들어가며
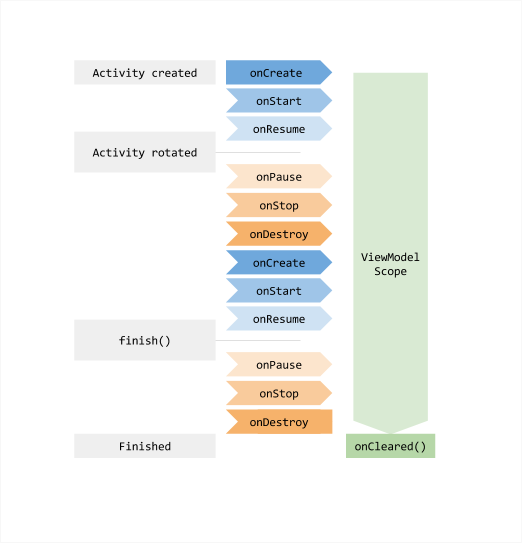
viewmodel을 사용해본 사용자라면 위의 생명주기를 본적이 있을 것이다.
도대체 onCleared 이녀석은 언제 호출되는 것이며 viewmodelScope이놈은 무엇일까?
onCleared
ViewModel은 수명 주기 과정에서 ViewModelStoreOwner에 의해 ViewModel이 소멸될 때 onCleared 메서드를 호출합니다. 이렇게 하면 ViewModel의 수명 주기를 따르는 모든 작업 또는 종속 항목을 정리할 수 있습니다.
공식문서에 따르면 생명주기에 따라 소멸될때 onCleared를 호출한다고 한다.
SampleViewModel
다음과 같은 SampleViewModel이 있다 하고
class SampleViewModel : ViewModel() {
fun test() {
Log.d(TAG,"hello this is SampleViewModel")
}
override fun onCleared() {
super.onCleared()
Log.d(TAG,"onCleared 호출")
}
}MainActivity2
다음과 같은 MainActivity2가 있다고 할때
class MainActivity2 : ComponentActivity() {
companion object {
const val TAG = "JWH"
}
private val sampleViewModel: SampleViewModel by viewModels()
private val callback = object : OnBackPressedCallback(true) {
override fun handleOnBackPressed() {
Log.d(TAG, "뒤로가기 클릭")
this@MainActivity2.finish()
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate")
this.onBackPressedDispatcher.addCallback(callback)
sampleViewModel.test()
setContent {
PostViewmodelTheme {
Surface(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.background
) {
Greeting("Android2")
}
}
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
Log.d(TAG, "onStart")
}
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
Log.d(TAG, "onResume")
}
override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
Log.d(TAG, "onPause")
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
Log.d(TAG, "onStop")
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
Log.d(TAG, "onDestroy")
}
}작업
이제 앱을 실행하면 MainActivity에서 startAcitvity를 통해 MainActivity2로 이동한다.
그뒤 뒤로가기를 눌러 MainActivity2를 finish 하였을때 로그를 살펴보면
11:06:07.235 D onCreate
11:06:07.237 D hello this is SampleViewModel
11:06:07.244 D onStart
11:06:07.245 D onResume
11:06:09.709 D 뒤로가기 클릭
11:06:09.721 D onPause
11:06:10.262 D onStop
11:06:10.267 D onCleared 호출
11:06:10.267 D onDestroy로그가 찍히는 시간을 보면 onDestroy가 호출된 시점과 같은 시간에 onCleared가 호출된다.
그렇다면 ViewModel에서 onCleared가 어떻게 동작하는지 확인해보자.
ViewModel onCleared 과 clear
실제로 ViewModel의 내부코드를 보면 다음과 같다.
/**
* This method will be called when this ViewModel is no longer used and will be destroyed.
* <p>
* It is useful when ViewModel observes some data and you need to clear this subscription to
* prevent a leak of this ViewModel.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
protected void onCleared() {
}
@MainThread
final void clear() {
mCleared = true;
// Since clear() is final, this method is still called on mock objects
// and in those cases, mBagOfTags is null. It'll always be empty though
// because setTagIfAbsent and getTag are not final so we can skip
// clearing it
if (mBagOfTags != null) {
synchronized (mBagOfTags) {
for (Object value : mBagOfTags.values()) {
// see comment for the similar call in setTagIfAbsent
closeWithRuntimeException(value);
}
}
}
// We need the same null check here
if (mCloseables != null) {
synchronized (mCloseables) {
for (Closeable closeable : mCloseables) {
closeWithRuntimeException(closeable);
}
}
}
onCleared();
}onCleared()의 내용은 비어있고 실제로는 clear() 메서드가 호출되고 그뒤에 onCleared()가 추가로 작업된다.
clear을 호출하는 곳을 타고 들어가면 ViewModelStore에서 다음과 같이 호출을 하게된다.
/**
* Clears internal storage and notifies `ViewModel`s that they are no longer used.
*/
fun clear() {
for (vm in map.values) {
vm.clear()
}
map.clear()
}그리고 해당 메서드를 호출하는 곳을 찾아보면 ComponentActivity에서 다음과 같이 사용되고있다.
getLifecycle().addObserver(new LifecycleEventObserver() {
@Override
public void onStateChanged(@NonNull LifecycleOwner source,
@NonNull Lifecycle.Event event) {
if (event == Lifecycle.Event.ON_DESTROY) {
// Clear out the available context
mContextAwareHelper.clearAvailableContext();
// And clear the ViewModelStore
if (!isChangingConfigurations()) {
getViewModelStore().clear();
}
mReportFullyDrawnExecutor.activityDestroyed();
}
}
});ON_DESTROY 이벤트가 왔을때 getViewModelStore().clear()를 통해 viewmodel의 onCleared가 호출된다고 이해하면된다.
viewmodelScope?
viewmodelScope를 알아보기 전에 다음과 같이 코드가 수정되었다고 하자.
SampleViewModel
class SampleViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var job: Job? = null
fun call() {
job = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Main).launch {
var cnt = 0
while (true) {
Log.d(TAG, cnt++.toString())
delay(1000)
}
}
}
override fun onCleared() {
super.onCleared()
Log.d("JWH", "onCleared 호출")
}
}그리고 MainAcitivty2에서 다음 메서드를 호출한뒤 해당 액티비티를 finish 시키면
11:18:19.787 D onCreate
11:18:19.797 D onStart
11:18:19.798 D onResume
11:18:19.807 D 0
11:18:20.811 D 1
11:18:21.814 D 2
11:18:22.818 D 3
11:18:22.934 D 뒤로가기 클릭
11:18:22.947 D onPause
11:18:23.480 D onStop
11:18:23.489 D onCleared 호출
11:18:23.490 D onDestroy
11:18:23.821 D 4
11:18:24.821 D 5
11:18:25.825 D 6종료되었음에도 job은 계속 실행되고있으므로, 우리가 원하던 결과가 아닐것이다.(계속 작업되면 메모리누수..)
그래서 onCleared에 다음과 같이 추가해주자.
override fun onCleared() {
super.onCleared()
Log.d("JWH", "onCleared 호출")
job?.cancel()
}11:20:16.127 D onCreate
11:20:16.138 D onStart
11:20:16.139 D onResume
11:20:16.153 D 0
11:20:17.156 D 1
11:20:18.158 D 2
11:20:19.160 D 3
11:20:19.330 D 뒤로가기 클릭
11:20:19.381 D onPause
11:20:19.893 D onStop
11:20:19.901 D onCleared 호출
11:20:19.903 D onDestroy실행해보면 위와 같이 job이 잘 종료되어 실행되지 않는 모습이다.
SampleViewModel(2)
그렇다면 매번 모든 job에 대하여 cancel()을 일일히 호출해주는것은 매우 힘든 작업이 될것이다.
그래서 등장한 놈이 viewmodelScope이다.
다음과 같이 수정하여 작동시키면
class SampleViewModel : ViewModel() {
fun call() {
viewModelScope.launch {
var cnt = 0
while (true) {
Log.d(TAG, cnt++.toString())
delay(1000)
}
}
}
override fun onCleared() {
super.onCleared()
Log.d("JWH", "onCleared 호출")
}
}11:23:06.182 D onCreate
11:23:06.185 D 0
11:23:06.195 D onStart
11:23:06.195 D onResume
11:23:07.189 D 1
11:23:08.192 D 2
11:23:09.196 D 3
11:23:10.200 D 4
11:23:11.201 D 5
11:23:12.203 D 6
11:23:12.281 D 뒤로가기 클릭
11:23:12.312 D onPause
11:23:12.861 D onStop
11:23:12.868 D onCleared 호출
11:23:12.869 D onDestroy바로 위의 결과와 동일하게 나타나는 것을 알 수 있다.
원리?
viewmodelScoped의 코드를 봐봅시다.
private const val JOB_KEY = "androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelCoroutineScope.JOB_KEY"
public val ViewModel.viewModelScope: CoroutineScope
get() {
val scope: CoroutineScope? = this.getTag(JOB_KEY)
if (scope != null) {
return scope
}
return setTagIfAbsent(
JOB_KEY,
CloseableCoroutineScope(SupervisorJob() + Dispatchers.Main.immediate)
)
}
internal class CloseableCoroutineScope(context: CoroutineContext) : Closeable, CoroutineScope {
override val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext = context
override fun close() {
coroutineContext.cancel()
}
}setTagIfAbsent를 통해 기본이 MainThread로 작동하는 CloseableCoroutineScope 를 반환해 줍니다.
setTagIfAbsent는 무엇일까요? ViewModel에 구현되어있는 메서드 이며 다음과 같습니다.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
<T> T setTagIfAbsent(String key, T newValue) {
T previous;
synchronized (mBagOfTags) {
previous = (T) mBagOfTags.get(key);
if (previous == null) {
mBagOfTags.put(key, newValue);
}
}
T result = previous == null ? newValue : previous;
if (mCleared) {
// It is possible that we'll call close() multiple times on the same object, but
// Closeable interface requires close method to be idempotent:
// "if the stream is already closed then invoking this method has no effect." (c)
closeWithRuntimeException(result);
}
return result;
}mBagOfTags 라는 hashmap을 체크하며 값을 반환해주는 함수네요.
그렇다면 viewmodleScope는 mBagOfTags이란곳에 key-value 형태로 저장해두고 사용하는 scope라 이해할수있겠습니다.
그런데 아까 clear() 메서드를 살펴보면 다음과 같은 부분이 있습니다.
if (mBagOfTags != null) {
synchronized (mBagOfTags) {
for (Object value : mBagOfTags.values()) {
// see comment for the similar call in setTagIfAbsent
closeWithRuntimeException(value);
}
}
}mBagOfTags의 value를 돌며 closeWithRuntimeException를 호출해주네요.
private static void closeWithRuntimeException(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Closeable) {
try {
((Closeable) obj).close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}즉 viewmodlescope Closeable하므로 close가 호출되겠네요.
close호출시 CloseableCoroutineScope에서는 해당job을 cancel하구요
따라서 viewmodlescope는 별도 처리 없이 cancel 구현이 되어있는 좋은 친구로 이해 할수 있겠네요.
잘못된 부분이 있거나 질문이 있으시다면 댓글로 남겨주세요.
감사합니다.
