런타임에 가상 DOM을 만들고 비교하는 대신, 빌드(컴파일) 단계에서
“어떤 상태가 바뀌면 어떤 실제 DOM 노드를 어떻게 업데이트해야 하는지”를 미리 계산
1. 컴파일 타임에 JSX → 업데이트 모델로 변환
-
JSX 파싱
기존에는 JSX가 React.createElement(…) 호출로 바뀌고, 런타임에 이 호출을 통해 가상 DOM 트리 -
정적 분석
React Compiler는 이 createElement 호출들을 분석해서
각 컴포넌트가 사용하는 state/prop 변수 목록
이 변수들이 바뀌었을 때 영향을 받는 DOM 노드 위치를 추출 -
업데이트 함수 생성
컴파일러는 “state A가 바뀌면 이 텍스트 노드의 .textContent만 교체” 같은 작은 업데이트 단위 함수들을 만들어 코드에 삽입
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function MyComponent() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<h1>{count}</h1>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>
Increment
</button>
</div>
);
}위 코드가 기존에는 Babel이 JSX를 아래처럼 바꿈
function MyComponent() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return React.createElement(
'div',
null,
React.createElement('h1', null, count),
React.createElement(
'button',
{ onClick: () => setCount(count + 1) },
'Increment'
)
);
}
런타임에는 이 호출 결과로 가상 DOM 트리가 매번 생성되고,
이전 트리와 비교(diff)된 뒤 실제 DOM이 갱신React19 컴파일러가 삽입하는 “업데이트 함수” 예시
import { makeNode, mount, updateText, updateEvent } from 'react/compiler';
// (실제 경로나 API 이름은 예시)
export default function MyComponent() {
// 1) 초기 노드 생성
const rootDiv = makeNode('div');
const h1 = makeNode('h1');
const btn = makeNode('button');
// 2) 초기 설정
rootDiv.append(h1, btn);
mount(h1, () => { h1.textContent = count; });
mount(btn, () => {
btn.textContent = 'Increment';
btn.onclick = () => updateCount(count + 1);
});
// 3) 상태 및 업데이트 로직
let state_count = 0;
function updateCount(newCount) {
if (newCount !== state_count) {
state_count = newCount;
updateText(h1, newCount);
}
}
return rootDiv;
}makeNode, mount 같은 헬퍼가 “이 노드는 언제 어떻게 렌더링/업데이트”될지 미리 기록
updateCount 안의 updateText(h1, newCount)는 “count가 바뀌면 이 h1 노드의 텍스트만 교체”
런타임에는 비교(diff) 없이 곧바로 updateText만 실행2. 개발자가 체감하는 변화
useMemo/useCallback이 덜 필요
- “불필요한 리렌더링을 막기 위해 의존성 배열을 꼼꼼히 맞출 필요”가 크게 줄어듬
런타임 성능
- 복잡한 컴포넌트 트리에서도 가장 작은 단위의 DOM 조작만 수행하므로, 특히 큰 리스트나 자주 바뀌는 UI에서 성능 이점이 금
번들 크기
- 업데이트 함수들이 많이 추가되지만, 코드 자체가 단순한 DOM 조작이므로 가상 DOM 라이브러리보다 전체 번들 크기가 비슷하거나 작아지는 경우도 많음
3. React Git 소스 확인
1. JSX → DOM 업데이트 함수 변환:
- 위치: packages/react/src/ReactJSX.js
또는 Babel 플러그인 버전은 packages/react/packages/react-jsx 디렉터리 아래
간단 요약
-
Babel/컴파일러 단계
JSX → jsx(Type, {…props}, key) 호출로 변환 -
런타임 단계
jsxProd(또는 jsxDEV)가 호출되어,
config 오브젝트에서 key를 분리
나머지 props 정리
ReactElement 객체 생성 -
DOM 패치
React 렌더러가 이 ReactElement를 보고 “이 노드를 어떻게 만들고, 업데이트할지” 이미 알고 있는 메타데이터를 기반으로 직접 실행
2. 실제 DOM 업데이트 헬퍼:
- 위치: packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMHostConfig.js
prepareUpdate / commitUpdate / updatePayload 같은 함수가 핵심
// ————————————————————————————————
// 상태 변화 전후를 비교해 “무엇이 바뀌었는지” 계산
// ————————————————————————————————
export function prepareUpdate(
domElement, // 실제 DOM 노드
type, // 태그 이름 또는 컴포넌트 타입
oldProps, // 이전 props
newProps, // 변경된 props
rootContainerInstance, // 루트 컨테이너 정보
hostContext // 호스트 컨텍스트
) {
// diffProperties가 oldProps와 newProps를 비교해,
// 변경된 속성만 담은 배열(updatePayload)을 반환
// 변경된 게 없으면 null 반환
const updatePayload = diffProperties(
domElement,
type,
oldProps,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
hostContext
);
return updatePayload;
}
// ————————————————————————————————
// diff 결과(updatePayload)를 실제 DOM에 적용
// ————————————————————————————————
export function commitUpdate(
domElement, // 실제 DOM 노드
updatePayload, // prepareUpdate가 반환한 변경 사항
type, // 태그 이름 또는 컴포넌트 타입
oldProps, // 이전 props
newProps, // 변경된 props
internalInstanceHandle // Fiber 인스턴스 핸들
) {
// updateProperties가 updatePayload를 순회하며
// 속성, 스타일, 이벤트 핸들러 등을 실제 노드에 반영
updateProperties(domElement, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps);
// delegated event 시스템이 최신 props를 참조하도록 FiberProps 갱신
updateFiberProps(domElement, newProps);
}prepareUpdate
- diffProperties를 통해 이전 props와 새로운 props를 비교하여, 실제로 변경이 필요한 항목만 추려낸 updatePayload 배열을 생성 > 변경 사항이 없으면 null을 반환
commitUpdate
- prepareUpdate가 만든 updatePayload를 받아 updateProperties로 실제 DOM 노드의 속성, 스타일, 이벤트 리스너 등을 최소한으로 갱신 > 이후 updateFiberProps를 호출해 React의 이벤트 위임 시스템이 최신 props를 참조하도록 업데이트
4. 번들 크기 및 빌드 시간 영향
번들 크기
- 가상 DOM 라이브러리(ReactDOM) 코드가 경량화되거나 일부 모듈이 트리‑쉐이킹될 수 있어, 번들 크기가 비슷하거나 더 작아질 가능성이 있음
빌드 시간
- JSX → 노드 생성/업데이트 함수 분리 로직을 추가로 실행하므로, Babel 혹은 컴파일러 플러그인 실행 비용이 소폭 늘어남
- 1~2초 내외의 추가 오버헤드가 생길 수 있으나, incremental build(증분 빌드)나 persistent caching을 켜두면 실제 체감 증가는 거의 없다고 함
5. React Compiler 코드 적합성 진단, 관련 ESLint 플러그인
설치 및 실행
# 최신 베타 버전 설치 없이 바로 실행 가능
npx react-compiler-healthcheck --src ./src- --src 옵션에 검사할 엔트리 파일 또는 디렉터리 경로를 지정
- 별도 설치 없이 npx로 최신 버전을 실행
주요 출력 예시
✔ Successfully compiled 120 out of 150 components.
ℹ︎ Found 80% mode-safe components.
✔ <StrictMode> detected.
✖︎ 5 components use unsupported patterns (e.g. dynamic hooks).- Successfully compiled: 컴파일러가 최적화 가능한 컴포넌트 수
- mode-safe components: StrictMode 하에서도 안정적으로 작동하는 컴포넌트 비율
- unsupported patterns: Rules of React 위반으로 스킵된 컴포넌트 개수
ESLint 플러그인
eslint-plugin-react-compiler
module.exports = {
root: true,
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 2024,
sourceType: 'module',
ecmaFeatures: { jsx: true },
},
plugins: ['react-compiler'],
extends: [
'eslint:recommended',
'plugin:react/recommended',
// react-compiler의 권장 설정(없다면 rules 직접 설정)
],
rules: {
// 컴파일러가 최적화 대상이 아닌 코드를 경고/에러로 표시
'react-compiler/react-compiler': 'warn',
},
settings: {
react: { version: 'detect' },
},
};VSCode 등에서 ESLint 확장 활성화 시
“Rules of React” 위반 지점에 밑줄 또는 경고 아이콘 표시
실시간으로 최적화 스킵 사유를 파악 가능 react-compiler/react-compiler 룰 레벨을 'error'로 두면
CI 파이프라인에서 최적화 미지원 코드를 강제 차단
특정 파일만 검사하려면 overrides 섹션에 files: ["src/components/*/.jsx"] 등을 추가
5. 성능 실험
간단한 UI 테이블에 1,000건 상태 변화 렌더링 비교
import React, { useState, useEffect, useMemo, Profiler } from 'react';
import { createRoot } from 'react-dom/client';
function BigTable() {
// 0부터 999까지 1000개 아이템 생성 (한 번만)
const items = useMemo(
() => Array.from({ length: 1000 }, (_, i) => ({ id: i, text: `Row ${i}` })),
[]
);
// 상태값을 바꿀 때마다 전체 테이블이 다시 렌더링됩니다
const [tick, setTick] = useState(0);
// console.time 측정 시작
const handleClick = () => {
console.time('table-update');
setTick(t => t + 1);
};
// 상태가 바뀌고 나서 console.timeEnd 호출
useEffect(() => {
console.timeEnd('table-update');
}, [tick]);
// Profiler 콜백
const onRender = (id, phase, actualDuration) => {
console.log(`[Profiler][${id}] ${phase} – ${actualDuration.toFixed(2)}ms`);
};
return (
<div style={{ padding: 20 }}>
<button onClick={handleClick}>
리렌더링 트리거 ({tick})
</button>
{/* Profiler로 상세 렌더링 시간도 함께 로깅 */}
<Profiler id="BigTable" onRender={onRender}>
<table border="1" cellPadding="4" style={{ marginTop: 20 }}>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Text</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{items.map(item => (
<tr key={item.id}>
<td>{item.id}</td>
<td>{item.text}: {tick}</td>
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</table>
</Profiler>
</div>
);
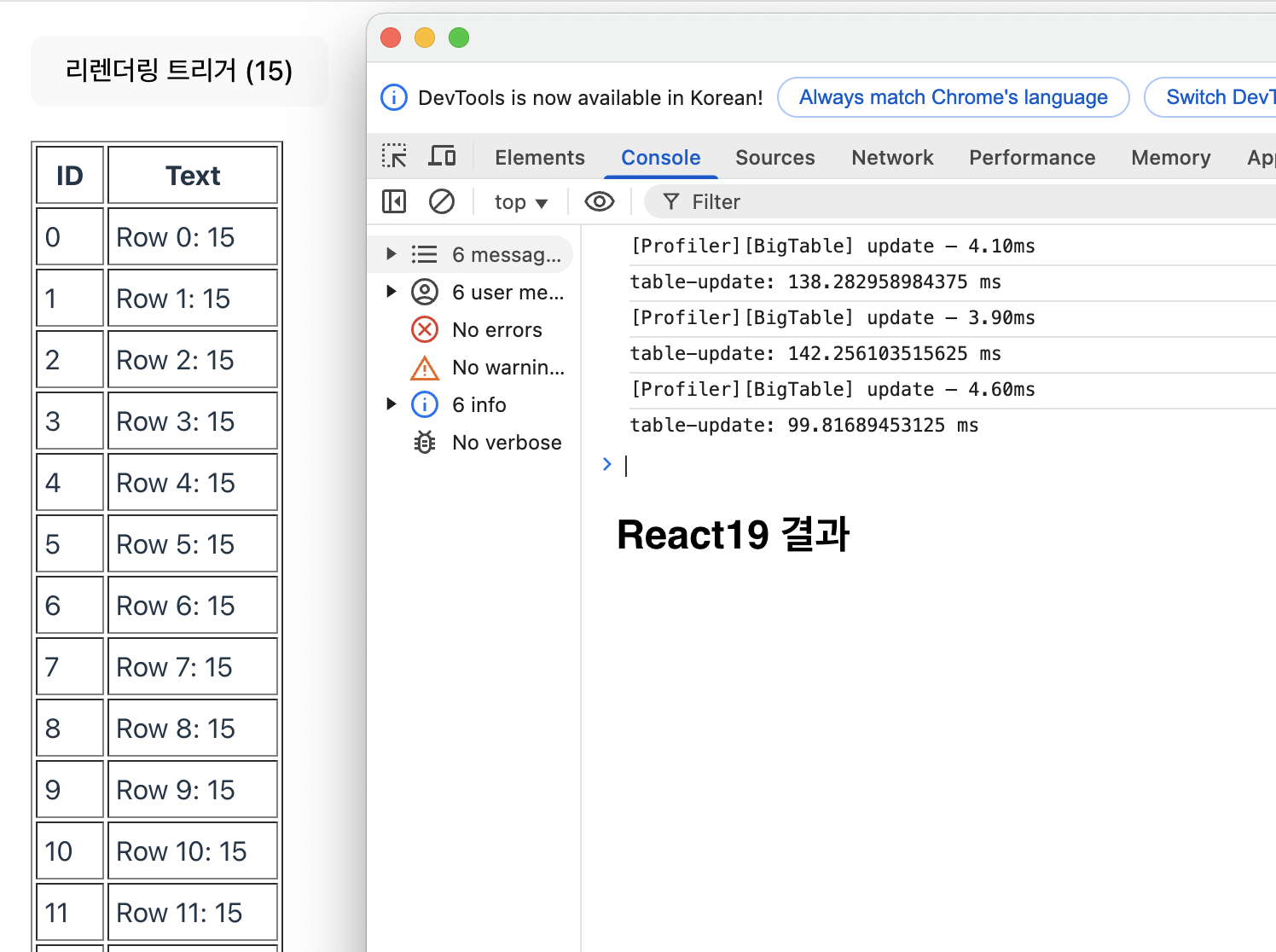
}- React18 결과
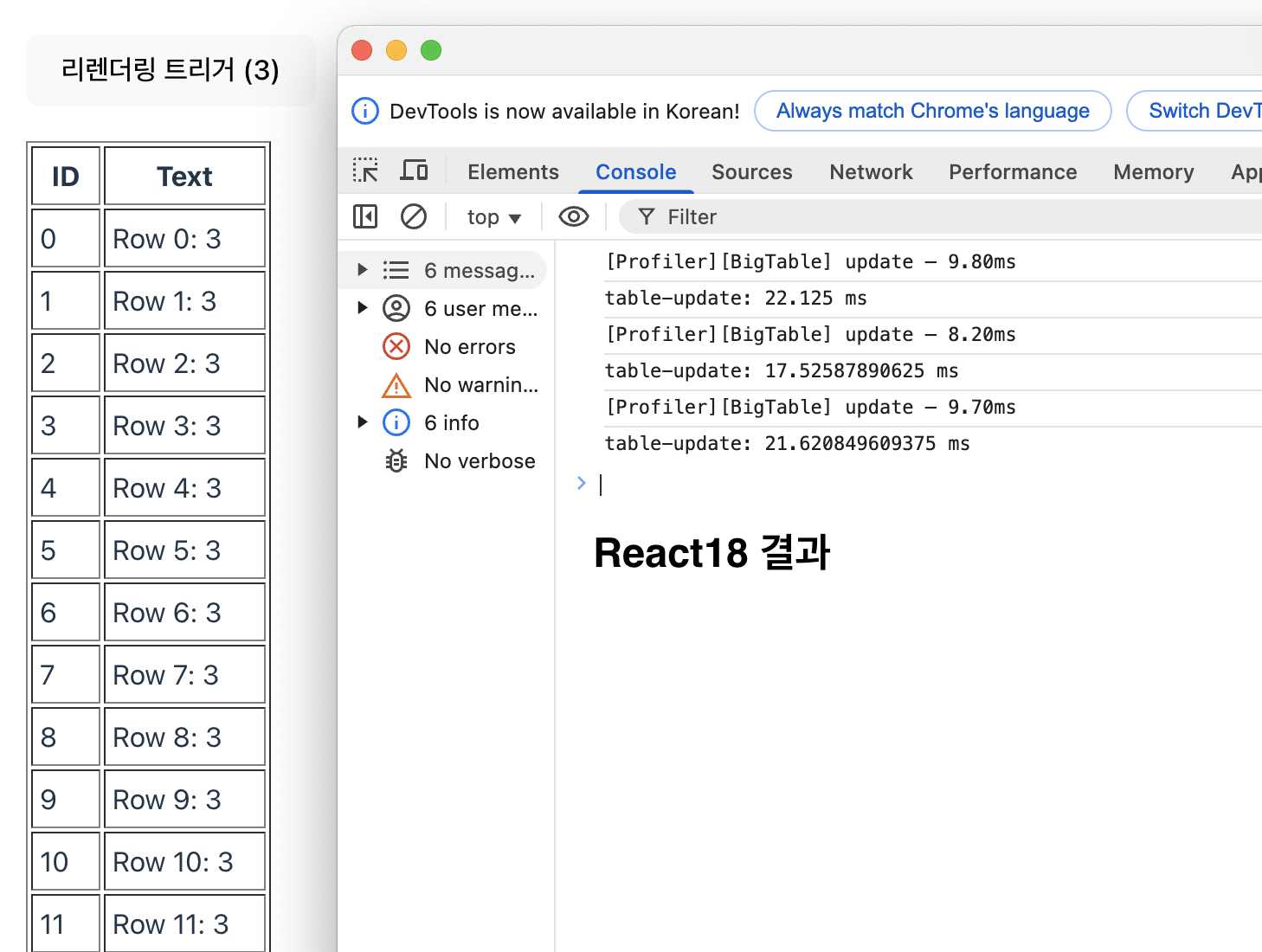
- React19 결과