 directory 를 가리키는 주소
- 등 register 값 저장.
- Process control information
- Scheduling and State information
- process state : 현재 프로세스가 어떠한 상태인지
( e.g. running, ready, blocked . . . )
- priority : 프로세스의 스케줄링 우선순위
- Schduling-related information : 스케줄링에 사용되는 정보
( 얼마나 기다렸는지, 가장 최근에 얼마나 실행되었는지 . . . )
- event : 프로세스가 들어오길 기다리고 있는 event
- Inter-process communication
-> 분리되어있는 두개의 프로세스가 통신하는 방법
-> flag, signal, message 들을 통신
- memory management : 프로세스가 할당받은 메모리주소
- resource : 컴퓨터자원
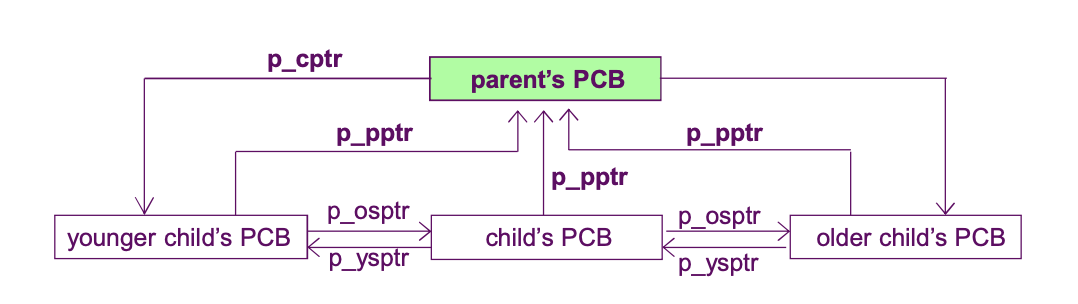
- PCB 의 data 구조
- PCB 는 본인의 형제, 부모, 자식프로세스와 서로 연결되어있음.
2) Process Context
- User Context : 프로그램 작성자에 의해 결정
- Code : 실행되는 user program code
- Data : 프로세스의 전역변수 ( global variable )
- User Stack :
-> 지역변수 ( local variable )
-> 함수의 인자 ( parameters of function )
-> 레지스터 값 ( register value ( return address ) )
- System Context : 운영체제에 의해 결정 ( 내부적으로 알아서 결정 )
- kernel stack ( System stack ) : argument, register 저장
-> system call 받으면 실행되는 공간
- PCB 저장.
- User Part of process Context
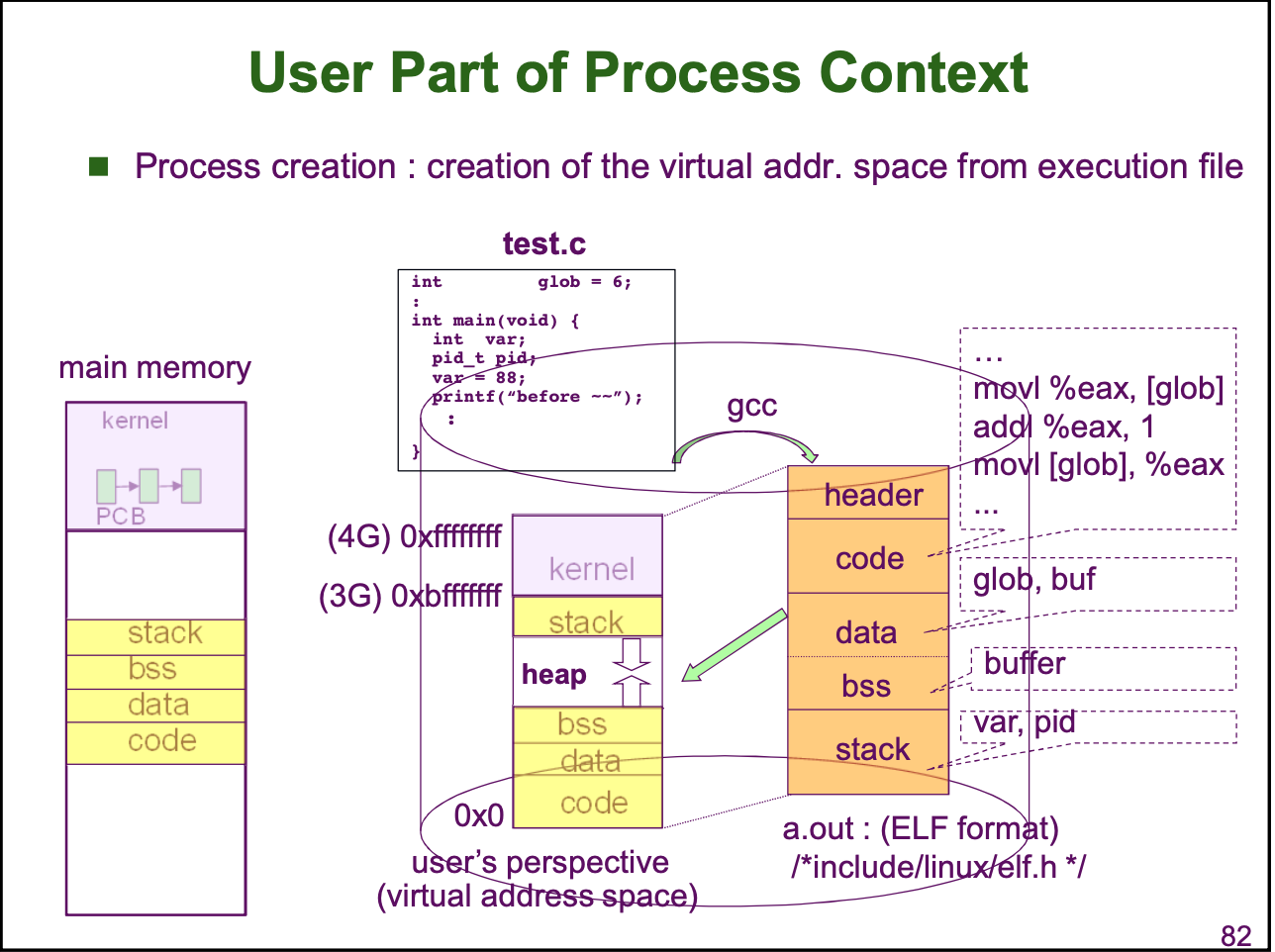
- address space 가 4 GB 인 이유 : 32 bit address 이므로 2³² 크기
- virtual address space 에 있으면 => new state
- main memory 에 있으면 => ready state
- main memory 에서 CPU 를 할당받으면 => running state



