코딩테스트를 준비하면서 자료구조와 알고리즘에 대한 개념을 정리하고자 한다.
Hash
해시 (Hash) : 입력 데이터를 고정된 길이의 데이터로 변환된 값
데이터의 KEY 값이 Hash 함수를 통해 변환된 간단한 정수이고,
정수로 변환된 Hash는 배열의 index, 위치, 데이터 값을 저장, 검색할 때 활용
특징
- Key - Value 를 매핑할 수 있는 데이터 구조
- Hash 함수를 통해 Key의 데이터를 배열에 저장할 수 있는 주소를 계산
- Key를 통해서 저장된 데이터를 빠르게 찾고, 저장 및 탐색 속도가 획기적으로 빨라진다.
Hash Function
Hash Function : 임의의 데이터를 고정된 길이의 값으로 리턴해주는 함수
HashFunction 은 '입력받은 데이터를 Hash 값으로 출력시키는 알고리즘'
예시)
Integer hashFunction(String key) {
return (int)(key.charAt(0)) % 100;
}String key에서 charAt(0) 으로 문자의 0번에 해당하는 부분을 (int)로 정수화하여 100으로 나머지를 반환하는 함수다.
반환된 값은 배열의 인덱스가 되고, 해당 인덱스에 맞게 저장할 수 있게 된다.
Hash Table
Hash Table : 키와 값을 함께 저장해 둔 데이터 구조
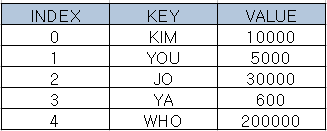
행과 열로 구성된 표에 저장되는 것과 유사하다.
추가 용어
- 버킷(bucket) : 하나의 주소를 갖는 파일의 한 구역, 버킷의 크기는 같은 주소에 포함될 수 있는 레코드 수
- 슬롯(slot) : 한 개의 레코드를 저장할 수 있는 공간, 한 버킷 안에 여러 개의 슬롯이 있다.
Hashing (해싱)
Hashing : Hash Function 에서 해시를 출력하고, Hash Table에 저장하는 과정까지의 행위
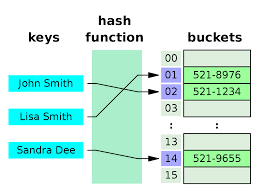
장단점
장점
- 데이터 저장 / 읽기 속도가 좋다.
- Hash는 key에 대한 데이터가 있는지 확인하기 쉽다.
단점
- 일반적으로 저장공간이 많이 필요하다.
- 여러 키에 해당하는 주소 (index) 가 동일한 경우 충돌을 해결하기 위한 별도의 자료구조가 필요하다.
HashMap
데이터를 저장할 때 key, value가 짝을 이루어 저장된다.
HashMap 생성방법
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Hash {
HashMap<String, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>(); // capacity : 16, load factor : 0.75
HashMap<String, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>(20); // capacity : 20, load factor : 0.75
HashMap<String, Integer> map3 = new HashMap<>(20, 0.8); // capacity : 20, load factor : 0.8
HashMap<String, Integer> map4 = new HashMap<>(map1); // Map(map1)의 데이터로 초기화
}capacity : 데이터 저장 용량
load factor : 데이터 저장공간을 추가로 확보해야하는 시점을 지정
HashMap 메소드
- 데이터 추가
1. V put(K key, V value) : key와 value를 저장
2. void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) : Map m의 데이터를 전부 저장
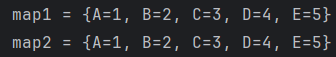
3. V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) : 기존 데이터에 key가 없으면 key와 value를 저장- 예제 코드
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Hash {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();
// put : key, value 저장
map1.put("A", 1);
map1.put("B", 2);
map1.put("C", 3);
// putIfAbsent : 기존 데이터에 key ("D") 가 없으면 key, value 저장
map1.putIfAbsent("D", 4);
map1.putIfAbsent("E", 5);
// putAll : Map map1의 데이터를 전부 저장
map2.putAll(map1);
System.out.println("map1 = " + map1);
System.out.println("map2 = " + map2);
}
}
- 데이터 확인
V get(Object key) : key와 맵핑된 value값을 반환
V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) : key와 맵핑된 value값을 반환하고 없으면 defaultValue값을 반환
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet( ) : 모든 key-value 맵핑 데이터를 가진 Set 데이터를 반환합니다.
Set<K> keySet( ) : 모든 key 값을 가진 Set 데이터를 반환
Collection<V> values( ) : 모든 value 값을 가진 Collection 데이터를 반환- 데이터 수정
V replace(K key, V value) : key와 일치하는 기존 데이터의 value를 변경
V replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) : key와 oldValue가 동시에 일치하는 데이터의 value를 newValue로 변경- 데이터 삭제
void clear( ) : 모든 데이터를 삭제
V remove(Object key) : key와 일치하는 기존 데이터( key와 value)를 삭제
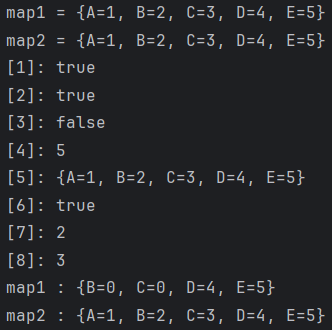
boolean remove(Object key, Object value) : key와 value가 동시에 일치하는 데이터를 삭제최종 예제 코드
package jehun.study.section01;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Hash {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();
// put : key, value 저장
map1.put("A", 1);
map1.put("B", 2);
map1.put("C", 3);
// putIfAbsent : 기존 데이터에 key ("D") 가 없으면 key, value 저장
map1.putIfAbsent("D", 4);
map1.putIfAbsent("E", 5);
// putAll : Map map1의 데이터를 전부 저장
map2.putAll(map1);
System.out.println("map1 = " + map1);
System.out.println("map2 = " + map2);
// 데이터 확인
System.out.println("[1]: " + map1.containsKey("A")); // true
System.out.println("[2]: " + map1.containsValue(1)); // true
System.out.println("[3]: " + map1.isEmpty()); // false
System.out.println("[4]: " + map1.size()); // 5
System.out.println("[5]: " + map1); // {A=1, B=2, C=3, D=4, E=5}
System.out.println("[6]: " + map1.remove("A", 1)); // true
System.out.println("[7]: " + map1.put("B", 0)); // 2
System.out.println("[8]: " + map1.replace("C", 0)); // 3
System.out.println("map1 : " + map1); // map1 : {B=0, C=0, D=4, E=5}
System.out.println("map2 : " + map2); // map2 : {A=1, B=2, C=3, D=4, E=5}
}
}
keySet()을 활용한 iterator 반복하기
import java.util.*;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map2.put("one", "java 17");
map2.put("two", "mariaDB 10");
map2.put("three", "servlet/jsp");
map2.put("four", "spring boot 3.0");
map2.put("five", "vue.js");
// keySet()을 활용한 iterator 반복하기
// key 값만 set으로 바꿔주면 가능해진다.
Set<String> keys = map2.keySet();
Iterator<String> iterator = keys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String key = iterator.next();
System.out.println("key = " + key + ", value : " + map2.get(key));
}
}
}entrySet()을 활용한 iterator 반복하기
import java.util.*;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map2.put("one", "java 17");
map2.put("two", "mariaDB 10");
map2.put("three", "servlet/jsp");
map2.put("four", "spring boot 3.0");
map2.put("five", "vue.js");
// entrySet()을 활용한 iterator 반복하기
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> set = map2.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iter = set.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iter.next();
System.out.println("entry.getKey() = " + entry.getKey() + "entry.getValue() = " + entry.getValue());
}
}
}