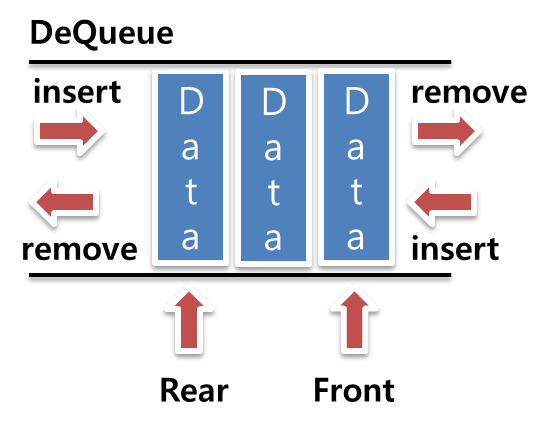
스택
스택은 LIFO(Last-In First-Out), 즉 후입선출의 자료구조이다. 구조는 사진과 같은 형태이며, 아래부터 쌓여서 나중에 삽입된 데이터가 먼저 빠져나가도록 되어있다.
아래 사진을 보면 top 변수는 가장 최근에 들어온 요소를 가리키며 스택이 비어있으면 -1이다.
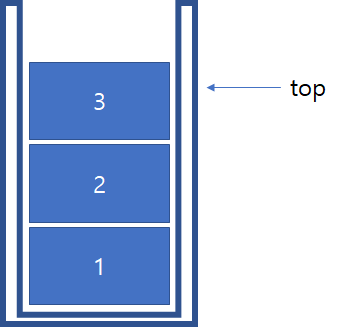
특징
- top으로 정한 곳을 통해서만 접근
- 정해진 방향으로만 쌓음
- LIFO, 가장 마지막에 삽입된 자료가 가장 먼저 삭제
용도
스택의 특징인 후입선출(LIFO)을 활용하여 여러 분야에서 활용 가능하다.
- 웹 브라우저 방문기록 (뒤로 가기) : 가장 나중에 열린 페이지부터 다시 보여준다.
- 역순 문자열 만들기 : 가장 나중에 입력된 문자부터 출력한다.
- 실행 취소 (undo) : 가장 나중에 실행된 것부터 실행을 취소한다.
후위 표기법 계산 - 수식의 괄호 검사 (연산자 우선순위 표현을 위한 괄호 검사)
- 그외에도 계산기, 미로 탐색, 함수의 복귀주소 저장 등
연산
-
삽입
삽입 연산(push) 시 top에 요소 하나를 추가한 후, top을 한 칸 위로 올려준다. -
삭제
삭제 연산(pop) 시 top에서 요소 하나를 뺀 후, top을 한 칸 아래로 내려준다. -
접근
접근 연산은 없다. 다만 top의 요소를 꺼내지는 않고 확인만 하는 용도의 연산(peek)은 있다.
구현
스택은 배열 또는 연결리스트로 구현할 수 있다. 연결리스트로 구현 시 스택의 크기 제한이 없다고 볼 수 있으며, 기타 장단점은 '연결리스트' 파트에서 설명한 바와 같다.
C++에서는
import <stack>;로 C++ STL 라이브러리를 불러온 후,stack<int> stk;과 같이stack<자료형>스택이름으로 변수를 생성한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Stack {
private:
int top;
int arr[5];
public:
Stack() {
top = -1; // 비어있음
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr[i] = 0;
}
}
bool isEmpty() {
if (top == -1) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool isFull() {
if (top == 4)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void push(int val) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "stack overflow" << endl;
}
else {
top++;
arr[top] = val;
}
}
int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "stack empty" << endl;
return 0;
}
else {
int popValue = arr[top];
arr[top] = 0;
top--;
return popValue;
}
}
int count() {
return (top + 1);
}
int peek(int pos) {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "stack underflow" << endl;
return 0;
}
else {
return arr[pos];
}
}
void change(int pos, int val) {
arr[pos] = val;
cout << "value changed at location" << pos << endl;
}
void display() {
cout << "All values in the Stack are " << endl;
for (int i = 4; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
}
};
int main() {
Stack s1;
int option, postion, value;
do {
cout << "What operation do you want to perform? Select Option number. Enter 0 to exit." << endl;
cout << "1. Push()" << endl;
cout << "2. Pop()" << endl;
cout << "3. isEmpty()" << endl;
cout << "4. isFull()" << endl;
cout << "5. peek()" << endl;
cout << "6. count()" << endl;
cout << "7. change()" << endl;
cout << "8. display()" << endl;
cout << "9. Clear Screen" << endl << endl;
cin >> option;
switch (option) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
cout << "Enter an item to push in the stack" << endl;
cin >> value;
s1.push(value);
break;
case 2:
cout << "Pop Function Called - Poped Value: " << s1.pop() << endl;
break;
case 3:
if (s1.isEmpty())
cout << "Stack is Empty" << endl;
else
cout << "Stack is not Empty" << endl;
break;
case 4:
if (s1.isFull())
cout << "Stack is Full" << endl;
else
cout << "Stack is not Full" << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "Enter position of item you want to peek: " << endl;
cin >> postion;
cout << "Peek Function Called - Value at position " << postion << " is " << s1.peek(postion) << endl;
break;
case 6:
cout << "Count Function Called - Number of Items in the Stack are: " << s1.count() << endl;
break;
case 7:
cout << "Change Function Called - " << endl;
cout << "Enter position of item you want to change : ";
cin >> postion;
cout << endl;
cout << "Enter value of item you want to change : ";
cin >> value;
s1.change(postion, value);
break;
case 8:
cout << "Display Function Called - " << endl;
s1.display();
break;
case 9:
system("cls");
break;
default:
cout << "Enter Proper Option number " << endl;
}
} while (option != 0);
return 0;
} 큐
큐는 FIFO(First-In First-Out), 즉 선입선출의 자료구조이다. 구조는 아래 사진과 같으며, 대기열처럼 밀려서 먼저 삽입된 데이터가 먼저 빠져나가도록 되어있다.
삽입은 back에서 일어나며, 삭제는 front에서 발생한다.
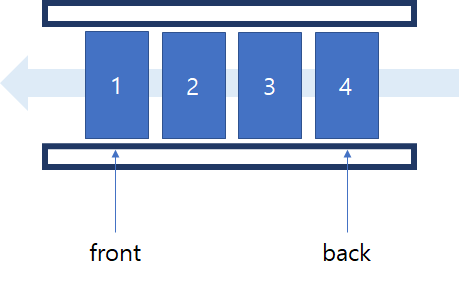
특징
- 큐의 가장 첫 원소를 front / 가장 끝 원소를 rear
- 큐는 들어올 때 rear로 들어오지만 나올때는 front부터 빠지는 특성
- 접근방법은 가장 첫 원소와 끝 원소로만 가능
- 가장 먼저 들어온 프론트 원소가 가장 먼저 삭제
종류
- 선형 큐
- 원형 큐: 오버플로우가 일어날 걱정이 없다.
- 우선순위 큐: 요소들의 우선순위를 매겨, 우선순위에 맞게 삽입 / 삭제 연산을 구현한 큐이다.
용도
큐는 주로 데이터가 입력된 시간 순서대로 처리해야 할 필요가 있는 상황에 이용한다.
- 우선순위가 같은 작업 예약 (프린터의 인쇄 대기열)
- 은행 업무
- 콜센터 고객 대기시간
- 프로세스 관리
- 너비 우선 탐색(BFS, Breadth-First Search) 구현
- 캐시(Cache) 구현
연산
-
삽입
삽입 연산(put == Enqueue) 시 back에 요소 하나를 추가한 후, back을 하나 뒤로 옮겨준다.
-
삭제
삭제 연산(get == Dequeue ) 시 front에서 요소 하나를 삭제한 후, front를 하나 뒤로 옮겨준다. -
접근
peek 연산을 이용하여 front에서 요소를 확인할 수 있다.
구현
큐 또한 주로 배열로 구현되고, 연결리스트로도 구현할 수 있긴 하다. 연결리스트로 큐를 구현하였을 때는 굳이 환형 큐가 아니더라도 오버플로우가 발생할 걱정은 없다.
C++에서는
import <queue>;로 C++ STL 라이브러리를 불러온 후,queue<int> q;과 같이queue<자료형>큐이름으로 변수를 생성한다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Queue {
private:
int front;
int rear;
int arr[5];
public:
Queue() {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr[i] = 0;
}
}
bool isEmpty() {
if (front == -1 && rear == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool isFull() {
if (rear == 4) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
void enqueue(int val) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Queue is FULL" << endl;
return;
}
else if (isEmpty()) {
rear = 0;
front = 0;
arr[rear] = val;
}
else {
rear++;
arr[rear] = val;
}
}
int dequeue() {
int x;
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is EMPTY" << endl;
return 0;
}
else if (front == rear) {
x = arr[front];
arr[front] = 0;
rear = -1;
front = -1;
return x;
}
else
{
x = arr[front];
arr[front] = 0;
front++;
return x;
}
}
int count() {
return (rear - front + 1);
}
void display() {
cout << "All values in the Queue are - " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
}
};
int main() {
Queue q1;
int value, option;
do {
cout << "\n\nWhat operation do you want to perform? Select Option number. Enter 0 to exit." << endl;
cout << "1. Enqueue()" << endl;
cout << "2. Dequeue()" << endl;
cout << "3. isEmpty()" << endl;
cout << "4. isFull()" << endl;
cout << "5. count()" << endl;
cout << "6. display()" << endl;
cout << "7. Clear Screen" << endl << endl;
cin >> option;
switch (option) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
cout << "Enqueue Operation \nEnter an item to Enqueue in the Queue" << endl;
cin >> value;
q1.enqueue(value);
break;
case 2:
cout << "Dequeue Operation \nDequeued Value : " << q1.dequeue() << endl;
break;
case 3:
if (q1.isEmpty())
cout << "Queue is Empty" << endl;
else
cout << "Queue is not Empty" << endl;
break;
case 4:
if (q1.isFull())
cout << "Queue is Full" << endl;
else
cout << "Queue is not Full" << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "Count Operation \nCount of items in Queue : " << q1.count() << endl;
break;
case 6:
cout << "Display Function Called - " << endl;
q1.display();
break;
case 7:
system("cls");
break;
default:
cout << "Enter Proper Option number " << endl;
}
} while (option != 0);
return 0;
}원형큐
배열을 이용한 큐는 이미 사용한 영역인 front의 앞부분에 대해서 다시 활용을 못하기 때문에 메모리를 낭비한다는 단점이 있음
또한, 이동 큐를 이용하여 큐가 다 찼을 경우 데이터들을 앞쪽으로 이동시켜 사용하는 방법이 있지만 남아있는 모든 데이터를 다 이동 시켜야 한다는 불편한 작업을 수행해야 하기 때문에 효율적이지 못함
- 원형 큐는 이와 같은 단점을 보완하는 구조로 큐의 맨 끝과 맨 처음이 연결된 형태의 구조이기 때문에 이미 꺼내어 사용한 큐의 앞부분에 다시 데이터를 저장하여 재사용이 가능한 형태의 큐
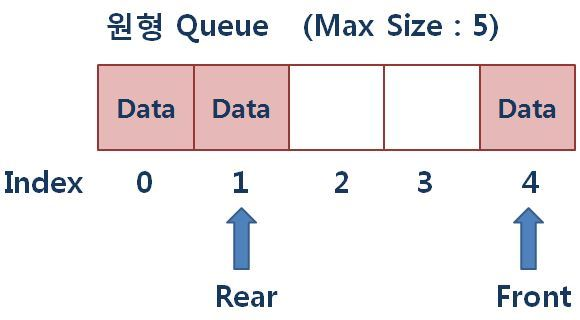
구현
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CircularQueue {
private:
int front;
int rear;
int arr[5];
int itemCount;
public:
CircularQueue() {
itemCount = 0;
front = -1;
rear = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr[i] = 0;
}
}
bool isEmpty() {
if (front == -1 && rear == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool isFull() {
if ((rear+1)%5 == front) { // queue와 다른점
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
void enqueue(int val) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Queue is FULL" << endl;
return;
}
else if (isEmpty()) {
rear = 0;
front = 0;
arr[rear] = val;
}
else {
rear = (rear+1)%5; // queue와 다른점
arr[rear] = val;
}
itemCount++;
}
int dequeue() {
int x = 0;
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Queue is EMPTY" << endl;
return x;
}
else if (front == rear) {
x = arr[front];
arr[front] = 0;
rear = -1;
front = -1;
itemCount--;
return x;
}
else
{
x = arr[front];
arr[front] = 0;
front = (front+1)%5;
itemCount--;
return x;
}
}
int count() {
return itemCount;
}
void display() {
cout << "All values in the Queue are - " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
}
};
int main() {
CircularQueue q1;
int value, option;
do {
cout << "\n\nWhat operation do you want to perform? Select Option number. Enter 0 to exit." << endl;
cout << "1. Enqueue()" << endl;
cout << "2. Dequeue()" << endl;
cout << "3. isEmpty()" << endl;
cout << "4. isFull()" << endl;
cout << "5. count()" << endl;
cout << "6. display()" << endl;
cout << "7. Clear Screen" << endl << endl;
cin >> option;
switch (option) {
case 0:
break;
case 1:
cout << "Enqueue Operation \nEnter an item to Enqueue in the Queue" << endl;
cin >> value;
q1.enqueue(value);
break;
case 2:
cout << "Dequeue Operation \nDequeued Value : " << q1.dequeue() << endl;
break;
case 3:
if (q1.isEmpty())
cout << "Queue is Empty" << endl;
else
cout << "Queue is not Empty" << endl;
break;
case 4:
if (q1.isFull())
cout << "Queue is Full" << endl;
else
cout << "Queue is not Full" << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "Count Operation \nCount of items in Queue : " << q1.count() << endl;
break;
case 6:
cout << "Display Function Called - " << endl;
q1.display();
break;
case 7:
system("cls");
break;
default:
cout << "Enter Proper Option number " << endl;
}
} while (option != 0);
return 0;
}우선순위큐
-
데이터의 우선순위에 따라 우선순위가 높은 데이터 부터 꺼내도록 만들어진 큐
-
데이터를 삽입할 때,
우선순위에 따라서 정렬하여 삽입한 후 한쪽 방향에서만 데이터를 꺼내어 쓰도록 작성 -
스택과 큐도 데이터의 저장 시간에 따라 우선순위를 부여하는 우선순위 큐의 한 종류라고 할 수 있음
-
스택은 가장 최근에 저장된 데이터의 우선순위가 높고, 큐는 오래지난 데이터의 우선순위가 높음
데크
-
일반적인 큐는 데이터의 삽입과 삭제가 한쪽 방향에서만 발생하지만 데크는 리스트의 양쪽 끝 모두에서 데이터를 삽입, 삭제 할 수 있도록 만들어진 특별한 형태의 자료구조
-
양쪽 방향 모두에서 삽입과 삭제가 발생할 수 있으므로 큐나 스택으로 모두 활용할 수 있음. 만약, 한쪽 방향에서 삽입과 삭제를 모두 처리하면, 스택으로 동작하는 것이고 한쪽 방향에서는 삽입만 발생하고 반대쪽 방향에서는 삭제만 발생하도록 처리하면 큐처럼 동작함