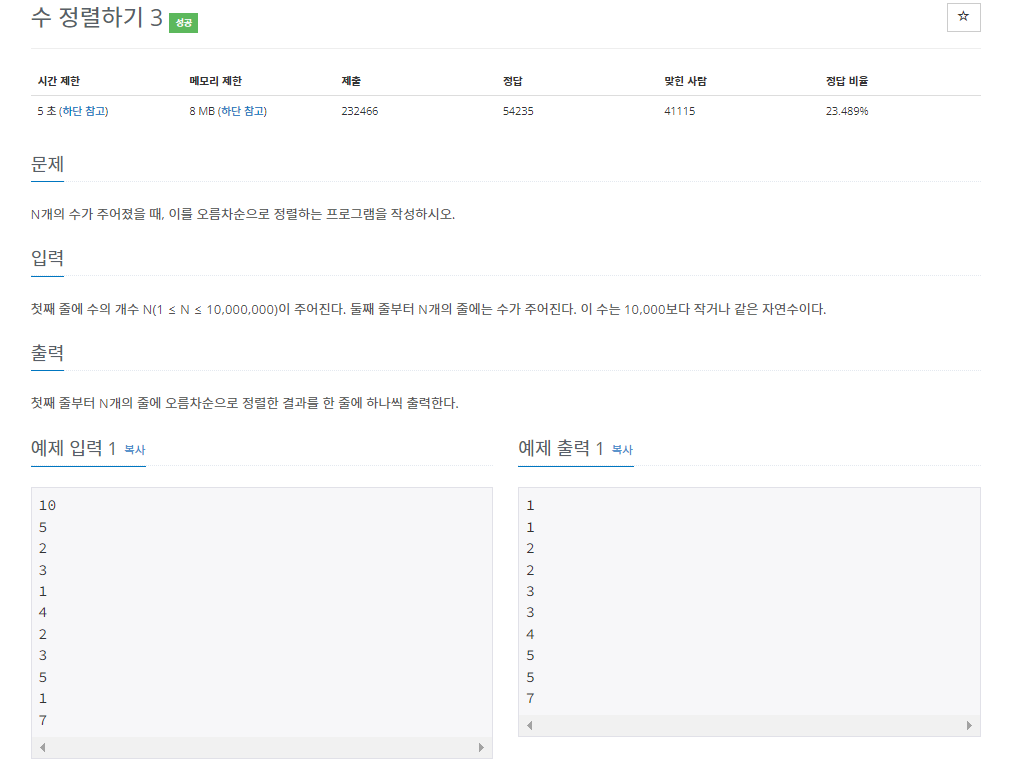
해당 문제는 범위가 지정되어 있기 때문에 계수정렬을 사용하는 것이 효율적이다. 정렬 방법은 매우 간단하다.
n번 반복하여 입력으로 주어지는 숫자를 count 배열에 저장한다. 이때, count 배열의 인덱스는 입력으로 주어지는 숫자가 된다. 예를 들어, 입력으로 주어진 숫자가 3이면, count[3]을 1 증가시킨다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); // 입력받을 숫자의 개수
int[] count = new int[10001]; // 숫자가 나타난 횟수를 저장할 배열
// 입력받은 숫자의 개수만큼 반복하여 계수 정렬을 수행
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
count[Integer.parseInt(br.readLine())]++;
}
// 계수 정렬 결과를 출력
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < count[i]; j++) {
bw.write(i + "\n");
}
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}.jpg)