4주차 : 제어문
학습할 것
- 선택문
- 반복문
선택문
자바의 선택문은 다음과 같다.
- if statement
- if-else statement
- if-else-if ladder
- nested if statement
- switch
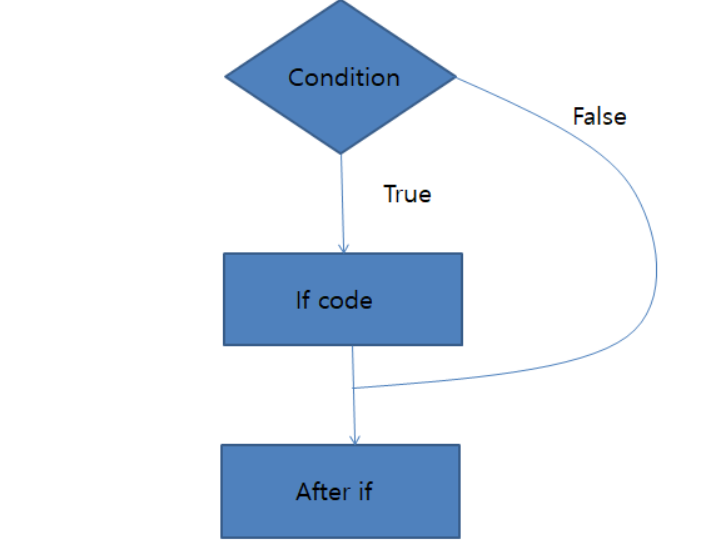
if statement
if(condition){
System.out.println("true");
}condition이 true일 경우 중괄호로 감싸진 코드가 실행되고, false일 경우 실행되지 않고 넘어간다.
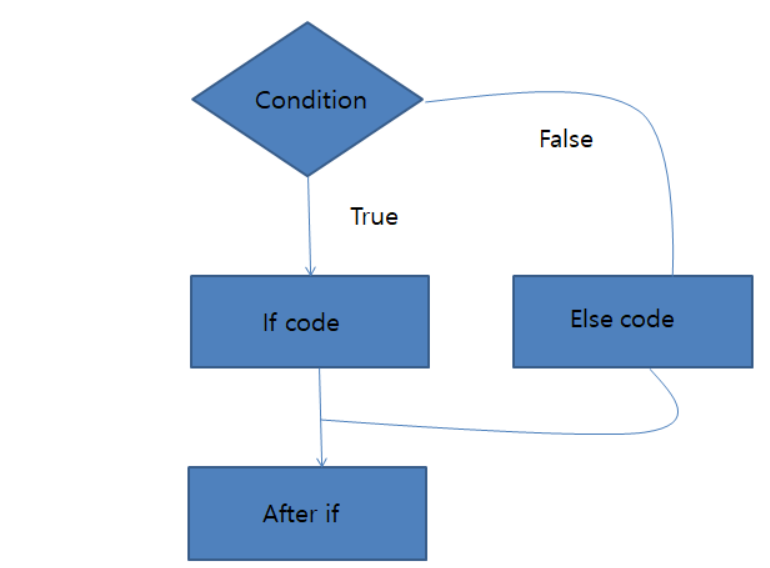
if-else statement
if(condition){
System.out.println("true");
}else{
System.out.println("false");
}condition이 true이면 if의 중괄호 내부 코드가 실행되고, false일 경우 else의 중괄호 내부 코드가 실행된다.
Ternary Operator(삼항 연산자)
if-else문은 3주차에 배운 삼항 연산자를 통해 간략하게 표현할 수 있다.
String s = condition ? "true" : "false";
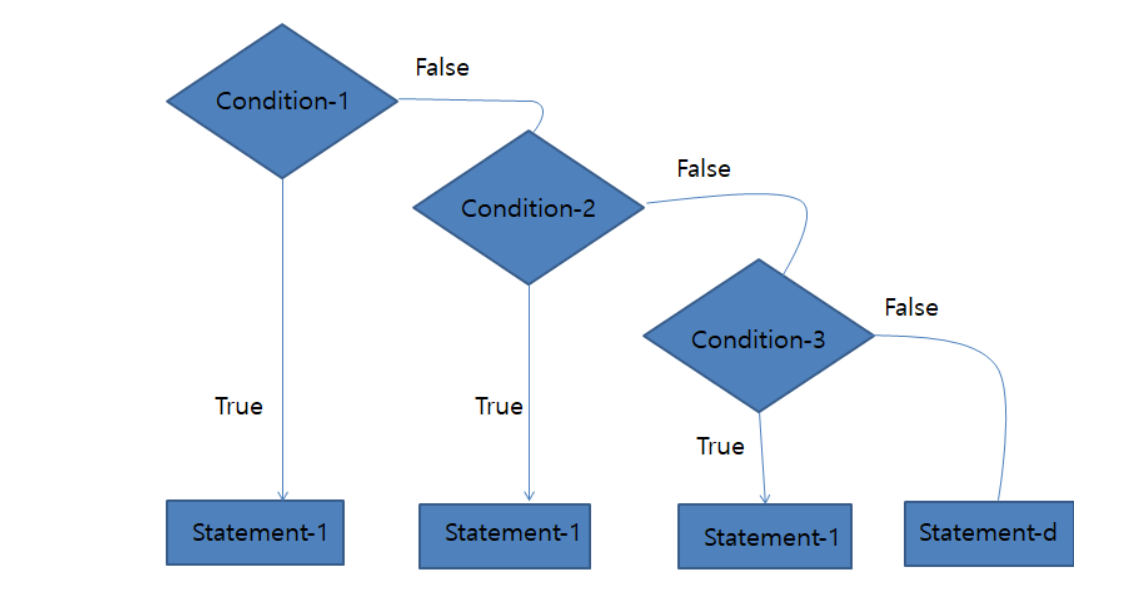
System.out.println(s);if-else-if ladder Statement
if(condition1){
}else if(condition2){
}else if(condition3){
}else{
}이때 상위 condition에는 하위 condition을 포괄해야 한다. 그렇지 않으면 상위 condition에서
true가 발생하여 하위 코드들은 계속 실행되지 않을 것이다.
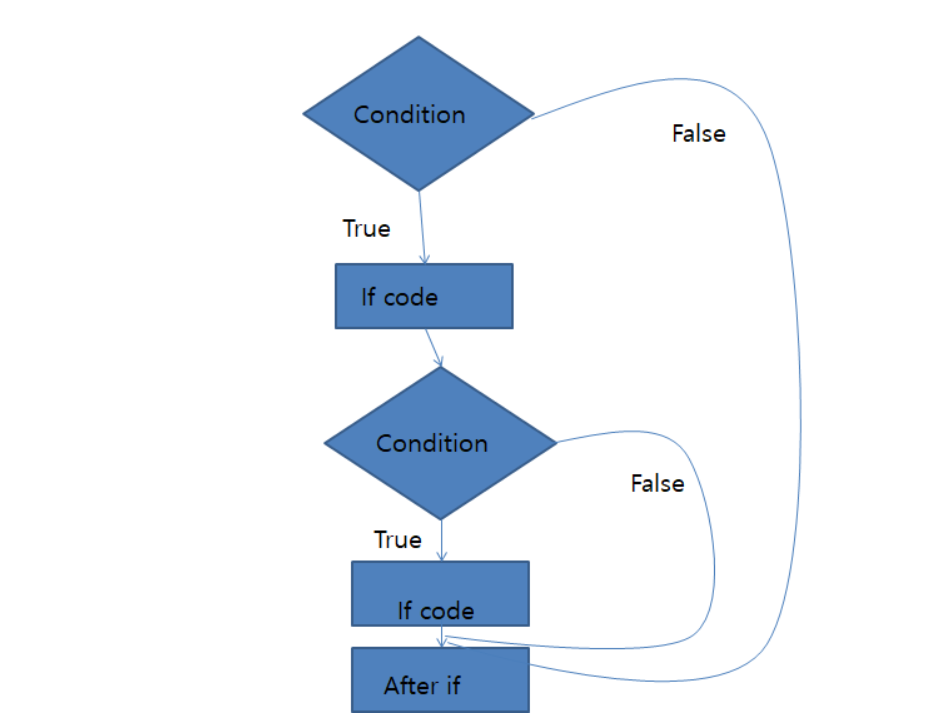
nested if statement
if(condition1){
if(condition2){
}
}
switch
switch문은 if-else-if ladder와 유사하다. 하나의 값을 전달하여 여러 조건들을 적용할 수 있는 방법이다.
값으로 들어갈 수 있는 type은 byte,short,int,long,enum,String이며, Wrapper type도 가능하다.
case value는 오직 들어온 값의 type과 일치해야 한다. 또한 case value는 리터럴이거나 constant해야 한다.
변수는 case value로 들어올 수 없다. case value는 중복될 수 없다.
각 case문은 break문을 포함할 수 있다. 만약 break문이 있다면 해당 case문을 실행한 후 다음 case문으로
넘어가지 않고 switch문을 종료시킬 것이다. 반대로 break문이 없다면 다음 case문으로 넘어간다.
switch(expression){
case value1:
~~~
break;
case value2:
~~~
break;
default:
~~~
}default는 모든 case에서 일치하지 않을 때 실행될 코드들이 들어간다.
int,String type의 expression을 넣었을 때 잘 동작하는 것을 알 수 있다.
int expression = 3;
switch (expression){
case 1:
System.out.println("1");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("3");
break;
default:
System.out.println("not matched");
}
// 3String expression = "hi";
switch (expression){
case "hello":
System.out.println("hello");
break;
case "hi":
System.out.println("hi");
break;
default:
System.out.println("not matched");
}
// hi만약 break;를 없앤다면 어떻게 될까? default문의 코드도 실행되게 된다.
String expression = "hi";
switch (expression){
case "hello":
System.out.println("hello");
break;
case "hi":
System.out.println("hi");
default:
System.out.println("not matched");
}
// hi
// not matched반복문
java에서 반복문의 종류는 다음과 같다.
- for loop : 반복의 횟수가 고정되있을 경우 for loop사용이 추천된다.
- while loop : 반복의 횟수가 고정되있지 않을 경우 while loop가 추천된다.
- do-while loop : 반복의 횟수가 고정되있지 않고, 적어도 loop가 한번은 실행되어야 할 때 추천된다.
for loop
간단한 for loop는 C/C++과 동일하다. 변수를 초기화하고, 조건을 확인하고, 변수의 값을 변경시키고, loop
의 statement를 실행시킨다.
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
// 0
// 1
// 2java에는 C/C++과 다르게 for-each문이 존재한다. 이는 배열이나 java의 collection을 순회하며 동작하도록 하는 loop문이다. 문법은 다음과 같다.
for(data_type variable : array_name){
~~~
}int[] array = {0,1,2};
for(int i : array){
System.out.println(i);
}
// 0
// 1
// 2java에는 for loop에 대해 이름을 붙을 수 있다. 이를 통해 중첩 for loop에서 상위 loop에서 break하도록 할 수 있다. 문법은 다음과 같다.
labelname:
for(initialization ; condition ; increment/decrement){
~~~
}upperLoop:
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
lowerLoop:
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
if(j > 1){
break upperLoop;
}
System.out.println(j);
}
}
// 0
// 1위 경우 break upperLoop;가 아닌 break라면 내부 loop에서만 탈출하고 상위 loop가 동작할 것이다.
그러나 상위 loop에 이름을 붙여 해당 loop에 대해서 break했으므로 상위 loop 탈출이 가능해졌다.
while, do-while
while문과 do-while문은 C/C++와 동일하기 때문에 생략한다.
과제
0. JUnit 5 학습하세요
JUnit은 java코드를 단위 테스트하기 위한 목적으로 만들어진 프레임워크이다.
JUnit을 학습하기 위해 계산기 프로그램을 작성하고 해당 메소드들을 테스트하는 코드를 작성한다.
Ref. https://ildann.tistory.com/5
public class Calculator {
public static int add(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
public static int sub(int a, int b){
return a - b;
}
public static int mul(int a, int b){
return a * b;
}
public static int divide(int a, int b) throws Exception{
return a / b;
}
}class CalculatorTest {
@Test
public void addTest(){
int result = Calculator.add(1,3);
Assertions.assertEquals(4,result);
}
@Test
public void subTest(){
int result = Calculator.sub(1, 3);
Assertions.assertNotEquals(result,-1);
}
@Test
public void mulTest(){
int result1 = Calculator.mul(1, 3);
boolean result2 = result1 == 3 ? true : false;
Assertions.assertTrue(result2);
}
@Test
public void divideTest(){
Exception e = Assertions.assertThrows(Exception.class,()-> Calculator.divide(1,0));
assertEquals(ArithmeticException.class,e.getClass());
}
}2. LinkedList를 구현하세요.
LinkedList란?
LinkedList는 연결리스트라고 부르며 연결리스트의 원소들을 노드라고 부른다. 노드는 자신의 데이터
필드와 다음 노드의 래퍼런스를 가지고 있으며, 연결리스트는 노드의 가장 앞 노드와
끝 노드의 래퍼런스를 가지고 있다.
연결리스트는 데이터를 삽입하고 삭제하는 데 특화되어 있다.
ListNode.java
public class ListNode {
private int data;
private ListNode next;
ListNode(){
data = 0;
next = null;
}
ListNode(int data){
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public ListNode getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public void setNext(ListNode next) {
this.next = next;
}
public boolean isEqual(ListNode node){
return this.hashCode() == node.hashCode();
}
public static void print(ListNode head){
ListNode curr = head;
do {
System.out.println(curr.data);;
curr = curr.getNext();
}while (curr != null);
}
// After add method, added Node is placed position's value
public static ListNode add(ListNode head, ListNode nodeToAdd, int position){
ListNode curr = head;
ListNode next = null;
for(int i = 0; i < position - 1; i++){
curr = curr.getNext();
next = curr.getNext();
}
nodeToAdd.setNext(next);
curr.setNext(nodeToAdd);
return nodeToAdd;
}
public static ListNode remove(ListNode head, int positionToRemove){
ListNode curr = head;
ListNode next = null;
for(int i = 0; i < positionToRemove - 1; i++){
curr = curr.getNext();
next = curr.getNext();
}
if(next != null){
curr.setNext(next.getNext());
}
return next;
}
public static boolean contains(ListNode head, ListNode nodeToCheck){
ListNode curr = head;
do {
if(curr.isEqual(nodeToCheck)){
return true;
}
curr = curr.getNext();
}while (curr != null);
return false;
}
}
ListNodeTest.java
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class ListNodeTest {
@Test
void add() {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curr = head;
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++){
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(i);
curr.setNext(newNode);
curr = newNode;
}
int data = 10;
int position = 3;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(data);
ListNode resultNode = ListNode.add(head,newNode,position);
Assertions.assertEquals(data,resultNode.getData());
// ListNode.print(head);
ListNode positionNode = head;
for(int i = 0; i < position ; i++){
positionNode = positionNode.getNext();
}
Assertions.assertEquals(data,positionNode.getData());
}
@Test
void remove() {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curr = head;
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++){
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(i);
curr.setNext(newNode);
curr = newNode;
}
int positionToRemove = 2;
ListNode removedNode = ListNode.remove(head,positionToRemove);
Assertions.assertEquals(2,removedNode.getData());
}
@Test
void contains() {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode curr = head;
for(int i = 1; i <= 3; i++){
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(i);
curr.setNext(newNode);
curr = newNode;
}
ListNode positionNode = head;
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
positionNode = positionNode.getNext();
}
boolean result = ListNode.contains(head, positionNode);
Assertions.assertTrue(result);
}
}3. Stack을 구현하세요.
Stack.java
public class Stack {
private int MAX_LENGTH = 100;
private int[] stack;
private int top;
public Stack(){
stack = new int[100];
top = -1;
}
public void push(int data){
if(top >= 99){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
stack[++top] = data;
}
public int pop() {
if(top < 0){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return stack[top--];
}
}StackTest.java
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class StackTest {
@Test
void push() {
Stack stack = new Stack();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
stack.push(i);
}
Assertions.assertEquals(2,stack.pop());
Assertions.assertEquals(1,stack.pop());
Assertions.assertEquals(0,stack.pop());
}
@Test
void pop() {
Stack stack = new Stack();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
stack.push(i);
}
Assertions.assertEquals(2,stack.pop());
Assertions.assertEquals(1,stack.pop());
Assertions.assertEquals(0,stack.pop());
Exception e = Assertions.assertThrows(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class,()->{
stack.pop();
});
Assertions.assertEquals(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class,e.getClass());
}
}4. 앞서 만든 ListNode를 사용해서 Stack을 구현하세요.
ListNodeStack.java
public class ListNodeStack {
private ListNode head;
private int top;
public ListNodeStack(){
head = null;
top = -1;
}
void push(int data){
if(top == -1){
head = new ListNode(data);
top++;
}else{
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(data);
ListNode.add(head,newNode,++top);
}
}
int pop(){
if(top < 0){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
ListNode curr = head;
for(int i = 0; i < top; i++){
curr = curr.getNext();
}
int topNodeData = curr.getData();
ListNode.remove(head,top--);
return topNodeData;
}
void print(){
if(head == null) return;
ListNode curr = head;
for(int i = 0; i <= top; i++){
System.out.println(curr.getData());
curr = curr.getNext();
}
}
}
ListNodeStackTest.java
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class ListNodeStackTest {
@Test
void push() {
ListNodeStack listNodeStack = new ListNodeStack();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
listNodeStack.push(i);
}
Assertions.assertEquals(2,listNodeStack.pop());
Assertions.assertEquals(1,listNodeStack.pop());
Assertions.assertEquals(0,listNodeStack.pop());
}
@Test
void pop() {
ListNodeStack listNodeStack = new ListNodeStack();
Exception e = Assertions.assertThrows(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class,()->{
listNodeStack.pop();
});
Assertions.assertEquals(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class,e.getClass());
}
}5. Queue를 구현하세요.
Queue.java
public interface Queue {
void createQueue();
boolean isEmpty();
void enQueue(int data);
int deQueue();
}QueueWithArray.java
public class QueueWithArray implements Queue {
private int MAX_LENGTH = 10;
// rear : 가장 뒤쪽에 있는 원소의 인덱스를 가리킨다
private int rear;
// front : 가장 앞쪽에 있는 원손의 앞 인덱스를 가리킨다.
private int front;
private int[] queue;
public QueueWithArray(){
createQueue();
}
public int getMAX_LENGTH() {
return MAX_LENGTH;
}
@Override
public void createQueue() {
rear = -1;
front = -1;
queue = new int[10];
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == MAX_LENGTH -1;
}
@Override
public void enQueue(int data) {
if(isFull()){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("isEmpty");
}else{
queue[++rear] = data;
}
}
@Override
public int deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("isEmpty");
}else{
return queue[++front];
}
}
}
QueueWithArrayTest.java
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class QueueWithArrayTest {
@Test
void isEmpty() {
Queue queue = new QueueWithArray();
Assertions.assertEquals(true, queue.isEmpty());
queue.enQueue(1);
Assertions.assertEquals(false, queue.isEmpty());
}
@Test
void isFull() {
QueueWithArray queue = new QueueWithArray();
Assertions.assertEquals(false,queue.isFull());
for(int i = 0; i < queue.getMAX_LENGTH(); i++){
queue.enQueue(i);
}
Assertions.assertEquals(true,queue.isFull());
}
@Test
void enQueue() {
QueueWithArray queue = new QueueWithArray();
for(int i = 0; i < queue.getMAX_LENGTH(); i++){
queue.enQueue(i);
}
Exception e = Assertions.assertThrows(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class,()->{
queue.enQueue(1);
});
Assertions.assertEquals(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class,e.getClass());
}
@Test
void deQueue() {
Queue queue = new QueueWithArray();
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
queue.enQueue(i);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
Assertions.assertEquals(i,queue.deQueue());
}
Exception e = Assertions.assertThrows(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class,()->{
queue.deQueue();
});
Assertions.assertEquals(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class,e.getClass());
}
}QueueWithListNode.java
public class QueueWithListNode implements Queue{
// rear : 가장 뒤쪽에 있는 노드의 reference를 가리킨다
private ListNode rear;
// rear : 가장 뒤쪽에 있는 노드의 reference를 가리킨다
private ListNode front;
private int length;
public QueueWithListNode(){
createQueue();
}
@Override
public void createQueue() {
rear = null;
front = null;
length = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == null;
}
@Override
public void enQueue(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(front == null){
front = node;
}
if(rear != null){
node.setNext(rear);
}
rear = node;
length++;
}
@Override
public int deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new NullPointerException();
}else{
int returnVal = front.getData();
if(length == 1){
length--;
front = null;
rear = null;
}else{
ListNode curr = rear;
for(int i = 0; i < length-2; i++){
curr = curr.getNext();
}
front = curr;
front.setNext(null);
}
length--;
return returnVal;
}
}
}QueueWithListNodeTest.java
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class QueueWithListNodeTest {
@Test
void isEmpty() {
Queue queue = new QueueWithListNode();
Assertions.assertEquals(true,queue.isEmpty());
queue.enQueue(1);
Assertions.assertEquals(false,queue.isEmpty());
}
@Test
void enQueue() {
Queue queue = new QueueWithListNode();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
queue.enQueue(i);
}
Assertions.assertEquals(0,queue.deQueue());
}
@Test
void deQueue() {
Queue queue = new QueueWithListNode();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
queue.enQueue(i);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
Assertions.assertEquals(i,queue.deQueue());
}
Exception e = Assertions.assertThrows(NullPointerException.class,()->{
queue.deQueue();
});
Assertions.assertEquals(NullPointerException.class,e.getClass());
}
}참고링크
conditional statement : https://www.javatpoint.com/java-if-else
java loop : https://www.javatpoint.com/java-for-loop
