Youtube 코드 없는 프로그래밍 채널의 백트래킹 playlist 따라서 관련 문제들 풀어보았습니다.
기본적인 BackTracking 풀이
-
일반적인 경우, iteration 보다 recursion으로 푸는 것이 좀더 편함
- Maximum Call Stack을 초과할 가능성이나 메모리 문제 가능성 있는 경우 등은 iteration으로 해결 -
helper 재귀 함수 구성
- exit part: 탈출 조건
- process part: 조건에 해당하는 경우 추출
- recursion part: process part에서 나온 경우들에 대해 재귀 적용
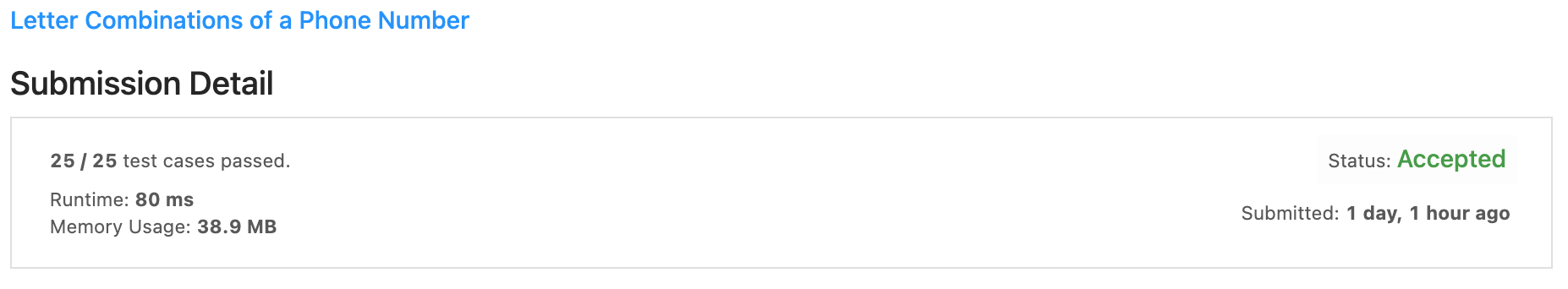
17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
- 숫자로 구성된 문자열에 따라
- 만들어질 수 있는 모든 문자열 조합 구하기
// 번호-letters mapping
const letters = {
2: ["a", "b", "c"],
3: ["d", "e", "f"],
4: ["g", "h", "i"],
5: ["j", "k", "l"],
6: ["m", "n", "o"],
7: ["p", "q", "r", "s"],
8: ["t", "u", "v"],
9: ["w", "x", "y", "z"],
};
/**
* @param {string} digits
* @return {string[]}
*/
const letterCombinations = (digits) => {
// 예외처리; 길이가 0인 경우 빈 배열 반환
if (digits.length === 0) return [];
const answer = [];
// helper/재귀 함수 정의
const getCombi = (idx = 1, combi = "") => {
// exit part
// 조합 문자열 길이가 충족된 경우 정답 배열에 추가
if (idx > digits.length) {
answer.push(combi);
return;
}
// process-recursion part
// 해당 번호의 문자 배열을 문자열에 추가하고
// 인덱스 1 증가시켜 재귀 호출
[...letters[digits[idx - 1]]].forEach((l) =>
getCombi(idx + 1, combi + l)
);
};
// helper 함수 호출
getCombi(1, "");
return answer;
};
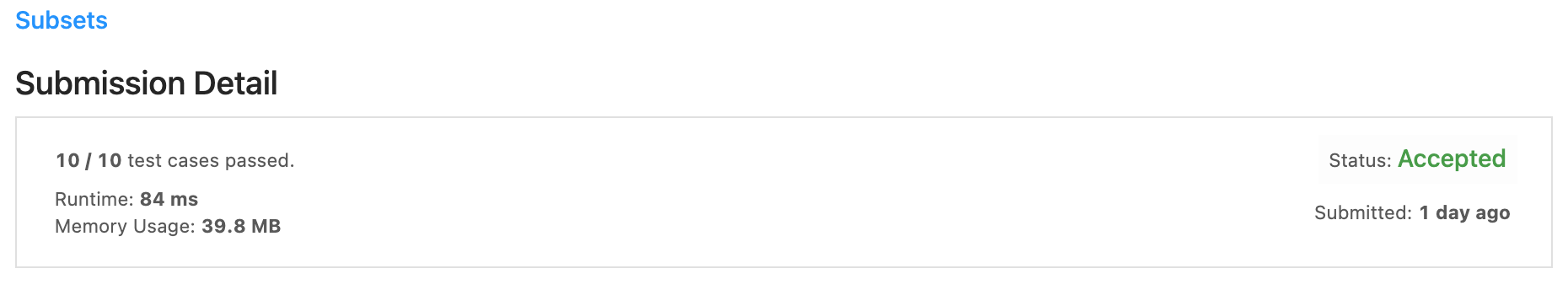
78. Subsets
숫자 배열의 부분 집합 구하기
recursion 대신 reduce 함수 활용하여 iteration 방식으로 풀이함
- 이전 iteration 결과를 가져와서, 기존 부분 집합과 새로운 element를 추가한 신규 부분 집합 생성
- JS의
reduce메서드를 잘 활용하면, 재귀보다 좀더 편하게 풀 수 있을 것 같다
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[][]}
*/
const subsets = (nums) =>
// 문제 조건에 배열 내 순서는 상관 없기 때문에(any order), `reverse`는 사용하지 않아도 됨
nums.reverse().reduce(
(acc, val) => {
const curr = [];
acc.forEach((e) => {
// 기존 부분집합 그대로 추가
curr.push(e);
// 새로운 원소(`val`) 추가한 신규 부분집합 생성하여 추가
curr.push([val].concat(e));
});
return curr;
},
[[]]
);
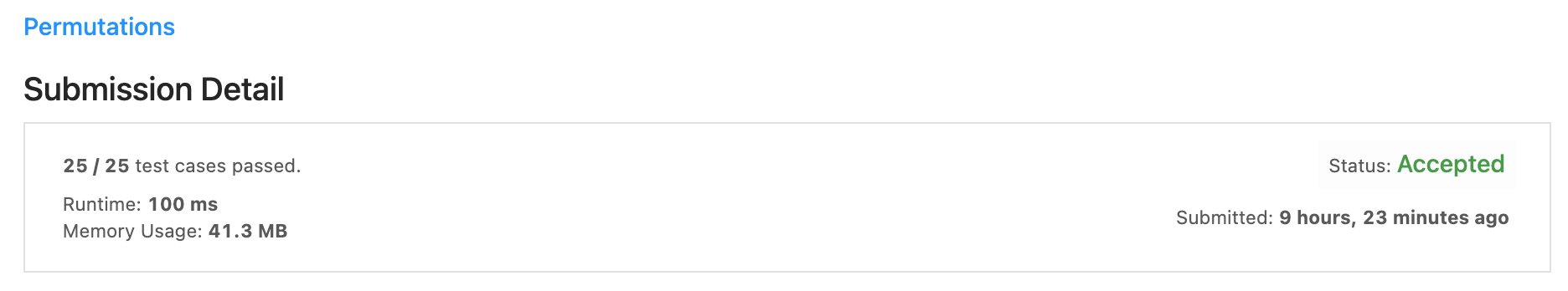
46. Permutations
순열
- 위 Subsets 문제와 마찬가지로, reduce, forEach 등 functional 배열 메서드가 있어서 좀더 편하게 풀 수 있는 듯
- reduce를 이렇게 써도 괜찮을지 모르겠지만, python의 range 함수 대용으로 가볍게 쓸 수 있지 않을까?
- iteration 방식에서 이중 for-loop은 어쩔 수 없는 것 같다
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[][]}
*/
const permute = (nums) =>
// reduce 메서드에서 accumulator(previousValue)만 넘기게 되면,
// 배열의 length만큼만 loop을 돌면서
// 이전 loop 결과를 활용할 수 있음
nums.reduce(
(acc) => {
const curr = [];
// 원본 배열의 각 원소(num)마다
nums.forEach((num) => {
// 이전 생성된 각각의 배열에 num이 포함되어 있지 않으면 추가
acc.forEach(
(a) => !a.includes(num) && curr.push(a.concat(num))
);
});
return curr;
},
[[]]
);
39. Combination Sum
target sum을 만족하는 모든 조합(중복 제외)
1차 제출
모든 경우의 수를 구한 뒤, 중복은 sort, map 활용해 제거
// helper/재귀 함수
const getSum = (candidates, currentTarget, ans, sum = []) => {
// exit part
if (currentTarget === 0) {
// 만들어진 조합 배열을 오름차순 정렬
const sortedSum = sum.sort((a, b) => a - b);
// join 메서드로 문자열 생성
const sumToStr = sortedSum.join(",");
// 기존 map에 해당 문자열 key가 있는 경우는 중복이므로 제외
// 기존 값 없는 경우 추가
if (!ans[sumToStr]) ans[sumToStr] = sortedSum;
return;
}
// process-recursion part
// currentTarget이 candidates의 해당 원소 값보다 큰 경우 === 해당 원소로 조합 만들 수 있는 경우
candidates.forEach((can) => {
if (currentTarget >= can)
// currentTarget에서 해당 원소 값 차감; 조합에 더 추가해야 하는 값
// 조합 배열에 해당 원소 값 추가
getSum(candidates, currentTarget - can, ans, sum.concat(can));
});
};
/**
* @param {number[]} candidates
* @param {number} target
* @return {number[][]}
*/
const combinationSum = (candidates, target) => {
const ans = {};
// helper 함수 실행
getSum(candidates, target, ans);
// 찾은 조합 배열들 반환
return Object.values(ans);
};
개선된 방법
위 코드로는 중복을 포함한 모든 경우의 수를 찾기 때문에 memory 사용이 좀더 많을 수 밖에 없음
재귀함수의 arguments에 candidates index를 추가하여 process part를 개선
- 현재 index 이상인 경우에만 재귀 호출
const getSum = (candidates, currentTarget, idx, ans, sum = []) => {
if (currentTarget === 0) {
const sortedSum = sum.sort((a, b) => a - b);
// 애초에 중복 배열이 만들어지지 않기 때문에 배열에 바로 추가
// 배열 내 순서는 신경 안써도 됨
ans.push(sortedSum);
return;
}
candidates.forEach((can, i) => {
// 현재 후보값 인덱스가 arguments로 넘어온 인덱스 이상인 경우에만
if (currentTarget >= can && i >= idx)
getSum(candidates, currentTarget - can, i, ans, sum.concat(can));
});
};
const combinationSum = (candidates, target) => {
const ans = [];
getSum(candidates, target, 0, ans);
return ans;
};
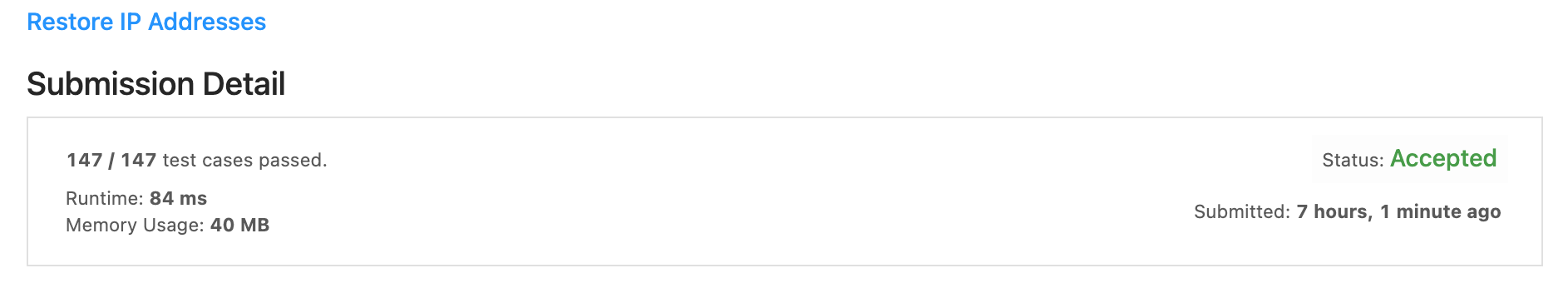
93. Restore IP Addresses
숫자 문자열 입력으로 만들어질 수 있는 모든 IP 주소
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {string[]}
*/
const restoreIpAddresses = (s) => {
const ans = [];
/**
* 각 자리의 주소가 유효한지 판단
* @param {string} num 숫자 문자열
* @returns {boolean}
*/
const isValid = (num) => {
if (num.length === 0) return false;
if (num[0] === "0" && num.length > 1) return false;
if (+num < 0 || +num > 255) return false;
return true;
};
/**
* helper / 재귀 함수
* @param {string} rest 남은 문자열
* @param {number} dots 남은 구분점 3~0
* @param {string} str 만들어진 문자열
*/
const getIps = (rest = s, dots = 3, str = "") => {
// exit part
// 마지막 자리에 대한 판단만 남은 경우, 무조건 종료해야 함
// 자리값이 유효한 경우 결과 배열에 추가
if (dots === 0) {
isValid(rest) && ans.push(str + rest);
return;
}
// process-recursion part
[1, 2, 3].forEach((idx) => {
// 남은 문자열의 앞 한글자~세글자 각각 분리
const current = rest.slice(0, idx);
const next = rest.slice(idx);
// 현재 자리수가 유효한 경우만 다음 자리 수 재귀 호출
isValid(current) && getIps(next, dots - 1, `${str}${current}.`);
});
};
// IP 복구 시작
getIps();
return ans;
};