Java의 기본 동작 원리
public class HelloWorldApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!!");
}
}원인
source
code
language
결과
application
program
Java Source code(.java)
사람이 이해 하는 형태 compaile을 통해 컴퓨터가 이해할 수 있는 형태인(.class) Java Application 형태로 변환한다.
Java Virtual Machine이 .class확장자의 파일을 읽어서 computer에
실행시킨다.
Data&Operation
Data type
Number
String
etc.
각각의 데이터 종류에 따라 요구되는 처리방식이 요구된다.
public class Datatype{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(6); // Number
System.out.println("six"); // String
System.out.println("6"); // String 6
System.out.println(6+6); // 12
System.out.println("6"+"6"); // 66
System.out.println(6*6); // 36
// System.out.println("6"*"6");
System.out.println("1111".length()); // 4
// System.out.println(1111.length());
System.out.println("Hello World"); //String 문자열
System.out.println('H'); //Char 문자
System.out.println("H");
}
}숫자와 연산
연산자: Operator
Math
eclipse에서 쓸 수 있는 연잔자들의 메소드 캐비닛
public class Number {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Operator
System.out.println(6 + 2); // 8
System.out.println(6 - 2); // 4
System.out.println(6 * 2); // 12
System.out.println(6 / 2); // 3
System.out.println(Math.PI); // 3.141592653589793
System.out.println(Math.floor(Math.PI));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(Math.PI));
}
}문자열의 표현
"": string 문자열
'': Character 문자(한 글자 표현)
\n: 줄바꿈에 사용 (new line)
\: 뒤따라오는 기능이 있는 기호, "" 등을 그 기능에서 해방시켜 일반 문자열로 인식되게 한다. (escape)
public class StringApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
System.out.println('H'); // Character
System.out.println("H"); // String
System.out.println("Hello "
+ "World");
System.out.println("Hello \nWorld");
System.out.println("Hello \"World\"");
}
}
**Variable(변수)
int : integer : 정수
double : real number : 실수
String : 문자
해당하는 변수에 해당하는 Data type을 지정해야 한다.
public class Variable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1; // Number -> integer ... -2, -1 , 0, 1, 2 ...
System.out.println(a);
double b = 1.1; // real number -> double ... -2.0, -1.0, 0, 1.0, 2.0 ...
System.out.println(b);
String c = "Hello World";
System.out.println(c);
}
}변수의 활용
변수를 통해 값이 가진 의미를 파악할 수 있게 한다.
ex)
public class Letter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "leezche";
System.out.println("Hello, "+name+" ... "+name+" ... egoing ... bye");
// 문자열을 변수로 받아서 문장에 삽입할 수 있다.
double VAT = 10.0; // 10.0은 단순히 숫자이지만 변수로 정의하여 문서를 읽는 사람으로 하여금 그 의미를 파악할 수 있게 한다.
System.out.println(VAT);
}
}Casting
변수를 컨버팅하는 방법
데이터의 손실이 발생할 수 있는 경우 변수의 타입은 자동 컨버팅(캐스팅)되지 않는다.
예를들어 정수 1은 실수 1.0으로 자동 컨버팅이 가능하지만, 실수 1.1은 정시 1로 자동 컨버팅이 불가하다. 0.1의 손실이 발생하기 때문. 이때 사용할 수 있는 기능이 캐스팅이다(데이터를 명시적으로 바꿔주는 방법). 컨버팅하고자 하는 데이터 앞에 ()를 두고 바꾸고자하는 데이터 타입을 넣는다. ex) int e = (int) 1.1;
숫자를 문자열로 바꾸는 캐스팅 방법은 toString 메소드를 사용한다.
ex) String f = Integer.toString(1);
ex)
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double a = 1.1;
double b = 1;
double b2 = (double) 1;
System.out.println(b);
// int c = 1.1;
double d = 1.1;
int e = (int) 1.1;
System.out.println(e);
// 1 to String
String f = Integer.toString(1);
System.out.println(f.getClass());
}
}라이브러리 Import하는법
import org.opentutorials.iot.Elevator;
import org.opentutorials.iot.Lighting;
import org.opentutorials.iot.Security;최상단에 기입
입력과 출력
Arguments: 입력값
Parameters: 매개변수
입력값을 받는 방법
- showInputDialgog : 입력창을 띄워서 입력값을 받아서 사용
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class OkJavaGoInHomeInput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String id = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter a ID");
String bright = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter a Bright level");- args : Run Configuration에서 입력한 parameter를 args 배열에 하나씩 받아서 사용
import org.opentutorials.iot.DimmingLights;
import org.opentutorials.iot.Elevator;
import org.opentutorials.iot.Lighting;
import org.opentutorials.iot.Security;
public class OkJavaGoInHomeInput {
// paramter, 매개변수
public static void main(String[] args) {
String id = args[0];
String bright = args[1];
// Elevator call
Elevator myElevator = new Elevator(id);
myElevator.callForUp(1);
// Security off
Security mySecurity = new Security(id);
mySecurity.off();
// Light on
Lighting hallLamp = new Lighting(id+" / Hall Lamp");
hallLamp.on();
Lighting floorLamp = new Lighting(id+" / floorLamp");
floorLamp.on();
DimmingLights moodLamp = new DimmingLights(id+" moodLamp");
moodLamp.setBright(Double.parseDouble(bright));
moodLamp.on();
}
}API vs UI
API : Applicatoin Programming Interface
자바의 기본 라이브러리를 사용하기 위한 조작방법(조작장치)
UI :User Interface
API를 사용하여 만든 프로그램을 사람이 사용하기 위해 가공된 조작방법(조작장치)
Java API Documentation
Pachage & Class
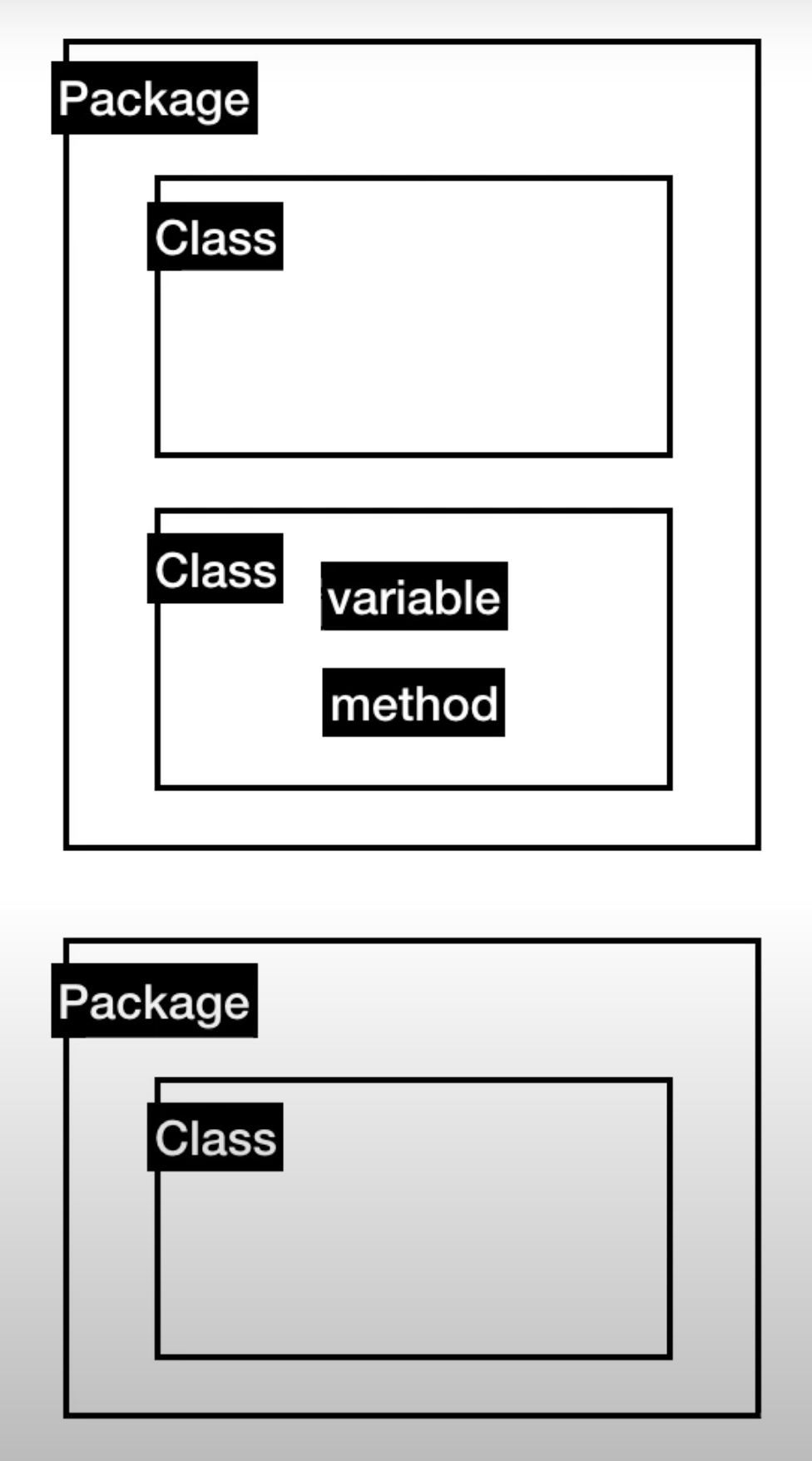
Class: 유사한 변수(Variable)과 수식(Methods)들의 집합체
Package: Class들을 기능과 종류에 따라 그룹핑한 집합체
Instance
복잡하고 연속된 작업을 위한 클래스를 사용시 반드시 new를 클래스 앞에 붙혀서 그 클래스의 개별적인 복사본을 만들어 개별적인 작업을 최적화 시킨다. 클래스중에는 일회성의 new가 필요없는 Math같은 클래스도 있고 반드시 new가 필요한 constructor를 가진 PrintWriter같은 클래스도 있다.
new : 복사본을 만든다.
ex)
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class InstanceApp {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintWriter p1 = new PrintWriter("result1.txt");
p1.write("Hello 1");
p1.close();
PrintWriter p2 = new PrintWriter("result2.txt");
p2.write("Hello 2");
p2.close();
}
}
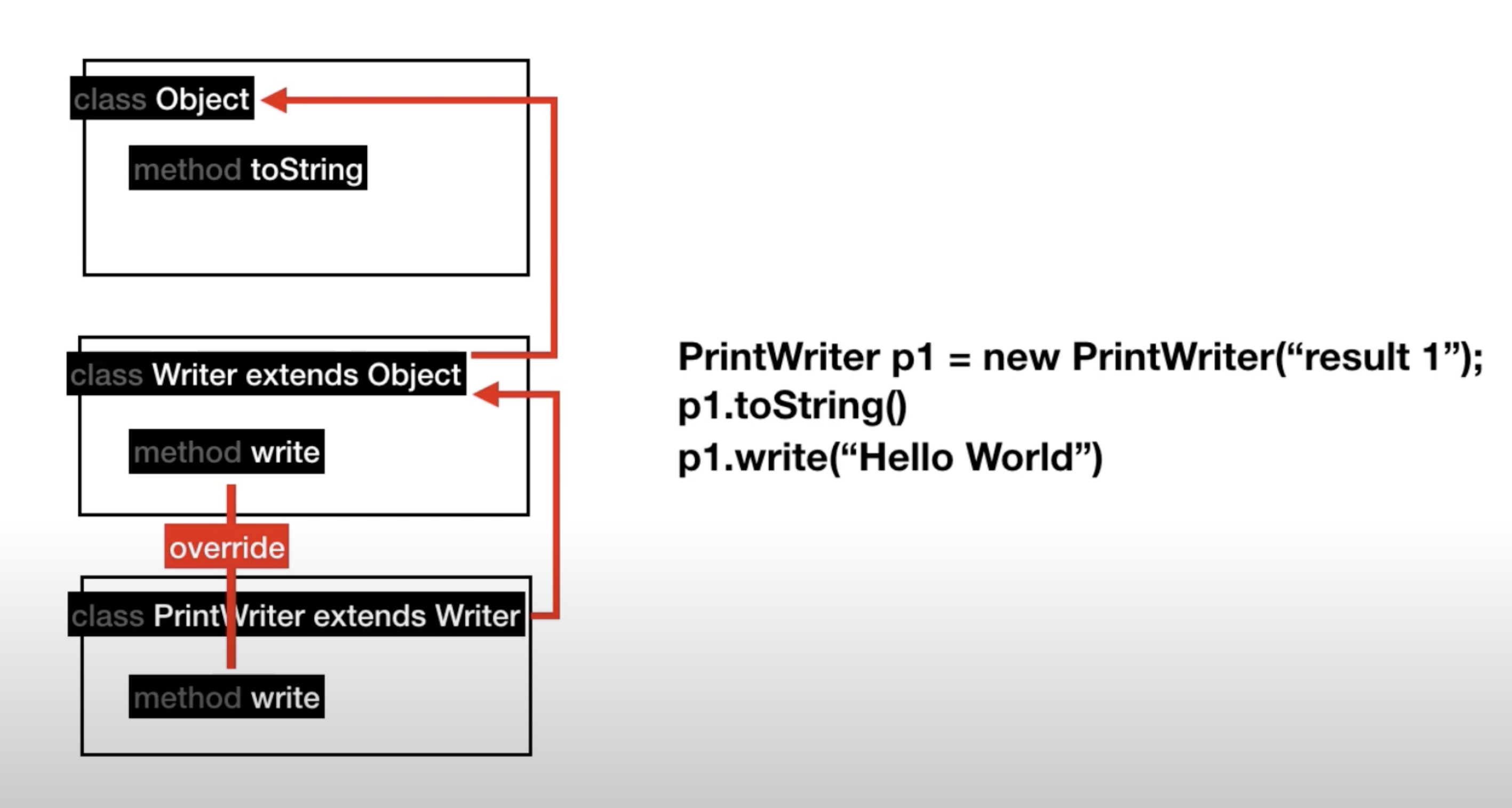
Inheritance
상속: 이미 있는 클래스의 기능과 요소에 덧붙혀 새로운 추가된 기능(Variable & Method)을 가진 클래스를 만드는것
Java의 모든 클래스는 Object클래스를 기본으로 상속받는다.(extends를 사용해서 상속) 이때 Method를 덮어쓸 수도 있다.
관계도