[OS 공룡책] Ch09. Main Memory
Address bindingContiguous Memory AllocationDynamic LinkingDynamic LoadingEATFixed Contiguous AllocationFragmentationHashed Page TablesLogical AddressMultiple-partition Contiguous AllocationOSPagingPhysical Addressmain memorypage tablesegmentationtlb공룡책
Operating System
목록 보기
6/14

Chapter 9: Main Memory
Background
- Register 접근 : 1개의 CPU clock
- Main Memory 접근 : 수많은 cycles → stall 발생 : 일정 cycle동안 아무런 작업 수행없이 대기
Base and Limit Registers
- 메모리에 여러 개의 process들 동시 유지 → 분리된 메모리 공간 확보
- Base register : 물리 메모리 시작 주소
- Limit register : 프로세스 주소 공간의 크기 → end - base + 1
Address Binding
- symbol, 주소 → 물리 메모리의 실제 위치에 Mapping
- Address 종류
- symbol : 프로그램에서 변수, 함수 식별을 위한 기호
- relocatable address
- 상대적인 주소
- compile time에 생성
- loader에 의해 absolute address로 변환
- absolute address : 실제 메모리 주소를 직접 참조하는 주소
- logical address
- 프로세스가 생성하는 주소
- 실행시간에 MMU에 의해 physical address로 매핑
- Address Binding 시점
- Compile time Binding
- absolute address 생성
- OS가 없는 메모리 독식하는 소프트웨어(임베디드)에서 가능 → logical, physical이 1:1 매핑
- Load time Binding(실행→메모리)
- 대부분의 process : 메모리에 load 되는 시점에 주소 결정
- relocatable address → absolute address (Loader)
- Execution time Binding
- 동적으로 로드되거나, 물리적 메모리 주소가 옮겨짐
- logical address → physical address (MMU)
- Compile time Binding
Logical vs. Physical Address Space
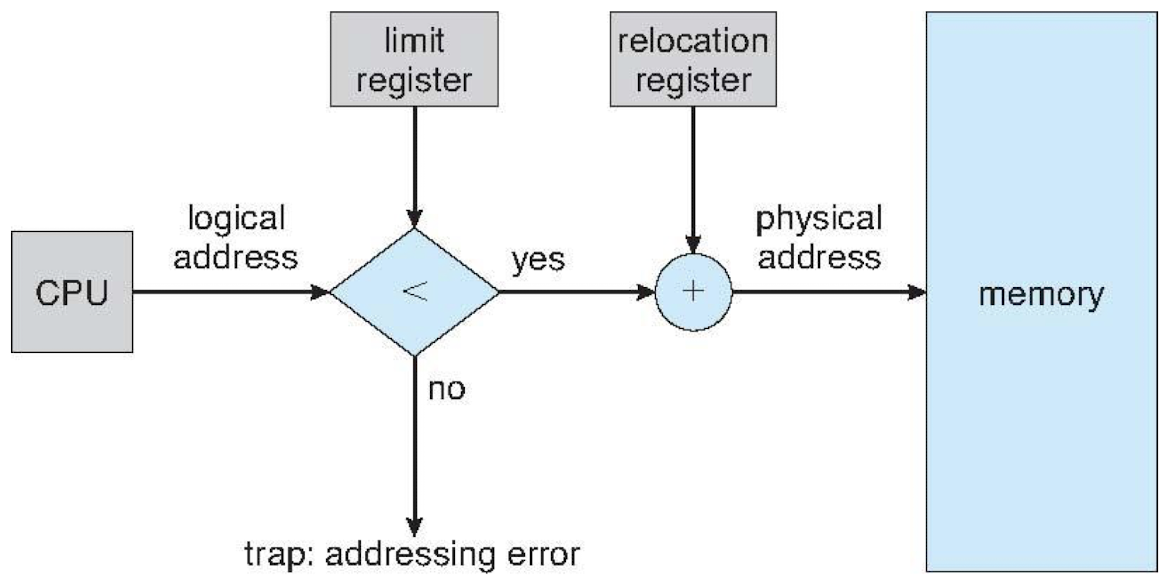
- Logical address space
- virtual address
- CPU에 의해 생성 base + limit
- process가 보는 주소 공간
- Physical Address Space
- memory의 실제 물리적인 주소 공간
- MMU (Memory-Management Unit)
- runtime에 virtual addr → physical addr 매핑
- physical = logical + Base register(relocation register)
Dynamic Loading
- Dynamic Loading
- cf. Static Loading : 상시 위치 → 메모리 낭비
- 사용자가 작업을 해야할 때만 메모리에 로드
- Dynamic Linking
- Linking : 오브젝트 파일 + 라이브러리
- cf. Static Linking :
#include로 사용한 라이브러리 - Dynamic Linking : shared memory에 있는 라이브러리
Contiguous Memory Allocation
Contiguous Memory Allocation
- 메모리의 연속적인 공간에 할당
- Fixed Contiguous Allocation
- Multiple-partition Contiguous Allocation
Fixed Contiguous Allocation
- 고정 분할 기법
- 메모리를 동일한 크기의 파티션으로 분할 → 프로세스 크기의 최댓값
- 하나의 프로세스는 하나의 파티션에
- 메모리를 동일한 크기의 파티션으로 분할 → 프로세스 크기의 최댓값
- 장점
- 유지 관리 용이
- 구현/관리 쉬움
- 단점
- 메모리 낭비 → 요즘은 사용 X
- Internal Fragmentation 으로 인한 메모리 낭비 ⭐️
Multiple-partition Contiguous Allocation
-
가변 분할 기법
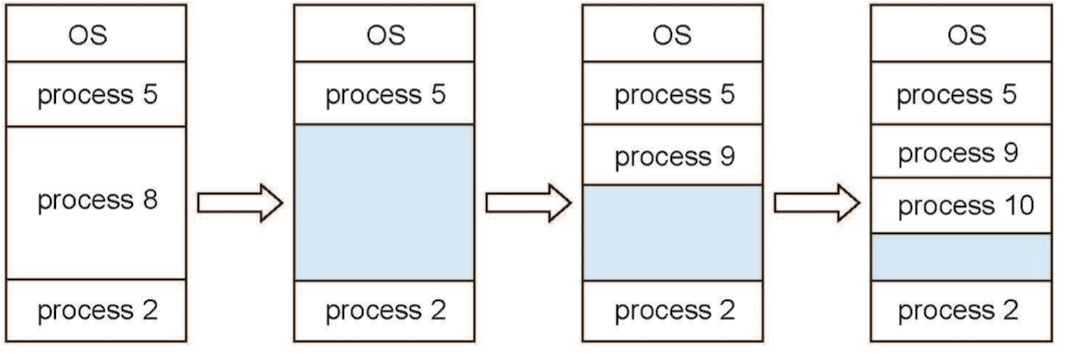
- 테이블 관리 : 어느 부분이 free, free한 영역 중 가용 공간 위치
- 가용 공간에 프로세스 할당
-
hole : 비어있는 공간, free memory list
-
Dynamic Storage-Allocation Problem
- First-fit : 들어갈 수 있는 크기를 가진 가장 첫 번째 hole부터
- Best-fit : 들어갈 수 있는 크기를 가진 가장 작은 hole부터
- Worst-fit : 들어갈 수 있는 크기를 가진 가장 큰 hole부터
-
단점
- External Fragmentation → 연속적인 공간의 hole이 없어서 할당 X
- External Fragmentation → 연속적인 공간의 hole이 없어서 할당 X
Fragmentation
- Contiguous하게 memory 관리했을 때의 단점 → 50% rule : 메모리 1/3은 fragmentation으로 낭비
- External Fragmentation
- 메모리의 연속된 공간이 충분하지 않아 발생
- 해결) Compaction
- fragmentation 조각들을 한 곳으로 모으기
- 복잡 → 성능 저하
- I/O 오버헤드 발생
- Internal Fragmentation
- 할당된 메모리 영역 내에서 사용되지 않는 메모리 공간 발생
Paging
Non-Contiguous Allocation
- Segmentation
- 메모리를 여러 개의 segment로 구분
- segment들의 사이즈 동일 X → variable size
- 각각의 논리적 공간은 contiguous 하게 할당
- Paging
- 메모리를 여러 개의 page로 구분
- page들의 사이즈 동일 O → fixed size
- linux : 4KB 단위로 쪼갬
- 단점
- paging table overhead
- memory access 증가
Segmentation Architecture
- logical(virtual) address 정보 : <segment-number, offset>
- segment-number : 인덱싱 기능
- offset(displacement)
- segment table : 해당 segment의 base, limit → running상태일 때 값 변경
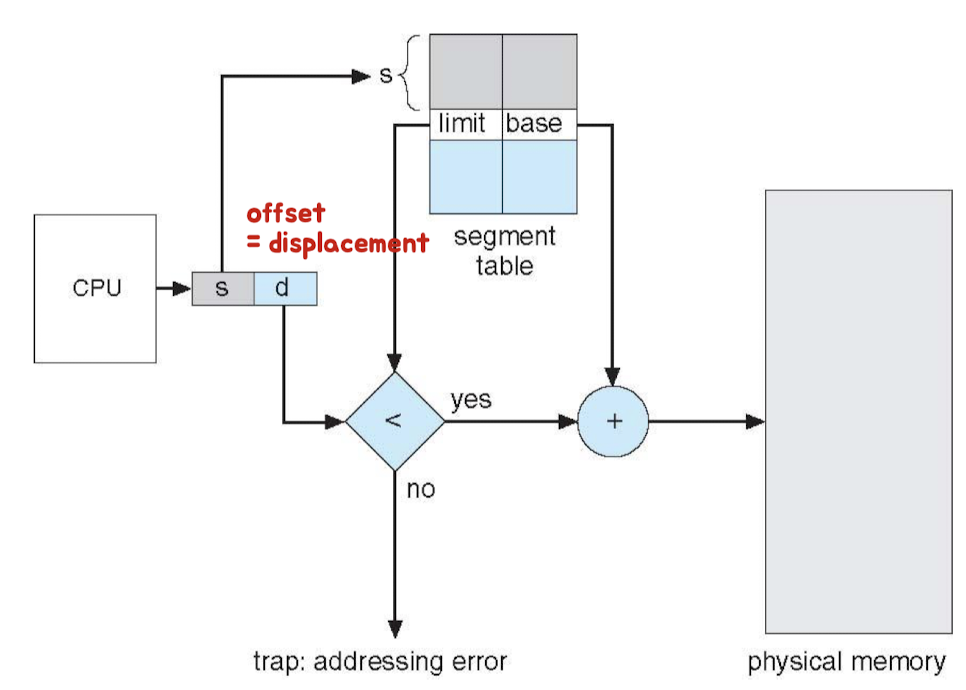
- MMU(하드웨어) : logical → physical addr 변환
- Protection : 정보 추가 가능
- 조각난 상태이기 때문에 목적 달리 설계 가능
- Read only / Read write / Write only / Execute
- 단점 : External Fragmentation 발생
Paging
- 똑같은 size로 분할 → Memory에서는 frame, OS에서는 page
- Page Table : <page-number, offset>
-
page size ⬇️, 단편화 ⬇️, table entry 개수 ⬆️
-
page size : 2^n
-
page offset : n-bit
-
page number : (m-n)bit
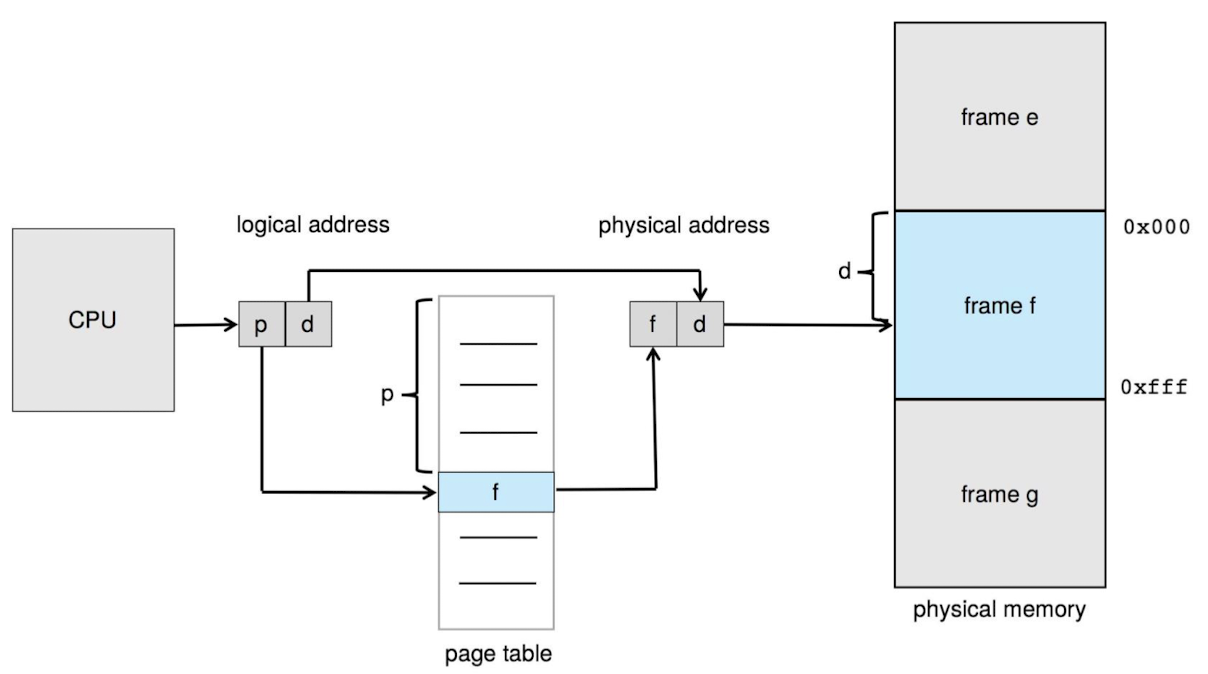
-
- protection bit 추가 가능
- 단점 : Internal Fragmentation 발생 → 최대 크기 1page보다 작게
Paging Example
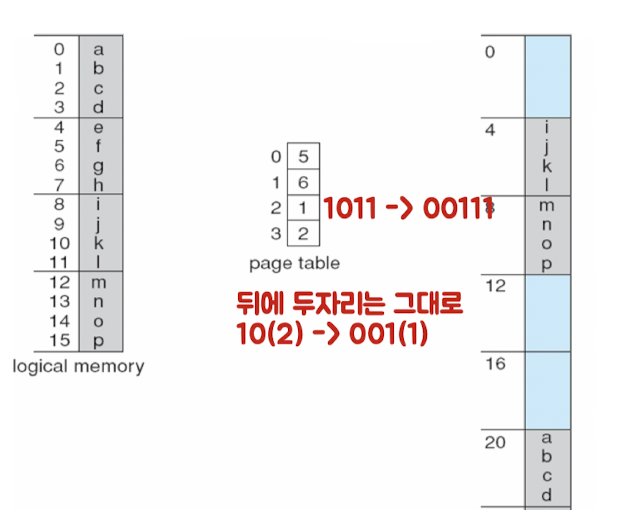
- page 크기 : 4bytes = 2^2
- offset : 2bits
- physical memory : 32bytes (8frames)
- 물리주소를 위한 5bits
- page frame을 위한 3bits
- logical memory : 16bytes
- 4page
- logical addr을 위한 4bits
- logical addr : 4bits
- 상위 2bits : page number
- 하위 2bits : page offset
ex. logical addr = 11(1011)
→ 2번 페이지, offset = 3
→ 1 * 4 + 3 = 7 = physical addr
- Internal fragmentation
-
page size = 2048bytes
-
process size = 72766bytes
→ 35pages + 1086bytes (총 36개의 page 할당)
-
Internal fragmentation = 2048 - 1086 = 962bytes
→ 최악의 경우 : 1frame - 1byte
-
Free Frames
- 프로세스의 실행 요구 → 몇 개의 페이지 필요한 지 조사하여 할당
- Frame table
- OS가 글로벌하게 유지
- 비어있는 page 번호 리스트
Implementation of Page Table
- PTBR (Page-table base register)
- page table의 시작 주소
- PTLR (Page-table length register)
- page table의 size
- 잘못된 접근 방지
- 테이블은 연속적인 공간 → 너무 크면 안 된다.
- 여러 개 페이지 테이블 계층 구조 → 계층 나눌 때마다 memory access 증가 → TLB 탄생
- TLB
- 모든 process가 공유
- Page Table의 일부만 저장하는 cache 역할
- full associated 사상 : 10비트 모두 비교 cf. set associative 사상 : index, tag cf. direct 사상 : 찾아갈 공간 지정 (한 칸만)
TLB (Translation Look-aside Buffers)

Effective Memory Access Time (EAT)
-
메모리 접근 시간

- TLB에 있으면 memory 1번 접근 (100ns) 없으면 메모리 2번 접근 (200ns)
- 현실은 Hit ratio = 99%
- TLB에 있으면 memory 1번 접근 (100ns) 없으면 메모리 2번 접근 (200ns)
Memory Protection
- page 단위로 valid-invalid bit +) read-only, write-only, read-write bit : 권한 관리
Shared Pages
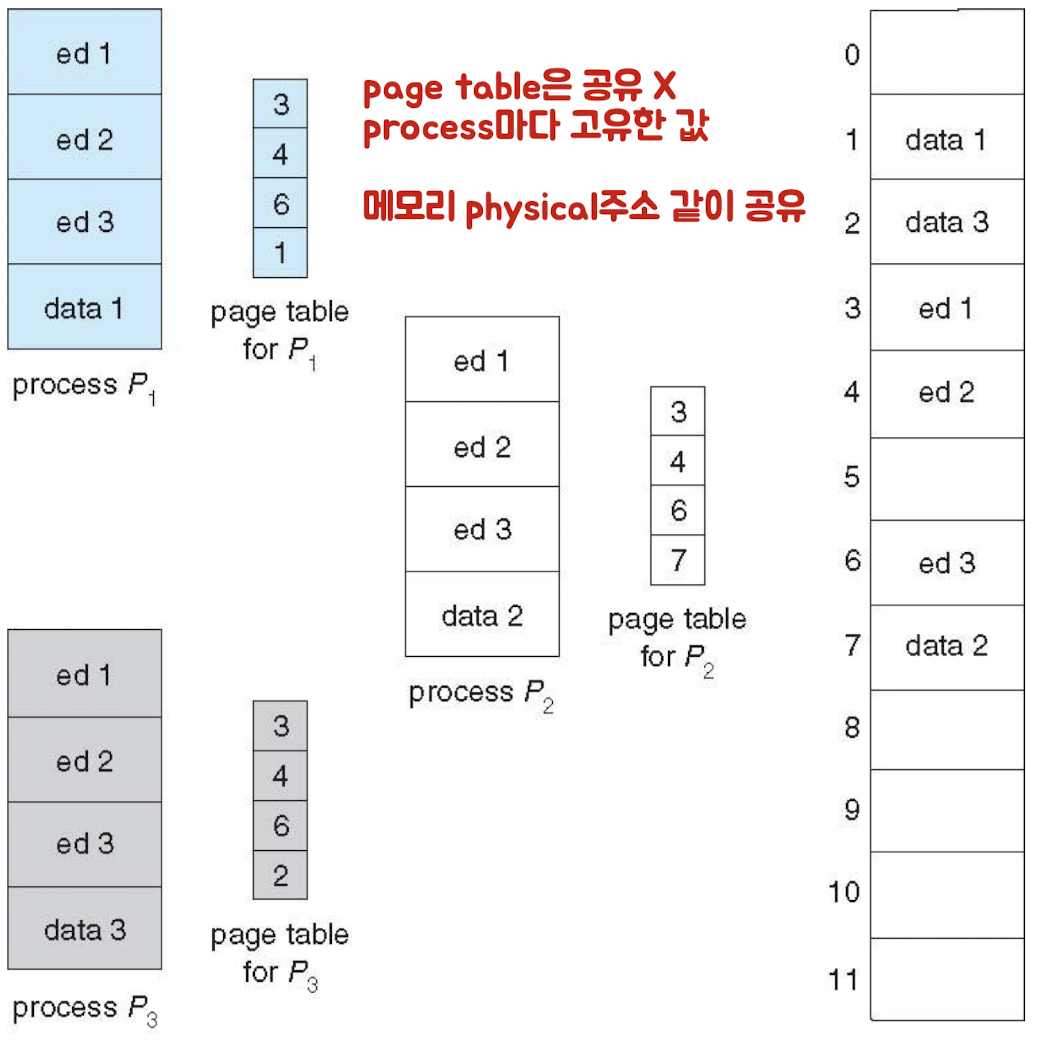
- Shared code
- page 통째로 공유, read-only
- Private code and data
Structure of the Page Table
- 문제
- page table의 연속적인 공간
- 큰 메모리 비용
- 해결
- Hierarchical Paging
- Hashed Page Tables
- Inverted Page Tables
Two-Level Page-Table ⭐️
- page table을 page 단위로 쪼개기

- outer page table : 각 page table의 시작 주소 저장
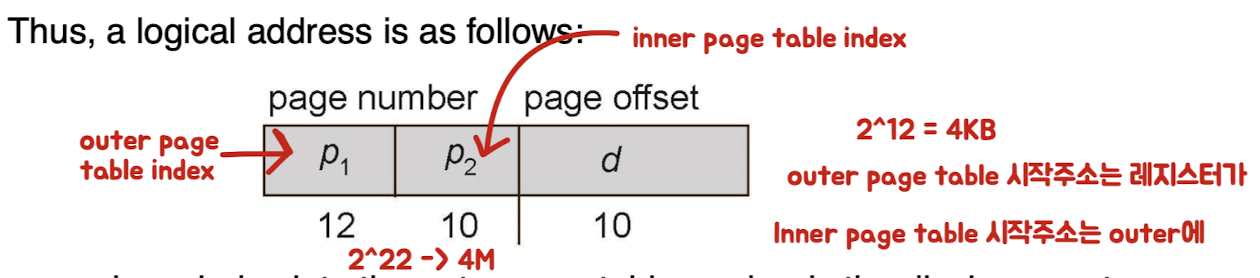
- Hierarchical Paging
- Example>
- page size = 256B (8bit)
- offset : 8bit
- p1 : 2nd outer page (8bit)
- p2 : outer page (8bit)
- pe : inner page (8bit)
Hashed Page Table
-
Hash function
-
입력에 대해 동일한 패턴의 출력 반환

-
하나에 여러 개가 연결되도록 (링크드리스트)
-
direct map X
→ 메모리 찾아가는 시간 > 자료구조 읽는 시간
-
-
page table의 size를 줄이는 효과
-
clustered page table
→ 요즘 컴퓨터
